If the husband draws up a will before his death, all property will be divided into shares exactly as stated in the document. But even in this case, if there are compulsory heirs, which are also provided for by current laws. Moreover, their share will no longer be more than half of what they could have received.
As for the spouse, she must be in a marriage registered on the basis of a submitted application to the civil registry office. Otherwise, she cannot even dream of any inheritance; she will not have the right. That is, a civil marriage will not bring any benefit after the death of the common-law husband, since the spouse will not be able to receive any property.
Who inherits the husband's property
The loss of a loved one is associated with the pain of loss, the complexities of paperwork, and paperwork. The main burden of organizational issues falls on the shoulders of the closest people. The wife of the deceased has to go through many steps. The family peacefully and with understanding goes through the stage of property division. There may be controversial issues that are common in remarriages and children from previous relationships.
Parents are considered first-order candidates. Deprivation of parental rights and arrears in child support payments are the reasons for refusal to receive part of the property. Incapacity is the basis for the allocation of a special part established by law.
The sons and daughters of the deceased have equal rights of claim to the property of the testator. The legality of birth, the fulfillment of duties by the father do not matter. Judicial practice is familiar with the situation of proving kinship in court through genetic testing. Unborn children have the right to claim a share.
The legal spouse receives the right to inherit after the death of her husband. In addition to allocating a share of the property on an equal basis with other applicants, she is entitled to additional payments, which will directly depend on the years lived together. The order of inheritance can be determined by the will of the deceased or indicated by a will.
An adult, capable citizen has the right to leave orders for the division of property after death that do not contradict the law. The paper is notarized.
The law establishes inheritance according to kinship in a certain order. A separate article regulates the rights of vulnerable citizens.
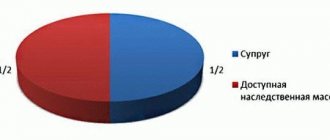
The claimant to the inheritance is the spouse, who has the right to receive half of the jointly acquired property. The division of the hereditary mass occurs in equal shares.
Recommended reading: Enterprise inheritance
The right to claim property is given to the parents of the deceased, children, more distant relatives, and applicants specified in the will. We will consider the features of separation between children, wife and children from previous marriages in more detail.
Arbitrage practice
Disputes related to civil marriages and inheritance are very common in judicial practice. Some of them end happily with the satisfaction of the claims of the cohabitants of the deceased. Let us give two examples of such proceedings.
Example 1
Tatyana lived in a civil marriage with Sergei for 10 years. The woman has a minor son from her first marriage. Having died suddenly at a fairly young age, the husband did not have time to draw up a will. Tatyana was faced with the impossibility of receiving an inheritance from her former partner. Since the property is significant (two plots of land, on one of which a house is built), the widow decided to enlist the help of a lawyer.
Having studied the case materials, the lawyer found out that the property left behind by Sergei is escheatable, since he has no heirs according to the law, and a will was not drawn up for his cohabitant. However, the specialist took into account the presence of a minor child who was dependent on the deceased.
As a result, a claim was sent to the court to assign the property that Sergei had to his dependent on the rights of legal inheritance. The court granted the claim.
Example 2
Victor and Natalia cohabited for 18 years. The woman had a son from her first marriage; she and Victor had no children together. Having been in a car accident, Natalia died suddenly without leaving a will.
All valuable property earned by the spouse’s labor was registered in Natalia’s name. According to the law, her son Andrei was supposed to be the direct and main contender for him. The young man, who had reached adulthood by that time, refused to leave Victor at least part of the inheritance. The man was forced to go to court.
He supported the statement of claim with a certificate of income (his and his wife’s), testimony of relatives and friends, receipts for payment for goods/services, information about loans taken and repaid.
After analyzing the information provided, the court found that it was Victor’s income that made it possible to acquire material goods that were supposed to go to Andrey. The court satisfied the claim, allocating in favor of the deceased's husband the share of property due to him.
If this topic is interesting to you, then in the material “Examples of judicial practice in inheritance cases” you will find other cases.
How is property divided after the death of a husband?
There are several principles for dividing the hereditary mass. Property is divided according to the will of the deceased, certified in writing by a notary. The spouse could not leave recommendations, hoping for the family’s trustworthiness. The state has established rules for the division of property.
Inheritance of jointly acquired property of spouses occurs according to the rules established by law. The inheritance of a share in the apartment of a deceased spouse will directly depend on the period in which the property was acquired. The inheritance after death may include vehicles, real estate, and valuables. The wife's share of the inheritance is greater than the other claimants. A will can make adjustments to the division of property; this will not affect the marital part.
The inheritance consists of real estate, vehicles, securities, and savings. Liabilities, credits, mortgages, loans, obligatory payments are also part of the inheritance mass.
The legal spouse has the right to claim half of the jointly acquired property. The remaining properties will be divided in equal shares with the children, mother, and father.
A will changes the conditions of inheritance. If there are violations, the paper is challenged in court.
An actual marriage without registration, regardless of the duration, is not recognized by the state. The widow of the deceased has no rights of inheritance. Illegitimate children are entitled to a share of the inheritance. The solution to a de facto marriage may be to draw up a will.
Unborn children can receive an inheritance share. A young son and daughter receive a mandatory share.
The father and mother of the deceased are first-order claimants. Incapacity is the reason for allocating a compulsory share to them as well.
The greater the value of the property, the more eventful the life of the deceased, the more quarrels and misunderstandings arise during the division process. A reasonable solution is to make a will, which allows you to protect the rights of those closest to you.
We recommend reading: How to register an inheritance in another city without going there
What nuances should you know in advance?
The Family Code has a separate part that regulates property relations between married spouses. When resolving issues with inheritance, lawyers rely on Article 34, which states that all property acquired during the years of marriage is the common property of both spouses. Moreover, this fact is not affected by whether only one person worked or both; if the wife ran the household and raised children, but did not have a job or source of income, she can also receive her husband’s inheritance.
If he managed to draw up a will before he died, real estate, furniture and other property will be inherited according to the statement drawn up. Also in such a situation, the provisions of Article 39 are used, taking into account which spouses own jointly acquired property in equal shares, even if they did not enter into a marriage contract. Regardless of the presence or absence of such a contract, the widow retains the right to 50% of the total value of the property acquired during the marriage. It means not only movable or immovable property, but also:
- income from labor, entrepreneurial or intellectual activities;
- pensions and non-targeted benefits;
- property that was purchased by one of the parties;
- securities, shares, share capital and shares.
How to enter into an inheritance?
There are infinitely many features of the division of property of the deceased. Complex issues are resolved by the court. They consider the age of the applicants, state of health, family ties, and the wishes of the deceased. Applicants can accept a share, refuse, or agree to settlement agreements. Let's take a closer look at the correct approach to the design issue.
The question of who inherits property after death is quite relevant.
The state considers the specifics of each situation and prescribes specific solutions to issues. Controversial situations can be appealed in court. In order of succession, after the death of one of the spouses, property is divided into the marital share and the inheritance estate. The legal wife will inherit the housing or apartment after the death of her husband. Shares in the apartment of the deceased spouse can be allocated to the parents and children of the deceased.
Who receives the inheritance depends on the health status of the immediate family, family composition, and the age of close relatives.
The right to inherit property after the death of a husband belongs to the legal spouse, parents, children from any marriage, and illegitimate children.
It is necessary to prove the relationship through documentation, medical means, and facts. Registration is carried out within six months.
To obtain the right to receive an inheritance, you must provide the notary with a statement of intent, a package of documents for registration: the death certificate of the testator, the applicant’s passport, the grounds for receiving the inheritance.
It is necessary to contact any notary to clarify whether a will exists. The will has been drawn up - the registration procedure is carried out by the office that compiled the document.
If there is no will, you must contact the notary office closest to your place of residence and the location of the estate.
To complete the part required by law, provide:
- Passport;
- Document confirming death;
- The basis for selecting a part;
- Documentary proof of marriage;
- Certificate from your last place of residence.
Each situation is unique, the list of papers is different. If there are illegitimate children, recognized or not, they also have the right to claim a portion of the inheritance.
A will may provide special wishes for the division of property. The terms of the paper cannot be contrary to legal norms. Violation will serve as grounds for recognizing the paper as invalid.
Recommended reading: Aunts and uncles inherit in line
Spouse's share
As mentioned earlier, the concluded marriage contract will be of great importance. This is what will be used as a starting point when dividing property after the death of a spouse. But if it is not there, then we pay attention to the property that is acquired jointly. This includes everything that was acquired as a result of living together in an official marriage. The property of the spouses is as follows:
- Real estate and movable property, deposits and shares. But in this case, everything should be purchased and invested only from jointly earned money.
- Any type of income, which may include wages, pension payments, benefits, etc. But if the spouse, for example, received financial assistance, then this can no longer be included here.
- It will not matter in whose name any other property is registered if it was acquired during a registered marriage. Everything will be considered joint property.
The common property does not include property that was given to the spouse or passed to him by inheritance. In addition, this list includes personal items other than jewelry.
Thus, half of everything acquired after the death of a spouse goes to his wife, and the second half - in the same amount to each of the heirs.
Division of movable and immovable property
After the death of a man, movable and immovable property that belonged to him by right of ownership is subject to inheritance. This includes:
- real estate - apartment, country house, land, shared share in a cooperative;
- movable property – vehicles, means of labor, equipment, technical means;
- valuables - precious metals, bank deposits, jewelry, cash, antiques;
- other – shares, shares in the authorized capital, business, securities.
Debt obligations are also inherited. The division is made in accordance with the “remoteness” of family ties and the number of claimants to the property of the deceased.
House and apartment
If the house and apartments were purchased during marriage, then the widow has the right to half of this property. If real estate was acquired by the deceased before marriage, then they are divided in equal shares between the heirs.
For example, an apartment and a house were purchased during marriage. The successors are the daughter of the deceased, the widow. The real estate will be divided as follows:
- the widow will receive half of the house and apartment;
- the remaining half will be divided between her and her daughter.
The daughter will receive ¼ of the property, and the widow – ¾ of the house and apartment.
Another example is when the property was purchased before marriage. The heirs are a daughter and a widow. They will both receive ½ of the real estate.
Automobile
It is divided in the same manner as real estate. But a car is recognized as an indivisible thing, so only one successor can receive property rights to it. Other heirs will receive monetary compensation.
The vehicle is assessed by a specialized company. The cost of the car is divided among all applicants, and the one who wants to take ownership of it (an agreement must be reached between relatives) pays compensation to the others.
Securities
These are tangible assets that are inherited by law in the order of relatives. To obtain property rights, you must contact a notary. You must provide the necessary documentation:
- an extract from the register of shareholders' accounts when inheriting shares;
- statement on bond issuers;
- extract from the special depository when inheriting mutual funds.
If the securities are placed abroad, the notary will issue a special certificate for registration of property rights outside the Russian Federation.
Business
If there is no will, then the business of the deceased is divided equally among the heirs, taking into account the priority right of the spouse. If a husband and wife opened their own business during their marital relationship, then the widow has the right to half of it. The rest will be divided among other successors.
If a will is made, the business will be passed on according to the last wishes of the deceased. The successor can be not a relative, but a partner. The will can also stipulate the obligation of the new owner to pay a monthly portion of the profits to the family of the deceased man.
Cash section (cash and non-cash)
The deceased could have owned cash, as well as non-cash money - on debit cards, in accounts and deposits. If relatives know about this money, the notary requests bank statements. If there is no certainty in which bank the money is kept, finding it will take some time.
After opening an inheritance case, all cash and non-cash funds are deposited in a separate depository account opened at the place where the inheritance was opened.
Documents required for inheriting a spouse's property
When contacting a notary regarding entering into an inheritance, the widow should have with her:
- Identity documents;
- Certificate of death of the spouse;
- Certificate of registration of marriage with the deceased. Since it is precisely this that confirms the close relationship and line of inheritance of the spouse;
- Certificate of residence containing information about all persons living together with the deceased;
- Documents for property acquired jointly during marriage;
- Documents for property related to the personal property of the deceased.
If necessary, the notary may request other documents. In addition, the office will have to write an application according to the established template.
What deadlines should you be aware of?
The heirs must enter into rights no later than six months from the date of death of the testator. This figure is briefly reflected in Article 1154 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation and applies to most cases, but there are exceptions to this rule regarding compliance with time frames. There are often cases when a widow enters into inheritance rights after the due date has expired. They are often considered as part of a court case when there is a disagreement between the widow and other beneficiaries and they have to divide the property of the deceased. In this case, they will receive shares within the framework of the law.
Amounts of state duties
Any heir is interested in the question of how much the procedure for registering escheat property that the deceased managed to acquire during his lifetime might cost. In addition to the general tax, the widow and other heirs will need to pay a state duty, the amount of which is regulated by the Tax Code of the Russian Federation. One list of expenses should also include notary services and registration of the transfer of inheritance into shared ownership, the fee for which depends on the type of movable or immovable property. It must be remembered that 0.3% will be withheld from the total assessed value of the property received; this rate and price is intended for heirs of all categories.
Civil marriage
The absence of official certificates is not a basis for claiming inheritance. Even if things were purchased with common money, they are not subject to the regime of common ownership. In this case, the surviving spouse can prove joint ownership through the court.
If the “common-law” husband (wife) is a disabled dependent who lives for more than a year without registering the relationship with the deceased spouse, this is the basis for claiming the right to property.
How to renounce the spousal share
The peculiarity of the marital share is that it is not included in the estate, even if the surviving spouse did not file an application for its allocation, because filing it is the right of the spouse, and not an obligation.
If a spouse wants his part of the joint property to be included in the inheritance, he should write a statement refusing to allocate the marital share in the inheritance.
The consequence of refusal to allocate the marital share is the refusal of ownership of this property and its division between the heirs on a general basis.
Relinquishment of the share is voluntary. When accepting an application, the notary is obliged to inform the applicant about all the consequences of this action, but he has no right to interfere with the wishes of the widower or widow.
Right to inheritance of a deceased man
Not only the wife , but also other successors can claim the property of the deceased husband Exact recipients can be determined in two ways:
Free legal consultation
+7 800 350-51-81
- on the basis of a will , which the man drew up before his death and certified by a notary, and he can even indicate here strangers, but it is not allowed to violate the rights of persons represented by obligatory heirs;
- if a man did not take care of the competent formation of an official order, then successors are determined taking into account the requirements of the law .
Important! Initially, the wife should find out from the notary at her husband’s place of residence whether he left a will, since this document indicates the exact heirs.
In law
Many people do not think about possible death, therefore, after their death, property owned by property is distributed among their successors. Here, all those who are heirs after the death of the husband are determined by law. In this case, a special order , for which the degree of relationship is assessed.
So, the first heirs after the death of a husband are his wife, children and his parents. They can count on an equal division of the property of the deceased citizen. If the testator does not have parents or offspring, then on the basis of Art. 1142 of the Civil Code, all his valuables are transferred to his wife. If the mother, wife and son claim the apartment, dacha and car of the deceased, then all valuables are distributed among the applicants, and they can count on equal shares.
If a wife wants to receive the property of her deceased husband, then within 6 months she prepares an application and other documentation. The package of documents is transferred , who is involved in the management of this case.
A woman has the right to refuse inheritance, for which the provisions of Art. 1157 Civil Code . This usually occurs if the deceased's debts exceed the value of the property, so the widow will still have to sell those assets to pay off the debt. To renounce an inheritance, a special written application is drawn up and submitted to a notary.
There are situations in which property is not divided equally. For example, if an apartment belongs equally to spouses, then the woman receives half of the property, as well as the husband’s share, which is calculated based on the number of successors. As a result, the share of women in the apartment increases significantly.
At the end of the term, the notary issues each successor a special certificate , which serves as the title documentation for the property. Based on it, the right is registered in Rosreestr or other government agencies.
By will
If a man made an official disposition before his death, then when dividing his property, only the information contained in this document is taken into account. The compiler can be an adult and capable citizen, and the notary is obliged under Art. 1123 of the Civil Code to keep information from the will secret. The rules for its compilation include:
- the document is formed exclusively in writing and is also certified by a notary;
- the text describes all property belonging to the testator, and the person must confirm the right to a particular item using official documents and extracts from the Unified State Register of Real Estate;
- persons who will receive specific values are listed.
The will is formed in two copies, since one remains with the drafter, and the second is transferred to the notary for safekeeping. After the death of her husband, the wife must carefully examine his belongings to find the disposition. If she cannot find the documentation, then you can find out about its availability from a notary.
Agreement on the allocation of spousal share
Although the law determines which property can be divided into a marital share and which is the personal property of one of the spouses, in practice many controversial issues arise related to the legal regime of property. This entails claims against the widow/widower from other heirs of the deceased.
The dispute can also be resolved in court, although the law allows the situation to be resolved pre-trial. To do this, you need to draw up an agreement on the allocation of the marital share.
The document is drawn up in writing between the heirs. The text specifies what property the surviving spouse receives as a marital share.
In essence, the agreement is an agreement between relatives on the division of property, recorded in writing.
Then the notary checks the contract and certifies it, after which the document becomes legally binding. All agreements are subject to full execution.
There is no will
The surviving member of the married couple is entitled to half of the joint property and additionally has the right, on an equal basis with other heirs, to part of the property of the deceased, inherited in order of priority. The primary heirs of the deceased spouse in this case are:
- Children.
- His husband.
- Parents.
Children inherit: those born in marriage between spouses; illegitimate; from other marriages; adopted, adopted.
Adopted children and their future descendants inherit like their own. A child who has been adopted and his biological father (mother) are not heirs or testators for each other. When maintaining a relationship, this option is possible on the basis of a court decision.
If the children refuse the inheritance or die, the right of inheritance passes to the grandchildren of the deceased spouse.
The second line of inheritance includes: sisters and brothers (and step-brothers), grandmother, grandfather of the deceased. If a sister or brother died or did not want to accept the inheritance, their children become heirs.
The essence of queues is that a representative of the next queue can inherit in the absence of applicants from the previous queue.
For example, the spouse died. He is survived by his wife, son, brother. The wife and son are the heirs of the first priority, so the inheritance will go to them, they will own the acquired property. My brother will be left with nothing.
The procedure for dividing the inheritance
Taking into account inheritance legislation, the property of the deceased must be divided in equal shares among all heirs according to their priority and rights. The property that he managed to buy before his death will become their legal possession six months after filing the application. If the division is carried out by the judicial authorities or a notary, the property of the deceased can be transferred and divided in equal parts between all applicants, depending on the situation. The ideal option is always an even distribution of shares, but this is not always the case. Some heirs have more advantages based on their category, this list includes:
- minor children;
- spouses whose marriage was formalized;
- mother, father, brother and sister of the deceased;
- dependent persons;
- other heirs, if there are no others available.
There are situations when the deceased did not have time to express his will regarding personal property. The deceased testator could be in a coma before death and die without regaining consciousness, or be killed as a result of violent acts. In this case, inheritance rights must be transferred and distributed according to the law. The period for receiving an inheritance is limited, so it is advisable for the heirs to enter into the rights to use the property within a month from the date of death of the testator.
Debentures
If a wife had to survive her husband, who still had debt obligations, the debt of the deceased passes to her according to the law. This occurs when the deceased was forced to default on loans or had other debts, the cost of which was not covered by him during his lifetime. Since the shares of the inheritance must be distributed taking into account the categories of heirs, debt obligations in addition to the wife also pass to children, parents and other heirs.
Important! It is advisable to privatize municipal property that was previously owned by the deceased after assuming the rights of inheritance. The privatization procedure can be carried out either in standard or accelerated terms.
Since persons who were officially married have common property, their debt obligations should also be common. An inheritance cannot be accepted without existing debts, so if the heir does not want the debt of the deceased to pass to him, he can refuse his share. Unfortunately, it is impossible to obtain a share of the property of a deceased person without his debt obligations, taking into account current legal norms. In general, problems with inheritance and debts can usually be resolved in most cases.