What is personal data?
Personal data (hereinafter referred to as PD) is any information that is directly related to a specific individual.
Individual
PD of ordinary citizens includes:
- FULL NAME;
- information about place and date of birth;
- residence;
- data contained in the passport;
- SNILS;
- benefits for individuals.
Employee
Employee PD includes information that is important for the employer in connection with employment.
It is also worth noting that the issue that concerns the management of employees’ personal files has not yet been regulated at the legislative level, so most often in practice the employer includes complete information .
Namely:
- data specified in the passport;
- SNILS;
- military registration;
- existing education;
- a completed application form, which is given to the employee upon employment;
- employment contract.
In addition, information about the employment agreement and termination of employment :
- data from orders that talk about salary increases, incentives, starting work and dismissal, transfers;
- explanatory letters, employee statements;
- documents indicating that the employee has been promoted or passed an interview.
Municipal employee
According to Federal Law dated 03/02/2007 N 25-FZ (as amended on 04/03/2017) “On Municipal Service in the Russian Federation”, Article 29, the PD of a municipal employee includes:
- some data taken from the biography;
- information contained in the passport;
- data on specialty, qualifications;
- information about length of service and experience;
- about family composition and marital status;
- military duty;
- salary and benefits;
- presence or absence of a criminal record;
- residence and telephone number;
- employment contract;
- statements that were provided and submitted to the tax office;
- health information.
civil servant
According to Article 24 of the Federal Law of July 27, 2004. N 79-FZ “On the State Civil Service of the Russian Federation”, a person applying for a job must provide the following PD to the inspectorate:
- an application to begin work or enter the civil service, this also includes an application to replace an absent employee;
- salary information;
- a questionnaire given to an employee upon employment;
- SNILS;
- work book;
- a copy of the certificate of registration of an individual with the tax authority at the place of residence in the Russian Federation;
- addresses from Internet resources on which the civil servant posted publicly accessible information;
- information about specialty, work experience, advanced training;
- When concluding an agreement, it may be necessary to provide other documents.
Transfer of personal data to third parties can only be carried out with the written permission of their owner, except in cases where this is required by the Federal Law.
Salary cannot be a commercial secret due to the fact that it relates to the remuneration system . But this does not exclude it from the list of PD, for the distribution of which an employee can be fired in accordance with the Labor Code.
And if the employee begins to challenge this decision in court, then the employer is obliged to prove that the disclosed information relates to a secret, the information of which the employee undertook not to disclose to anyone.
Classification of personal data
According to the Federal Law “On Personal Data”, this is any information that directly or indirectly relates to the life of the subject. What applies to personal data:
- Name;
- surname and passport details;
- place and date of birth;
- registration or residence address;
- Family status;
- information about income and debts;
- specialty, profession,
- employment information;
- income.
This may also include information about social connections, contacts, personal life, purchases of a citizen or his family members.
According to Part 1, Article 85 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation, personal information of an enterprise employee includes all information necessary for the manager to regulate all labor processes associated with a specific employee.
A telephone number is personal information in the Russian Federation, as it is tied to passport data.
General PD
General data includes those that are “on the surface”. Public personal data is the name that can be seen on the badge of a company employee, his phone number in the questionnaire on the website, specialty and position. If a person himself distributes data that does not belong to the “General” section, this does not give citizens the right to dispose of it or publish it in open sources.
Biometric PD
This includes weight, height, hair and eye color, fingerprints, nationality, and special features. This data is used by intelligence officers to create leads and search for criminals in databases.
Police and law enforcement agencies do not have the right to fingerprint citizens without probable cause and enter their information into a database.
Special PD
This includes race and nationality, political views, religious or philosophical beliefs, health, and intimate life. Dissemination of this information is not permitted, except as provided for in Part 2 of Federal Law No. 152.
No circumstances oblige a citizen to disclose this data to police officers or publicly. This request may be denied under legal circumstances.
Anonymized PD
This is data whose ownership cannot be determined. Depersonalization is the process of “alienation” of data that makes personal information public.
Example: An organization has 2 employees – a man and a woman. The man follows a dress code, and the woman wears a burqa. If the employer provides statistics on the number of believers and/or religious people, and specifically one atheist, one believer, it will be easy to calculate who is who.
Such a clumsy example is not a direct violation of the law; nevertheless, it transfers personal data (and, in addition, special data) to third parties.
Kinds
Types of personal data can be classified into:
- The content contained in them:
- Type and purpose of processing personal data:
The category, which includes the list specified in Article 10: race, nationality, religion, health, personal life, political beliefs.
However, according to Federal Law 152, there are restrictions here, namely, access can only be carried out with the written permission of the owner.
What does the processing of personal data mean, read our article.
PD of a physiological nature , which allows the operator to determine the identity of their owner.
Foreign distribution of PD . This type of information dissemination can be divided into three types:
- countries belonging to the Council of Europe Convention (CCE);
- countries that are not members of the CSE, but are implementing a set of measures aimed at protecting personal data rights;
- countries belonging to the CSE do not implement a set of measures aimed at protecting personal data rights.
If data is transferred to the latter group, then a legal pretext, supported by law, or the consent of the owner, or a serious reason to preserve the interests of the owner himself is necessary.
Transfer of PD to state information systems and municipal information systems. Here the processing takes place in accordance with the functioning Federal Laws.
Processing of personal data during political speeches or when promoting any goods, services or works. Restrictions controlled by the Federal Law: despite the acquisition of information from sources that are public, an indication of the owner’s agreement is required, the presentation of which may not be in writing.
Personal data: what is it, regulatory framework
The state regulates the field of personal data through a number of regulations. The basis is the Constitution of the Russian Federation, the basis is Federal Law No. 152 of January 27, 2006. The law explains what personal data is and what applies to it. This term means information that directly or indirectly characterizes the subject of personal data - an individual. In simple terms, they can be used to accurately determine that we are talking about a specific person.
There is an indirect mention of personal data in the Russian Constitution. Articles 23–24 of the Basic Law give citizens the right to privacy, inviolability and protection. Everything that is included in the concept of personal data belongs only to its owner and cannot be controlled by the government or third parties. Citizens themselves are free to manage this information, prevent its dissemination, or, conversely, pass it on to others. The state, for its part, guarantees and protects this opportunity.
Federal Law No. 152 determines who has the right to use personal data other than its carrier, under what conditions, according to what rules. Only operators with his permission can receive and process personal information about the subject. The citizen signs consent to verify his personal data when applying for a loan, filling out questionnaires or applying for a job.
Operators have access to the amount of data required to solve their problems. They have no right to keep or use them after the purpose has been achieved. For example, the employer must destroy records, questionnaires - everything that relates to the employee’s personal data after his dismissal. Otherwise, there is a risk of liability for the disclosure of the employee’s personal data.
The norms of Federal Law No. 152 must be followed by all legal entities and individuals. Special rules apply when the PD:
- received for personal or family needs, if this does not infringe on the rights of 3 persons;
- contained in archival documents;
- constitute state secrets;
- are collected by judicial act.
Other legislative acts clarify the provisions on personal data in relation to different situations, introduce a system and classification of means of protection. For example, Chapter 14 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation reveals the concept of employee personal data. This is information that allows you to characterize him as an employee of a certain organization (salary amount, length of service, qualifications, information from the Federal Tax Service and the Pension Fund, etc.), his business qualities. They must be used and kept to assist the employee in performing his job duties, increasing experience and knowledge, promoting careers, and protecting company personnel and property.
Special categories
According to the Federal Law dated July 27, 2006 N 152-FZ (as amended on February 22, 2017) “On Personal Data,” categories of personal data are divided into four groups:
- It is not permitted to process data that in one way or another touch on the topic of religion, political views, personal life, nationality, not counting those individual points indicated in paragraph 2.
- Processing of the PD listed in paragraph 1 is permitted.
But provided that:
- written permission has been received from their owner for processing personal data;
- they are publicly available;
- PD is associated with information related to the health of its owner, and access to it is currently necessary to preserve his life;
- it is necessary when implementing judicial measures;
- it occurs due to the entry into force of the legislation of the Russian Federation on security and investigative activities.
- Processing of PD about a criminal record can be carried out by state or municipal authorities in accordance with the Federal Law of the Russian Federation.
- The processing of personal data, which is specified in paragraphs 2 and 3, must be immediately suspended when the reasons for which it was carried out cease to exist.
What should I do if I process PD on my website?
When collecting information about users, you may ask the question: “How to process personal data to avoid penalties?” There are a number of conditions for processing personal data for the site. You need:
- Install a secure protocol for the transfer of personal data on the site (SSL certificate). Your hosting provider will help you choose a certificate: for example, at REG.RU you can even get a basic SSL certificate for free.
- Draw up a privacy policy and post it on the website.
- Ask visitors for consent to process their PD.
- Notify Roskomnadzor that you are collecting personal data.
Just in case, we emphasize that you need to complete all these steps. Let's go through each of the points.
SSL certificate
An SSL certificate is a security standard for data exchange between a site and a user. The main advantage of an SSL certificate is an encrypted connection that protects traffic, preventing it from being intercepted and personal data left on the site being used for fraudulent purposes.
It is critically important to switch to the SSL protocol for all sites that contain information of the first and second categories (more information about the categories of information can be found here). This is, for example, bank card data, logins and passwords for accounts, forms indicating the full name and address, etc.
Privacy Policy
When drawing up a privacy policy, pay attention to the principles of processing personal data. It must contain the following information:
- Name of the personal data processing operator. If the site belongs to an individual entrepreneur or just an individual, indicate your full name; if it belongs to a legal entity, indicate the name of the company and TIN.
- Operator address : legal (for legal entities) or actual (for individuals).
- List of collected data : full name, email, telephone, cookies, passport data and more. The list should be as complete and detailed as possible.
- Purpose of data collection . Be sure to indicate what the PD will be used for. Collect only necessary data.
- Data processing timeframes . Personal data must be deleted after being used for its intended purpose. Their processing is possible only for a limited time.
- The fact of involving third parties in data processing. This also includes various affiliate programs, for example the REG.RU affiliate program. If you bring new clients to another company, then it is the third party that will process the PD.
- Your contact details . In the privacy policy details, indicate contacts where you can be contacted. This information will be useful to your customers if they wish to delete or change their personal information.
- Data Security Measures . Tell clients that their personal data is stored on secure servers located in Russia (yes, by law, data of Russian citizens can only be stored on servers located in the Russian Federation).
Visitors to your site should be able to easily read your privacy policy, so we recommend placing it in the footer of every page.
Consent to the processing of personal data
In accordance with the Personal Data Law, the user must independently decide whether to provide you with their data and agree to their processing. At the same time, consent to the processing of personal data must be specific, informed and conscious. Make a checkbox notifying that the client agrees to the processing of PD and has read the privacy policy (don't forget to provide a link to it). The site visitor must independently tick the checkbox, and we do not recommend doing this for him.
But there are a number of cases when consent to PD processing can be obtained in another way. These include, for example, signing an agreement to which the user is one of the parties.
Roskomnadzor notification
The Personal Data Law states that you must notify Roskomnadzor about the collection and processing of personal data of visitors to your website. This can be done through a special form.
But there are exceptions when it is not necessary to notify Roskomnadzor. Among them, for example, the processing of publicly available information (that is, that which the user has made available to an indefinite number of people, for example, data about himself published on a personal website or in an open social network profile) or data that includes only his full name.
Which ones are public?
The very fact of including PD into the category of “public” is possible only after the written agreement of its owner.
Public access data may include (subject to paragraph 1) the following:
If the individuality of personal data is lost, there is no need for permission from their owner to enter information into public access. All information is withdrawn from public access to personal data at the request of the owner himself or by court decision, as well as other government agencies.
Personal data information system and operator - what is it?
Personal data information system (IS) is a system that is a combination of PD located in a database and various types of equipment, thanks to which PD processing using automation tools becomes a reality.
A very important concept is “operator”. According to Federal Law-152, an operator is a state or municipal body, a legal entity or an individual who, alone or collectively with other persons processes personal data ; he also determines its purpose, necessity and composition.
All procedures carried out to establish the protection of personal data during their processing in the information system should be carried out only by those people or companies that are on the list previously created by the operator . And only they can have permission allowing them to access the data.
It is also necessary to take preventive measures to help avoid prohibited access to information.
For these purposes, all views and activity are recorded and reflected in an electronic log, which is the responsibility of the operator to check.
Roskomnadzor is constantly monitoring how PD is processed by operators, checking and monitoring, and the procedure for protecting documentation .
What is regulated
Federal legislation:
- “On approval of the list of information of a confidential nature” - Decree of the President of the Russian Federation dated March 6, 1997 No. 188 determines that personal data also includes information about facts, events and circumstances of a citizen’s private life, allowing his personality to be identified.
- 149-FZ “On information, information technologies and information protection” is a basic law that establishes general things.
- “On Personal Data” dated July 27, 2006 No. 152-FZ - it sets the framework for what PD is and how to process it (by the way, storage and transmission are subtypes of processing). Particularly interesting quotes:
“It is not permitted to combine databases containing personal data, the processing of which is carried out for purposes that are incompatible with each other.”
“Only personal data that meets the purposes of their processing is subject to processing.”
“The content and volume of personal data processed must correspond to the stated purposes of processing. The personal data processed should not be redundant in relation to the stated purposes of their processing.”
- Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation “On approval of requirements for the protection of personal data during their processing in personal data information systems” dated November 1, 2012 No. 1119 - the document describes the rules for determining the levels of personal data security and the basic requirements for protecting personal data.
- Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation “On approval of requirements for tangible media of biometric personal data and technologies for storing such data outside personal data information systems” dated 07/06/2008 No. 512 - contains requirements that must be applied when using tangible media on which biometric PD is recorded, and also when storing biometric personal data outside personal data information systems. Although the document is old, its requirements must be taken into account.
- Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation “On approval of the Regulations on the specifics of processing personal data carried out without the use of automation tools” dated September 15, 2008 No. 687 - everything is clear from the title: requirements for the processing and protection of personal data that are processed in paper form.
Key regulatory documents:
- Order of the FSTEC of Russia dated February 18, 2013 No. 21 “On approval of the composition and content of organizational and technical measures to ensure the security of personal data during their processing in personal data information systems” - a large set of organizational and technical requirements for information protection, as well as rules for creating security systems personal data. In short, see the post about how we passed the certification and how we help you get certified.
- Order of the FSB of Russia dated July 10, 2014 No. 378 “On approval of the composition and content of organizational and technical measures to ensure the security of personal data during their processing in personal data information systems using cryptographic information protection tools necessary to fulfill the requirements established by the Government of the Russian Federation for the protection of personal data” data for each security level" is a very useful document that contains not only requirements for the protection of personal data, but also allows you to determine the class of crypto-tools required for use.
- “On approval of requirements and methods for depersonalization of personal data” - Order of Roskomnadzor dated September 5, 2013 No. 996 (Registered with the Ministry of Justice of Russia on September 10, 2013 No. 29935) and “Methodological recommendations for the application of Roskomnadzor Order dated September 5, 2013 No. 996 “On approval requirements and methods for anonymization of personal data” approved. Roskomnadzor 12/13/2013, which ceases to make PD actual PD when depersonalized, for example, for the purposes of Data Mining.
Roskomnadzor paid significant attention to the subtleties of qualifying images as personal data in its explanations “On the issues of classifying photo and video images, fingerprint data and other information as biometric personal data and the features of their processing” (see 25.rsoc.ru).
Of course, the list is far from complete; above are only the main documents. There are also information messages and documents on modeling threats to information security from the FSTEC of Russia, methodological recommendations and documents on forming assumptions about the capabilities of violators from the FSB of Russia, documents from the Ministry of Telecom and Mass Communications, etc.
Means of protection and protection of personal data
reliability is ensured by:
- establishing risks when processing personal data in the information system;
- constant use of technical and organizational measures to establish security in accordance with the security levels established by the Government of the Russian Federation;
- procedure for improving the means and effectiveness of protection;
- constant review of machine PD media;
- instant detection of unauthorized entry;
- recovery of personal data that was infected with a virus or destroyed during a database hack;
- recording and accounting of all actions that are performed in the information system;
- cooperation with private security is used;
- the database is protected by passwords known only to people who have access rights;
Sample consent to provide personal data
Providing PD is an action of a certain nature through which PD is disclosed to any person or group of persons.
If you need to draw up an agreement to provide your PD , then in writing you must indicate the following:
- Full name, place of residence, data stated in the passport;
- Full name and place of residence of the representative of the PD owner, data contained in the passport, power of attorney;
- name or full name of the operator who receives consent;
- the purposes for which PD is processed;
- list of PD to which you consent to access;
- the name or full name and address of the person who, as designated by the operator, will process the data;
- the period during which permission to access the owner’s information will be valid;
- signature of the PD owner.
Refusal to provide to third parties
Federal Law N152 “On Personal Data” came into force in 2006. , but a full report on their PD had to be provided since 2010, when Federal Law No. 210 “On the organization of the provision of state and municipal services” was adopted.
And if now you receive calls from banks and collectors who will not leave not only you, but also your relatives and colleagues in peace, then it’s time to revoke your consent to process personal data. Of course, they have already been transferred to these organizations, but this step will help you scare away the ransomware.
Keep in mind that the application must be sent not only to the actual address of the bank branch where you took out the loan, but also to the legal address.
Send your application by registered mail: this way you will have notification of receipt. Indicate the address that you registered when concluding the loan agreement.
Attach a copy of your passport and loan agreement : this will help the organization quickly find your documents and make appropriate changes to them.
But do not forget that each situation requires individual measures. Some of them require cooperation with relevant authorities, such as the police.
According to Article 24 of Federal Law N 261-FZ, persons who are guilty of causing moral harm to the owner of personal data by violating the law of processing and storing them are required to bear criminal liability for disclosure and distribution, namely, compensation for moral damage, in addition to property damage, as well as losses incurred by the PD owner.
Download a sample application for revocation of personal data here.
Responsibility for disclosure of personal data
The liability for incorrect or unsecured storage of data is very serious. If an organization does something wrong, it will incur audits, inspections, administrative proceedings or criminal proceedings .
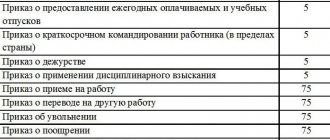
Administrative responsibility
An employer can pay a fine of up to 75 thousand rubles for:
- collection and processing of redundant information;
- lack of employee consent to data processing;
- access of third parties to personal data of employees;
- ignoring employee requests to delete his personal data (for example, after his dismissal).
Criminal liability
According to Article 137 of the Criminal Code of the Russian Federation:
- Disclosure of employee data in the public space, publication in the media of information that constitutes his personal or family secret. A fine of up to 200 thousand rubles, imprisonment for up to 2 years and a ban on holding certain positions for up to 3 years.
- The same thing with the use of official position - a fine of up to 300 thousand rubles, imprisonment for up to 5 years and a ban on holding a corresponding position for up to 6 years.
Read about responsibility for disclosing personal data in this material.
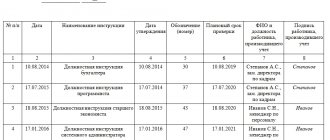
Changing an employee's personal data
Employee's application for amendments to documents
An employee whose PD has been modified needs to draw up a free-form statement in which he needs to indicate the reason for the changes that have occurred and say about the adjustments that should be made to the existing documents.
If you change your last name, then the application must be submitted under your old last name, because you are still listed under that name in the organization.
You must attach copies of relevant documents to your application that will confirm the changes that have occurred.
Order to amend documents
The need for the employer to draw up an order to change the employee’s personal data is not supported by Labor legislation. But this necessity is chosen to convey information to all interested parties (HR officers and accountants) .
The date of the completed order must be identical to the date on which the employee submitted the application with all proposed copies of documents. The order must be signed by the employee as a sign that he is familiar with it.
Notice about the processing of personal data
It is a very common mistake for operators to notify about the processing of personal data when it was possible not to do so. And if you still decide to notify Roskomnadzor, here are some recommendations:
- Read very carefully Part 2 of Article 22 of the Federal Law of the Russian Federation dated July 27, 2006. N 152-FZ “On personal data”.
- Look at the data that is processed for you. Some cases will require you to make adjustments with PD carriers.
One of the reasons why you may not notify about the processing of personal data is indicated in clause 2, part 2, article 22 of the Federal Law and looks like this:
Let's take the example of establishing a business relationship with an individual to perform a service. To make it clear that everything is ready and you didn’t have to just drive several tens of kilometers, the foreman prudently took your phone number to announce the good news. And in this case, the contract must stipulate “The workshop undertakes to notify the client by phone **** about the completion of the service.”
Learn how to protect your personal data from the video: