In the process of work, tense relations arise between the management of the organization and the employee. And if the employee himself has the right to resign of his own free will at any time (by notifying the employer 2 weeks in advance), then management has much less such opportunities. Situations in which the management of an organization is unilaterally allowed to dismiss workers are listed in Art. 81 Labor Code of the Russian Federation. Some categories of workers in such situations are especially protected by law. Let's consider whether a single mother or simply a woman with young children can be fired.
Is it possible to fire a single mother?
The authorities strictly monitor compliance with the benefits and guarantees provided to single mothers. For example, it is possible to terminate an employment relationship only in the presence of serious circumstances.
The procedure for dismissal of single mothers is fixed in the Labor Code of the Russian Federation. Article 261 reflects a list of grounds that allow you to sever a relationship with a subordinate at the initiative of the employer:
- immoral behavior of an employee;
- liquidation and other actions related to the termination of activities;
- health status reflected in the medical report and preventing further compliance with the job description;
- non-compliance with labor regulations;
- culpable behavior resulting in loss of trust.
Attention
The general rules do not apply to the unilateral dismissal of single mothers with children under 14 years of age.
You can't lay off a single mother if she doesn't receive child support.
Before downsizing, the employer must find out which of its employees cannot be dismissed on its initiative.
So, for example, an employee raising a small child alone is not subject to dismissal until he turns 14 years old. This is discussed in the Appeal ruling of the Moscow City Court dated November 20, 2019 in case No. 33-52672/2019.
The essence of the dispute
According to the court decision, although the child has a father, the employee is still subject to the ban on dismissal at the initiative of the employer, as a single mother. That's why.
Before being laid off, the employee warned the employer that she was raising a child under 14 years of age without the help of her father. She presented as evidence:
- child's birth certificate;
- certificate of divorce;
- a copy of the court order for the collection of alimony;
- certificate of arrears in payment of alimony.
But the employer did not take these documents into account and fired the employee, deciding that the ban on dismissal did not apply to her because the child had a father.
The Moscow City Court declared the layoff of a single mother illegal.
It should be noted that the employee’s reinstatement at work may also be affected by how much alimony the child’s father owes, whether he is trying to repay the debt, whether the woman demanded that the debt be forcibly collected, and whether there is other evidence that the father is not involved in the child’s life.
Single mom
The legislation does not specify who a single mother is. Because of this, disputes arise.
The Labor Code prohibits layoffs for single mothers raising children under the age of 14 (Part 4 of Article 261 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation). But this needs to be confirmed.
At a minimum, the mother must have a document about the child’s age - a copy of the birth certificate. Of course, this won't be enough.
To recognize a mother as single, it is necessary that the “Father” column in the birth certificate is left blank or information about the child’s father must be entered according to the mother’s words. In this case, a certificate from the registry office on the grounds for making an entry on the birth certificate is presented. In addition, the child's mother must not be married. This is confirmed by a copy of the passport.
A single mother is considered to be a single mother if she is raising a young child alone. Therefore, a woman can submit documents that confirm that the father is absent due to the fact that he:
- died, deprived of parental rights or limited in them;
- recognized as missing, incompetent, or with limited legal capacity;
- cannot personally raise and support a child due to health reasons.
Please note: a divorced woman cannot be considered a single mother, provided that the child’s father is alive and takes part in its maintenance, i.e. pays child support and is not deprived of parental rights.
Dismissal of a single mother
A single mother of a child under 14 years of age or a disabled child under 18 years of age cannot be fired at the initiative of the employer. Exceptions - liquidation of the company or dismissal due to the guilty actions of the employee specified in Part 4 of Art. 261 Labor Code of the Russian Federation.
In case of personnel reductions, the employer is obliged to offer such an employee another vacancy, similar in job functions and remuneration.
Note that in addition to single mothers, the following cannot be laid off:
- another person who is raising a child under 14 or a disabled child under 18 without a mother;
- a woman with a child under three years old;
- the sole breadwinner of a disabled child under 18 years of age or a child under three years of age in a family raising three or more young children, if the other parent is not in an employment relationship.
Therefore, for the sake of their safety, the employer needs to check in writing with the employee before dismissal whether she has the status of a single mother or other benefits, and ask her to provide documents confirming the benefits.
Normative base
The procedure for applying the regulatory framework regarding the work of single mothers is reflected in Resolution of the Plenum of the Supreme Court of the Russian Federation No. 1.
Federal Law No. 256 provides for additional state subsidies for families with children. A single woman who gave birth to 2 babies without male support is also entitled to maternity benefits.
Information about all other support options is contained in labor legislation. The list of guarantees is fixed in Art. 261 Labor Code of the Russian Federation. The employer can terminate the contract with a single mother, but only in the presence of exceptional circumstances set out in Art. 81 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation (except for paragraphs 2-4 and 9) and in Art. 336 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, if we are talking about a female teacher who ignored part 2.
Who is recognized as a single mother?
There is no single official definition of the term “single mother” in the legislation. It is different for each branch of law. In labor legislation there is the concept of “single mother”, in tax legislation - “sole parent”. For the purposes of receiving social benefits, federal and regional payments, each region of the Russian Federation can establish its own definition of this term.
Although the Labor Code of the Russian Federation contains such a term as “single mother,” it does not provide an explanation of who exactly falls into this category. Explanations are contained in Resolution of the Plenum of the RF Armed Forces dated January 28, 2014 No. 1.
Single mothers include women whose husband: (paragraph 2, paragraph 28):
- died or was declared missing;
- deprived of parental rights (or limited in them);
- is incompetent (partially capable) or due to health reasons cannot raise or support a child;
- is serving a sentence of imprisonment;
- avoids raising children (protecting the rights and interests of the child).
Women who have simply filed a divorce from their husband are not recognized as single mothers. For them, the legislation of the Russian Federation provides for various benefits and payments (for example, alimony). The only exception is when a court decision recognizes the fact that the woman’s ex-husband is not the father of the child.
Let's consider what labor rights a single mother can count on and how her dismissal occurs in 2021.
Dismissal of a single mother in different cases
Vulnerable groups of the population are provided with government support. Before parting with a single mother, the employer is recommended to study the norms of the Labor Code:
- Art. 77 on general rules for dismissal;
- Art. 79 on fixed-term working relationships;
- Art. 74 on legal ways to adjust the contract, as well as on the organizational and technological situation at work;
- Art. 179 on preserving the place of work on a preferential basis.
Attention
Failure to comply with the law when terminating a contract can result in serious consequences for the employer - punishment in accordance with the administrative and criminal codes.
Dismissal of a single mother for failure to perform work duties
Why can a single mother be fired if there are no gross violations of labor duties? Another reason for dismissal is violation of labor discipline standards, which are defined in the company’s internal regulations (clause 5, part 1, article 81 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation). However, a woman cannot be fired immediately on this basis. First, disciplinary measures must be applied to the violator: make a remark or reprimand (clause 33 of the Resolution of the Plenum of the Armed Forces of the Russian Federation dated March 17, 2004 No. 2).
The fact of violation of discipline must be documented (Parts 1, 2 of Article 193 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
Let us remind you that violations of labor discipline mean systematic tardiness, premature departure from work, and failure to fulfill work duties.
Dismissal of a single mother at her own request
Expressing a personal desire to change place of employment (Article 80 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation) should not and cannot give rise to complaints. But in practice the following circumstances occur:
- a single mother is forced to ask for leave;
- the boss grossly violates labor standards;
- I need to quit urgently.
What should I do? The creation of conditions in a team that force people to leave should be considered by the inspectorate that protects the rights of workers or the prosecutor's office. Only the presence of serious violations on the part of a single mother allows the manager to terminate the employment relationship.
Regular delays in salaries can result in administrative and even criminal prosecution for the director. Such issues are dealt with by the prosecutor's office, the labor inspectorate and the court.
Attention
No one should insist on leaving if a woman raising a child alone managed to change her decision during the notice period. The manager does not have the right to retain a subordinate after the regulated period has expired.
Dismissal due to reduction of a single mother
So, a single mother can be fired only for certain reasons, and layoffs are not one of them. But some courts allow the possibility of dismissing a single mother if she was legally married at the time of conclusion and termination of the employment contract.
The motivation of the courts is clear: the woman is no longer raising a child alone; her new husband helps her financially and morally in this. This means that she is no longer a single mother (JSC St. Petersburg City Court dated 03/07/2017 No. 33-4492/2017).
Dismissal at the initiative of the employer
Management often wonders whether it is possible to deprive a woman whose child is growing up without a father of a job if she does not express such a desire?
It is possible, but only under serious circumstances:
- Absenteeism (clause a part 6 of article 81 of the labor legislation).
- Failure to comply with the discipline in force at the enterprise (Part 5 of Article 81).
- Lack of knowledge and skills to obtain a vacant position, identified during the probationary period. The time worked must be paid (Part 3 of Article 81).
- Drunkenness (Article 81, Part 6, Clause b).
Attention
The state protects single mothers in many ways, but they should not break the law.
Reduction
Reduction of staffing based on clause 2, part 1, art. 81 codes are produced to implement various purposes:
- cost optimization;
- relocation of the company to another city;
- reduction in the scale of the enterprise.
Norms Art. 261 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation does not allow the dismissal of a single mother, since the type of termination of the employment agreement relates to the will of the employer. The ban applies during the period of independent education of a child under 14 years of age.
Information
A woman performing job duties that the company no longer needs is required to offer another vacancy. Qualification requirements and income level should not worsen the previous situation of a single mother. Only refusal of all possible options allows the employer to invalidate the contract with the subordinate.
Dismissal of a single mother due to liquidation of the organization
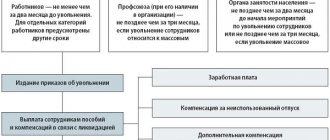
Termination of an employment contract with a single mother due to the liquidation of the organization occurs in accordance with the general procedure. First, you need to notify the employee about the upcoming dismissal, then draw up an appropriate order.
When dismissed due to liquidation, a single mother (like other employees) has the right to severance pay and payment during employment. More details on the procedure for dismissing a single mother during liquidation of an organization can be found in this article.
Liquidation of an enterprise or closure of an individual entrepreneur
The Labor Code gives the director the right to terminate relationships with subordinates, including single mothers, due to the liquidation of the organization. Mandatory conditions: advance notice 2 months in advance and provision of material payment - severance pay.
P. 1 part 1 art. 81, regarding liquidation measures, guarantees employees an average income for 1 month and the preservation of a similar amount during the time spent on employment, but not more than 2 months. There are exceptions: provision of the average salary for the 3rd month, if within 2 weeks the dismissed citizen officially began looking for a job, but could not find anything.
Dismissal of a single mother by agreement of the parties
The separation of the head of an institution from his subordinate by mutual consent is stipulated in Art. 78 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation and cannot be associated with any pitfalls. The pros and cons for the employee are given in the table.
| Positive points | Negative sides |
| For a future employer, dismissal in accordance with a mutual agreement looks more attractive than due to staff reduction. | The amount of material compensation is significantly reduced compared to the termination of the contract due to optimization of personnel or liquidation of the organization. The law does not oblige the manager to pay anything other than unused vacation and remaining salary. |
| The parties sign a preliminary document in which they stipulate the deadline for terminating the main agreement | The reason for dismissal is not subject to legal disputes |
| Written mutual agreement allows you to break off the relationship even while on legal leave | The conditions reflected in the signed agreement must be observed, even despite discrepancies with current legislation |
| The employee can set his own conditions, for example, not to leave during the entire period of searching for a new employer |
Dismissal procedure
A subordinate and a manager may separate for various reasons, as reflected in the Labor Code. Regardless of the surrounding circumstances, the employer must follow the sequence of termination of the relationship.
Preliminary documents
If the dismissal is related to the personal desire of the citizen or agreements reached with the employer, then the initial document is a handwritten statement or agreement signed by the parties.
Attention
Staffing reductions or liquidation measures require 2 months' notice to workers.
If a single mother violates current norms and does not obey the order established at the enterprise, then in order to terminate the contract, the employer must begin by drawing up internal documents - reports and orders.
Order, entry in the work book and necessary certificates
After the director of the organization has signed the preliminary document, the HR specialist must draw up a dismissal order (T-8a). The internal act usually reflects the position held, the true reason for leaving, an article of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation and the period for termination of the working relationship.
The order serves as the basis for making the final payment and creating an entry in the work book. The contents of the papers must be brought to the attention of the single mother against signature. The document on work experience must be returned to the worker on the day of separation.
Information
A certificate in form 2-NDFL may be required by a future accountant if a woman applies for leave, a certificate of temporary disability, etc.
The employee also has the right to request: information about legal rest, copies of employment orders, etc. The former employer must provide the necessary information no later than 3 days from the date of official registration of the request.
Notification to the employment center
According to Article 25 of Law No. 1032-1 of April 19, 1991, it is required to notify the employment service. This must be completed no later than two months before the start of the downsizing process. In case of mass layoffs, the period increases to three months. There is no single form of document at the legislative level, so companies create the document independently in free form.
The following information should be recorded in the document:
- Full name, profession and position of the person being laid off.
- Qualification requirements and working conditions of the employee.
- Date of preparation of the document.
- Timing of employee layoffs.
- Full name and signatures of authorized persons drawing up the document.
If the employer does not notify the Employment Center (employment center) in a timely manner, then he faces punishment in the form of administrative liability (Article 19.7 of the Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation).
Working off
Art. 80 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation gives the right to any citizen to terminate relations with superiors 2 weeks after notification. An agreement between the parties can reduce or cancel this period. Also, a parent can avoid working time by taking leave or providing compelling arguments (medical certificate, reaching retirement age, moving, etc.)
Attention
In accordance with Art. 71 of the Labor Code, the boss must be notified of the termination of official duties during the probationary period 3 days in advance.
Dismissal of subordinates in connection with liquidation measures requires the issuance of appropriate notices 2 months in advance. At the same time, the manager is obliged to notify the employment service. A manager who plans to exclude a position held by a single mother from the staffing table is also required to notify her of this 2 months in advance.
Payments and benefits
A single mother is entitled to certain payments upon dismissal:
- Monthly earnings.
- Compensation for unused rest time.
Information
Under certain circumstances, the boss may even withhold part of the earnings. For example, if an employee was paid vacation pay in advance, the accountant will deduct it from the final payment. The amount of deduction should not exceed 20% of monthly income (Part 1 of Article 138 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
The basis for providing severance pay may be:
- Liquidation measures. Material support is equal to the average monthly salary.
- Health status. Art. 178 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation guarantees the provision of income within 14 days.
AttentionAn employee who submits her resignation on her own initiative cannot exercise this privilege.
- Agreement reached. The procedure for assigning this “farewell” payment is not specified in any law, so it all depends on the boss.
The regulatory framework and internal local acts allow the employer to decide on awarding bonuses, allowances and other bonuses specified in the collective agreement (the amount depends on the employer’s decision).
How to challenge dismissal
A single mother can object to the unlawful termination of her employment relationship in court. Servants of Themis are subject to both recovery of lost profits and compensation for moral damage.
Important
In accordance with Art. 392 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, the injured employee is given 1 month from the date of provision of the work book or creation of the dismissal order.
The official paper must reflect arguments confirming the illegality of termination of the contract and the exact demands of the victim: restoration of status, compensation for moral shock, etc.
Important
Dismissal of a single mother for illegal reasons threatens the employer with a fine (Article 5.27 of the Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation).
Labor rights of a single mother
Single mothers, just like pregnant women, have a number of benefits in the field of labor law:
- reduced working hours (Article 93 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation);
- impossibility of dismissal at the initiative of the employer, except in certain situations: during the liquidation of the organization, due to absenteeism, committing an immoral act, etc. (Part 4 of Article 261 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation);
- the right to choose the most convenient time for annual leave (Article 262.1, Article 262.2 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation);
- additional days off (Article 262 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation);
- additional unpaid leave of 14 calendar days (Article 263 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation);
- the possibility of refusing to work at night, on weekends or holidays, as well as the right to refuse a business trip (Article 295 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
You can find out more about the labor rights of a single mother here.
Not only single mothers, but also single fathers are entitled to the above benefits. We talk more about this in the article “Is it possible to fire a single father?”
Let us further consider the features of dismissal of a single mother for various reasons.