Maintaining personal files of employees is not mandatory for all categories of employers. But more accurate and complete information about employees helps the manager manage the workforce more effectively. In order to have such information, recording data related to the work activities of employees and forming the received information into personal files is advisable. Who needs to maintain personal affairs without fail? What documents can be kept in personal files? You will find answers to these questions in the article.
The legislation provides for the mandatory maintenance of personal files only for state civil servants. For other employees, this obligation is determined by the local regulations of the organization.
Not too personal
Since the procedure for maintaining personal files is not regulated for budgetary organizations, we recommend that the employer adopt a local regulatory act that will regulate the issues of maintaining, registering and storing personal files.
For your information. A case is a document or a set of documents related to one issue or area of activity, placed in a separate cover. Cases are considered initiated from the moment the first executed document is included in them.
When managing employees' personal files, strict rules must be followed, even if this is not a mandatory requirement for the employer.
It is important to remember that regardless of what the created folders are called (“personal data”, “dossier” or something else), they contain the employee’s personal data, therefore it is necessary to comply with all the requirements stipulated by Chapter. 14 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation and other federal laws on the protection of personal data.
According to Art. 85 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, personal data means information necessary for the employer in connection with labor relations and relating to a specific employee.
As a rule, personal files are opened:
— for employees from among the management team of the organization (manager, his deputies (assistants), heads of structural divisions, etc.);
- for employees for whom financial liability may be established in accordance with the law (chief accountant (accountant), as well as deputy chief accountant, etc.).
However, in many organizations, personal files are kept for all employees, regardless of rank, status and work performed. This is primarily due to the fact that thanks to the information contained in one folder, you can quickly obtain objective information about the employee. After all, all copies of the employee’s personal documents, orders for this employee and other important papers are stored in the personal file.
Documents included in a personal file can be divided into three groups:
- submitted when applying for a job;
— recording hiring;
— arising during the employee’s labor activity in the organization.
The personal file form is not unified, so each employer decides this issue independently. When registering a case, it would be a good idea to study the requirements of GOST 6.30-2003 “Unified system of organizational and administrative documentation. Requirements for registration."
1.2. Grouping different categories of documents
1.2.1
. Protocols, orders, instructions, resolutions and other organizational and administrative documents of the organization are grouped into cases by type and chronology with related applications in accordance with the nomenclature of cases.
1.2.2.
Orders for core activities are grouped separately from orders for personnel.
1.2.3.
The provisions and instructions approved by administrative documents are appendices to them and are formed together with the specified documents. If they are approved as an independent document, then they are grouped into independent cases.
1.2.4
. Minutes of meetings are located in files in chronological order.
1.2.5.
Reports and plans are filed in the file of the year to which they relate, regardless of the date of their receipt or preparation (for example: the annual report of the organization (balance sheet), plans for organizational and technical activities, publications and technical training of the organization, work plans of the organization and structural divisions and etc.).
1.2.6.
Personal accounts of employees and personal files of dismissed employees are grouped into separate files and arranged in alphabetical order.
1.2.7.
Correspondence with ministries, departments, organizations, as well as correspondence on proposals, statements and complaints from citizens is filed in files according to the dates of preparation of responses, while the response document is placed behind the request document. When correspondence on a particular issue that began in the previous year is resumed, the documents are included in the current year's file, indicating copies of the response to the index of the previous year's case.
1.2.8.
Proposals, statements and complaints of citizens regarding the work of organizations and all documents for their consideration and execution are grouped separately from statements of citizens on personal issues.
Composition of personal file
The list of documents to be included in a personal file is approved only for civil servants. However, organizations not associated with the public service can also use this list and determine which documents they will include in their personal files.
So, we recommend including in your personal file:
1) documents presented by the employee when applying for a job:
— a copy of your passport or other identification document;
— copies of documents on education, qualifications or special knowledge;
— a copy of the insurance certificate of state pension insurance;
— copies of military registration documents for those liable for military service and persons subject to conscription for military service;
— a copy of the certificate of tax registration of an individual with the tax authority;
— certificates of the results of a preliminary medical examination (examination) conducted to determine the suitability of these workers to perform the assigned work (in cases provided for by law);
- a certificate confirming the presence (absence) of a criminal record and (or) the fact of criminal prosecution or the termination of criminal prosecution on rehabilitative grounds when applying for a job related to an activity to which, in accordance with the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, other federal law, persons with or have a criminal record, are or have been subject to criminal prosecution;
2) documents documenting employment:
- a handwritten application for employment;
— autobiography;
— personal sheet for personnel records;
— a copy of the employment order;
— a copy of the employment contract;
— a copy of the work record book with a record of employment;
3) documents issued during the employee’s activity in the organization:
— certificates of results of periodic medical examinations (examinations);
— copies of documents confirming the employee’s right to tax deductions provided for in Art. 218 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation (for example, a child’s birth certificate), when an employee submits an application to provide him with the specified deductions;
— copies of documents establishing disability and limited ability to work (for employees with these indications);
— a copy of additional agreements to the employment contract on changes in the conditions of labor relations;
— copies of orders on transfer, promotion, application and removal of disciplinary sanctions at work and other orders relating to a specific employee;
— job description;
— a copy of the agreement on full financial liability;
— non-disclosure agreement (for employees who have access to such information);
— certification materials;
— reports and explanatory notes, employee statements;
— documents confirming changes in biographical data (certificate of marriage or divorce, change of surname, etc.);
- a copy of the work book with an entry on the termination of the employment relationship.
Typically, a photograph of the employee (4 x 6 or 3 x 4 cm) is placed in the personal file, and it is recommended to update it periodically. As a rule, employee photographs are updated at least once every five years or when employees reach the ages of 20 and 45 years.
List of documents for the formation of a personal file when submitting to the archive
— Constitutional law — List of documents for the formation of a personal file when submitting to the archive
Personal things. In personal files, all documents are located only in the chronological order of their receipt. For all documents contained in the personal file, an internal inventory must be drawn up, which contains the following details:
- serial number of the document included in the inventory;
- document number and date (if necessary);
- Title of the document;
- number of sheets in the document;
- note;
- final record of the number of documents in the personal file.
The approximate order of arrangement of documents in a personal file is as follows: internal inventory of case documents, personnel records sheet or questionnaire, job application, autobiography, certified copies of personal documents, certified copies of orders for admission, appointment, relocation, job responsibilities, certification documents etc.
Preparing HR files for transfer to the organization’s archives
Inventory of files submitted to the archive After receiving cases, when submitting documents to the archive, the head of the archive signs on three copies of the inventory of permanent storage cases and on two copies of the Acceptance Certificate for the delivery of documents to the archive. The second copies are returned to the sender, the rest remain in the archive.
The end of submitting documents to the archive ends with filling out accounting documents. Documents are transferred to state archives after the expiration of storage periods, but there are cases of early transfer of documents. An example of early delivery of an archive could be the delivery of an archive for free storage during liquidation (bankruptcy) and vice versa, materials can be left for an additional period.
Documents archive
Important This event is also carried out in cases of reorganization, when documentation is transferred to the legal successor (the period for transferring cases in both cases is two months). It is also necessary to transfer files to departmental storage at intervals of approximately once every 3 years.
Maintaining personal files of employees
A personal file is maintained throughout the entire period of employment of each employee of the organization. Maintaining a personal file includes:
— keeping records in the relevant sections of the personal file;
— placement of documents to be stored as part of personal files;
— seizure of documents that are no longer needed;
— periodic checking of the state of the personal file for the safety of the documents included in it.
When creating an employee’s personal file, initial registration is also carried out, which means assigning an account number to the file, entering the relevant data in the lines on the front side, and drawing up an internal inventory.
Employees are required to promptly report any changes to personal data included in the personal file to the organization’s human resources department. As a rule, this is done in writing, accompanied by documents confirming the changes. After making entries in the personal file, the original documents are returned to the employee. If necessary, copies of these documents are first taken and certified and attached to the personal file.
In any case, entries in personal file documents are made on the basis of original documents (or duly certified copies of documents). All entries made in documents in the process of maintaining a personal file are made by hand with a fountain pen or ballpoint pen in black, blue or purple, legibly and without corrections. If necessary, these records are certified by the signature of an authorized official of the HR department and the seal of the organization (or the seal of the HR department).
To speed up the process of making entries in personal records, it is allowed to use facsimiles (stamps) of established samples. Documents accumulated during the management process are distributed in the personal file into sections and arranged in chronological order.
Sheets of documents filed in a personal file are subject to numbering. Information about these documents, including the numbering of the pages within which they are located in the personal file, is reflected in the internal inventory.
2.5. Drawing up a sheet of evidence for the case (to clause 2.1.4)
2.5.1.
To take into account the number of sheets in the case and record the peculiarities of their numbering, a document certifying the case is drawn up.
2.5.2.
The document certifying the case is drawn up on a separate sheet of A4 format according to the established form (Appendix 2).
2.5.3.
The document certifying the case indicates in numbers and in words the number of numbered sheets of the internal inventory (if any).
2.5.4.
The certification sheet specifies the following features of the numbering of case documents:
— presence of letter sheets and missing numbers;
— numbers of sheets with irreparable defects (torn sheets, sheets stained with ink, etc.).
2.5.5.
All subsequent changes in the composition and state of the case (damage, replacement of originals with copies, addition of new documents, etc.) are noted in the certification sheet with reference to the relevant act.
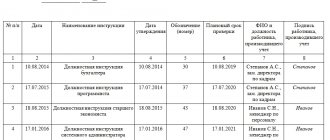
Sample of an internal inventory of a personal file
Internal inventory of personal documents
─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────
(last name, first name, patronymic of the employee)
| N p/p | Title of the document | Number of sheets | Document issue date | To whom was the document issued? | Document return date | HR employee's signature |
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 |
| 1 | Addendum to the personal personnel record sheet | |||||
| 2 | Personal sheet for personnel records | |||||
| 3 | Autobiography | |||||
| 4 | Copy of education diploma | |||||
| 5 | Employment contract | |||||
| … | ||||||
| Etc. |
Job title of the person
who compiled the inventory___________________________
____________ ________________________
(signature) (signature decryption)
date
An internal inventory is compiled to record documents of certain categories of permanent and temporary (over ten years) storage periods, the recording of which is determined by the specifics of this documentation (especially valuable, personal files, etc.).
The specificity of compiling an internal inventory of documents in a personal file is that it is included in the file immediately upon its establishment and is filled out as it is maintained. That is why the internal inventory provides for the inclusion of new documents in the personal file, as well as the removal of documents from the personal file, and the replacement of originals with copies (recorded in the “Note” column).
If the case is already bound and filed, the internal inventory of documents certified by the compiler is glued with the top edge to the inside of the front cover.
Please note that when preparing a case for submission to the archive, the sheets of the internal inventory are numbered separately from the sheets of the personal file.
After an employee is dismissed, his personal file is closed, that is, removed from the folder and stitched. At the same time, it is important not to forget to draw up a certification sheet.
2.1. Basic requirements for filing cases
2.1.1.
The registration of cases is carried out by employees of the documentation support service of the organization’s management or other structural divisions, whose responsibilities include the establishment and formation of files with methodological assistance and under the control of the organization’s archive.
2.1.2.
Depending on the storage period, full or partial registration of cases is carried out.
2.1.3.
Cases of permanent storage, temporary storage (over 10 years) and personnel files are subject to full registration.
2.1.4.
Full registration of cases includes:
— filing or binding of documents in files (clause 2.2);
— numbering of sheets in the file (clause 2.3);
— drawing up an internal inventory of case documents (clause 2.4);
— drawing up a document certifying the case (clause 2.5);
— entering the necessary information into the details of the case cover (clause 2.6).
2.1.5.
Temporary storage files (up to 10 years inclusive) are subject to partial registration. They can be stored in folders, do not re-systematize the documents in the file, do not number the sheets, do not create an internal inventory and a certifying sheet of the file.
Responsibility for personal affairs
All information stored in a personal file is classified as personal data, therefore employers must comply with the rules and requirements of the Personal Data Law and Chapter. 14 Labor Code of the Russian Federation. Since the employer is responsible for the protection of personal data, we recommend that the HR department be equipped in such a way as to eliminate the possibility of theft and loss of personal files. Remember that by virtue of Art. 90 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, persons guilty of violating the rules governing the receipt, processing and protection of employee personal data are subject to disciplinary and financial liability in the manner established by the Labor Code of the Russian Federation and other federal laws, as well as civil, administrative and criminal liability in the manner provided for by federal laws.
According to paragraphs. “c” clause 6, part 1, art. 81 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, an employment contract with an employee may be terminated due to the disclosure of a secret protected by law that became known to him in connection with the performance of labor duties, including due to the disclosure of personal data of another employee. Since such dismissal refers to dismissals for violation of labor discipline, such an employee must be dismissed in compliance with the procedure provided for in Art. 193 Labor Code of the Russian Federation.
In this case, material damage means compensation by the employer for moral damage to the employee, and the employee compensates for direct actual damage caused to the employer, as well as to third parties (Article 238 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation). If harm to an employee was caused by the fault of a person who was responsible for non-disclosure of personal data, the employer may hold this person financially liable for the damage caused to the employee by such actions. In accordance with clause 7, part 1, art. 243 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, financial liability in the full amount of damage caused is assigned to the employee in the event of disclosure of information that constitutes a secret protected by law.
Thus, administrative legislation provides for the imposition of administrative fines for violation of the procedure established by law for the collection, storage, use or dissemination of information about citizens (personal data).
Article 13.11 of the Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation provides for a fine in the amount of 500 to 1,000 rubles. for an official, from 5,000 to 10,000 rubles. - for the organization.
In accordance with Art. 13.14 of the Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation, a person who discloses information to which access is limited by federal law, provided that access to such information is obtained in connection with the performance of official or professional duties, must be subject to an administrative fine. The fine for civilians ranges from 500 to 1,000 rubles, for officials - from 4,000 to 5,000 rubles.
If an employee responsible for storing, processing and using the personal data of other employees, abusing his official powers, distributes information stored in his personal file about the private lives of other employees without their consent, he may be subject to criminal liability. Thus, for the illegal collection or dissemination of information about the private life of a person that constitutes a personal or family secret, or the disclosure of this information in a public speech, a publicly displayed work or the media, Art. 137 of the Criminal Code of the Russian Federation provides for such penalties as fines, correctional, forced labor with deprivation of the right to hold certain positions or engage in certain activities, and imprisonment.
Rules for submitting personal files to the archive
When preparing cases for submission to the archive or for subsequent storage in the personnel service, an examination of the value of the cases is carried out using the method of sheet-by-sheet review of the cases. It is not allowed to examine the value of cases by looking only at their titles.
When conducting an examination of the value of files in the personnel service, special attention must be paid to files with permanent and long-term (over 10 years) storage periods, since these are the files that are subject to transfer to the organization’s archive. Personnel service files with a temporary (up to 10 years inclusive) storage period are not transferred to the archive, they are stored in the personnel service and, upon expiration of the storage period, are subject to destruction according to established rules.
Registration of cases in the personnel service Registration of cases is carried out by employees of the personnel service with the methodological assistance of the organization’s archive. The HR service is obliged to submit files to the archives fully completed.
Personal file: current storage and transfer to the archive
Formation of cases And it should be carried out right up to the dismissal of the employee.
It is then transferred to the archive for storage. This document cannot be destroyed for a certain period of time.
Required or optional? It has already been said that it is not at all necessary to lead employees. But any self-respecting enterprise has this kind of documentation. When is it necessary to create a dossier and when is it not? Rules on this issue are not prescribed by law anywhere.
Maintaining an employee’s personal file A personal file consists of the cover of the personal file and the employee’s documents, which contain comprehensive information about the employee and his work activity (if we are talking about a student, then information about his training).
managers and their deputies; leading specialists; financially responsible employees (cashiers, storekeepers, etc.); employees with the prospect of promotion, etc.
State Archives: how to submit an employee’s personal file
When preparing files for filing (binding), metal fasteners (pins, paper clips) are removed from the documents. 3.6.5.
Storage and recording of personal files of employees
Employees' personal files should be kept in the HR department. Typically, the human resources department of an organization stores the personal files of working employees. Personal files of dismissed employees are stored, as a rule, in the organization’s archives or in the territorial archive.
Since Ch. 14 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation imposes on the employer the obligation to protect personal data; in order to limit access to personal information of employees by unauthorized persons, personal files must be stored in safes or cabinets. Moreover, employee work books should be kept separately from personal files.
Only responsible officials and heads of their departments may have the right to access personal files of employees. Records of personal files can be kept in a special journal (this option is used in the case of a large number of personal files of employees stored in the organization). Classification of personal files of employees can be carried out in numerical or alphabetical order, as well as in sections that correspond to the names of the company’s departments. Classification within sections of employees’ personal files is carried out in numerical or alphabetical order.
The transfer of personal files to the archive is carried out no later than three years after their completion in office work. The storage periods for various documents containing personal data of employees are defined in a number of legislative and regulatory acts. Thus, orders, instructions and other primary accounting documents, including documents on personnel records, working hours and wages, are stored for periods established in accordance with the rules for organizing state archival affairs, but not less than five years. The personal files of the head of the organization, members of governing, executive, and control bodies, employees with state and other titles, prizes, awards, degrees are stored in the archive permanently, and the files of other employees - for 75 years. O in a personal file means that some of the documents can be classified as permanent storage.
How an archive of personal files of dismissed workers is compiled
After the dismissal of employees at the enterprise, the HR department must know how to properly and for how long documents should be saved. They organize the process of storing personal files of workers who left the organization, not by their last name, first name, patronymic, but in order according to the dates of the orders. Next, they are carefully stitched together for the year by number, an inventory is attached and transferred to the archive of the personal files of dismissed employees, distributed by year.
The need for an archive
Cases for transferring documents to the archive are formed by name in different folders. This needs to be done correctly. In one folder you can store data for vacations, and in the second there should be documents for dismissals.
Separately, the personnel service employee lays down the grounds for transfers and awards.
But documents need to be folded and stapled to form an archive of dismissed employees in a sequential order. Must be stored for at least 75 years . During the archiving process, documents are divided taking into account standard storage periods. After the end of each year, it is necessary to staple all orders and archive the personal cards of employees dismissed from the enterprise.
The documents are then sealed and presented to the archivist. If you don't have a file cabinet, you can lock the folders in a fireproof cabinet. Documents of dismissed employees should be kept separately from those of active employees.
Legal entities, ordinary citizens and government officials are required to ensure the integrity of information about previously employed employees for a certain period. Representatives of companies and citizens have the right to request information to gain access to the archive of personal files of laid-off workers.
Personnel department employees issue certificates and copies of documents free of charge for presentation to the pension fund and social security authorities for receiving benefits.
The available data is also used as evidence. Then the previously seized documents are given to the owner.
Formation of a personal file
The procedure for collecting information about employees is strictly regulated. The documentation should include:
- Application form and resume.
- Personal sheet of the HR department.
- Characteristics of the employee.
- TIN, insurance certificate.
- Employment contract.
- Orders on transfers, vacations and business trips.
You need to know how to store the personal files of dismissed employees. Thus, an employee’s personal card, created on the basis of a dossier, is left in the company’s personnel policy until the end of the working year. Within three years after leaving the organization, documents undergo archival and technical processing. After this, they are transferred to the archives of the institution.
You can store documents in the archive if you have an annual inventory. The HR department collects a list of employees who left the company over a certain period of time. The date of dismissal is indicated on the cover of each case.
Storage systematization
According to the instructions, only original documents can be submitted to the archives. Photocopies may be left as attachments to orders for admission, dismissal or relocation. Personal cards of workers should be stored according to the following rules:
- Cards for former employees are kept on paper.
- They are put into folders with further numbering and firmware.
- On the cover of any created folder there are numbers and the number of cases in it.
- The HR department can store cards of currently employed employees.
- The personnel officer hands over all personal cards of employees dismissed from the organization to the archive and stores them by date, and within the dates they distribute them alphabetically.
Storage is organized in special cabinets to protect from fire and moisture.
The law establishes the time for which documents must be preserved. The main rules were approved back in February 2002 by the Board of Rosarkhiv.
The rules for creating an archival fund do not apply to papers with a storage period of less than ten years. Personal files of dismissed citizens are stored as follows:
- Employment contracts, cards and personal files are saved for 75 years.
- Data on admission and relocation - 5 years.
- Questionnaires - at least 12 months.
- Extracts from reports - 75 years.
- The lists of employees are also 75 years old.
- Informative data on tariffs and salaries - 10 years.
- Acts of accounting of labor books - 36 months.
- Substitution applications are valid for 3 years.
The files of dismissed workers are transferred to the archives. They are processed after the end of the year. Depending on the storage time and value of documents, cases can be processed in full or according to a simplified scheme. Documents of managers, managers and persons with degrees and awards are stored indefinitely, while personal cards of dismissed employees who do not hold management positions are stored for 75 years .
Source: https://trud.help/docs/arhiv-lichnyih-del/
What documents are prohibited from being stored in an employee’s personal file in 2021?
In order not to violate Russian legislation, it is recommended that each employer personally familiarize the personnel officer with the list of papers that should be in each employee’s LD.
This list of documents in 2021 includes such main papers as:
- an employment contract signed by the employee, as well as additional agreements accompanying it (if any);
- orders to impose penalties or rewards from superiors;
- an agreement on the individual financial responsibility of the employee, if his position requires the availability of this document;
- a non-disclosure agreement signed by the employee regarding information that is a company secret;
- acts of violation of labor discipline;
- explanatory and memos;
- The order of acceptance to work.
Each additional certificate is filed by the personnel officer in a folder in strictly chronological order, after which he draws up an inventory of documents (this is a mandatory item, failure to comply with which may lead to penalties).
It is worth noting that the documents stored in the employee’s personal file for verification by the labor inspectorate must be supplemented with a signed consent to the processing of his personal data.
According to a statement by Rostrud employees, the list of prohibited papers that cannot be filed in an employee’s personal file includes all documents and their copies that are not related to the citizen’s work activity, such as, for example:
- military ID;
- TIN;
- passport and copies of its pages;
- SNILS;
- birth certificates of children and marriage.
Thus, the presence of all the listed papers is a direct violation of the constitutional rights of a citizen of the Russian Federation to the inviolability of personal/private life. Collecting this information without a person’s permission is prohibited!
In addition, storage of the listed papers violates the norms of Federal Law No. 152, adopted on July 27, 2006 and entails punishment, namely the imposition of an administrative fine under Part 1 of Article 13.11 of the Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation.
In the last similar case, in which lawyers from the Legal Ambulance website participated, the employer was fined 50,000 Russian rubles simply for having a copy of the passport in the employee’s personal file. It is almost impossible to prove that you are right in this case.
When answering the question of what should be kept in an employee’s personal file in 2021, it is worth mentioning the medical records of employees, which some employers store in the LD. Indeed, if an employee’s position involves his contact with food, children or, for example, medicines, the employer, according to current legislation, has the right to demand this document. However, its storage becomes possible only after obtaining consent from the employee to process his personal data.
The same rule applies to the following documents:
- certification sheets;
- diplomas, certificates and other educational documents;
- certificates of no criminal record or its presence;
- documents on advanced training;
- characteristics from educational institutions, as well as past places of work.
We invite you to find out which standard of gold is the best
Let us also remind you that employee work books must be stored separately from the rest of the personnel documentation. Most companies use reliable safes for this purpose, to which only HR staff have access.
In any case, every employer must understand that maintaining an employee’s personal file is not a one-time, but a regular activity. After all, over time, the information and documents in the LD will have to be updated. This can only be done by obtaining a written statement of consent from the employee himself and introducing any papers, however, as well as removing them from the file - the personnel officer has no right!
At the same time, the release of the personal file in question can only be carried out by order of the head of the company. The same rule applies to the employee himself for whom the LD is opened. At the same time, each employee has the legal right to familiarize himself with his personal document at any time convenient for him, but to remove it from the personnel officer’s office only with the permission of the employer.
In the event that a third-party organization requests access to the folder, its employees must submit an official request for this, and the transfer of documents will become possible only after receiving the employer’s resolution and drawing up an act in 2 copies.
So, after determining the list of papers stored in the employee’s personal file, it is worth noting the fact that since the validity period of each document may differ, the storage period for papers in the employee’s personal file is determined for the entire folder. So, for 3 years after the dismissal of an employee, they remain stored in the personnel department, after which they are transferred for storage to the archive for the period established by law.
According to the information established in Article 22.1 of the Federal Law dated October 22, 2004, number 125, personnel documents can be stored for 50 and even 75 years! At the same time, their shelf life depends, among other things, on the date of their establishment/completion (before 2003 or after that).
The personnel officer is obliged to take into account every certificate, certificate or any other document in the appropriate journal, which he can keep in free form. The main thing in this is that the numbers in the column of this magazine and on the cover of the folder match.
Dear Readers of our website, if you still have questions about the documentation, be sure to ask our duty lawyer by filling out the form below.
If you find an error, please highlight a piece of text and press Ctrl Enter.
The composition of personal files, as well as the procedure for formation, for private entrepreneurship is not fixed at the legislative level, but it must be properly prescribed in the local act of the company.
Documents that usually belong to a personal file can be divided into several groups:
- Primary documentation for hiring. This includes those documents that employees provide upon employment, and those that are filled out and entered directly during registration. It can be:
- summary;
- documents on education and qualifications;
- copies of identification documents (passport, SNILS, identification code, if any);
- recommendations or reviews from previous employers (if necessary);
- a document or a copy thereof regarding military registration (if available);
- certificate of no criminal record (needed when applying for certain positions);
- medical examination data;
- completed application form (if provided);
- employment application;
- a copy of the admission order;
- concluded employment contract, etc.
- Papers that appeared in the process of working in this position. They may reflect the employee's professional achievements or his social dynamics. These may include:
- various qualification certificates;
- driver license;
- marriage or divorce certificate, if these events occurred during employment;
- birth certificates of children (same justification);
- job description;
- additional agreements concluded (if this was done);
- a copy of the agreement on financial responsibility (if the position provides for it);
- certification certificates;
- data from regular medical examinations;
- documents establishing medical restrictions or disability (if this happened during work);
- copies of orders about internal changes in position (transfer, promotion, demotion, etc.);
- data on disciplinary sanctions and work incentives;
- leave requests;
- reports, explanatory notes, memos, etc.
- Documents confirming the employment relationship with this employer. Before the case is dismissed, it must be properly completed. The latest documents in the personal file folder may be:
- resignation letter;
- a copy of the dismissal order;
- documents on dismissal due to external transfer;
- employee's death certificate.
The list of documents to be included in a personal file is approved only for civil servants. However, organizations not associated with the public service can also use this list and determine which documents they will include in their personal files.
— a copy of your passport or other identification document;
— copies of documents on education, qualifications or special knowledge;
— a copy of the insurance certificate of state pension insurance;
— copies of military registration documents for those liable for military service and persons subject to conscription for military service;
— a copy of the certificate of tax registration of an individual with the tax authority;
— certificates of the results of a preliminary medical examination (examination) conducted to determine the suitability of these workers to perform the assigned work (in cases provided for by law);
- a certificate confirming the presence (absence) of a criminal record and (or) the fact of criminal prosecution or the termination of criminal prosecution on rehabilitative grounds when applying for a job related to an activity to which, in accordance with the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, other federal law, persons with or have a criminal record, are or have been subject to criminal prosecution;
- a handwritten application for employment;
— autobiography;
— personal sheet for personnel records;
— a copy of the employment order;
— a copy of the employment contract;
— a copy of the work record book with a record of employment;
— certificates of results of periodic medical examinations (examinations);
— copies of documents confirming the employee’s right to tax deductions provided for in Art. 218 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation (for example, a child’s birth certificate), when an employee submits an application to provide him with the specified deductions;
— copies of documents establishing disability and limited ability to work (for employees with these indications);
Who do they file personal files against?
This question can be answered unequivocally only in relation to civil servants: for all, as required by law.
Since maintaining personal files is not necessary for private entrepreneurs, they themselves can decide which employees to keep this documentation for, and which ones can do without such detailed personnel records. Some managers who practice this system prefer to keep personal records for all personnel in order to systematize data for each employee. But some, in order to save time, organize the management of personal files only for certain categories of employees.
Personal files are usually opened for employees of what positions:
- management;
- deputy managers at various levels;
- key specialists;
- employees bearing financial responsibility;
- personnel reserve, etc.
FOR YOUR INFORMATION! It is advisable to open a personal file for such employees, regardless of the form and time of his employment - he works part-time or at his main job, under a fixed-term employment contract or on a permanent basis.
Less often, positions are provided with personal records for which educational, qualification or other special requirements are not provided, for example, cleaner, watchman, janitor, etc.
We invite you to familiarize yourself with Violation of procedural law in the arbitration process
Personal file: we form and formalize
Often a personal file is placed on the same level as a work record book, although this is wrong. The work book does not contain any information other than the past and present place of work, unlike the dossier. Nowadays, most archives no longer practice filling out the indicated lines by hand - they simply put a stamp identical to the previously accepted records. So it is considered advisable to set aside an empty space for it at the top.
However, all enterprises are subject to the provisions of the Personal Data Law, according to which the employer is recognized as the data processor, and therefore he must ensure the protection of the personal information of his employees and prevent its disclosure. So, a Personal File is a set of documents containing certain information about an employee or employee, including his biography, information about education, work experience, professional skills and categories of a particular specialty.
The main regulatory rules are GOST 51141-98 and 17914-72, as well as federal laws on public service. But their requirements are mandatory for establishments and institutions. Initially, the personal file includes only those documents that are necessary for hiring a specific employee (they will be discussed below).
Since the procedure for maintaining personal files of employees for organizations and entrepreneurs is not regulated in any way, it would be advisable to develop and approve a regulation on the procedure for creating and maintaining personal files. It can reflect the composition of personal files, the procedure for its formation and maintenance, the circle of employees for whom it is necessary to maintain files, the storage mode and the procedure for accessing files, etc. Since the personal files of employees relate to long-term storage documents, when forming them those documents whose storage period does not exceed five years are not included.
Features of creating a personal file
Correct registration of personal files greatly facilitates the work with personnel documentation. Practice has developed a number of recommendations regarding the effective formation of personal files:
- Documents are collected under one cover, most often a folder, less often just a file or binder. They must be separate for each employee.
- It is not advisable to form cases thicker than 4 cm.
- Documents for permanent storage should not be mixed with temporary documents.
- The personal file may contain both original documents and their certified copies.
- It is preferable to replace important documents of permanent storage for personal files with copies.
- It is not customary to store several copies of the same document within one personal file.
- If the document contains attachments, they must be stored along with the relevant papers.
- Documents in the file should be arranged chronologically, that is, as they arise.
REMEMBER! The archives accept personal files for storage only in cardboard folders. Binders and files are not acceptable for this purpose and may only be for internal use.
What documents from the employee’s personal file are archived?
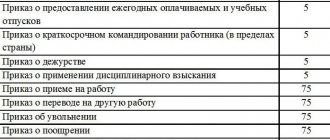
Ministry of Culture of Russia dated August 25, 2010 No. 558). Read more about dismissal here: Thus, orders for hiring, transfer, dismissal and other orders for personnel must be kept for at least 75 years. An exception to this rule is orders for granting vacations, sending on business trips in Russia (as well as other documents about business trips: assignments, reports, etc.), as well as orders for penalties.
They only need to be stored for five years. Employment contracts, personal cards and personal files of employees must also be kept for 75 years, and personal files of managers - permanently. The staffing table is also required to be maintained at all times. Workplace certification materials should be stored for 45 years, and in difficult, harmful or dangerous working conditions - 75 years. Keep the labor regulations even after replacing them with new ones. Shelf life is one year.
About assigning numbers to personal files
Therefore, personal files should be stored in places where access to unauthorized employees of the enterprise is limited. And requests for information contained in a personal file must be controlled and recorded in special registers. Unauthorized disclosure of personal information entails bringing the company to administrative liability. Each company has the right to develop rules for registering and maintaining personal files of employees, taking into account the specifics of its activities. But at the same time, one should take into account the general principles in accordance with which the personal affairs of employees are maintained.
Not all categories of employers are required to maintain personal files of their employees. But for the effectiveness of team management, it is advisable to form them. Today we will discuss how to do it correctly. Leave also a field indicating the end date of the employment contract. Also, after dismissal, you will need to indicate the number of pages in the file. 5 Do not forget to indicate the title of the case - the employee’s full last name, first name and patronymic. You can also write the position of the employee being employed. After dismissal, the file is filed and archived.
Is it necessary to keep personal files?
Most entrepreneurs consider personal files an essential component of personnel documentation. However, the law states that this is only true for civil servants.
Information about state and municipal employees must be systematized in the prescribed form (Decree of the President of the Russian Federation of May 30, 2005 No. 609). The personnel files of such employees are intended to reflect their entire track record so that it can be clearly seen how exactly their personal data has changed.
If an employee moves from one structure to another, his personal file must follow.
At a new place of work, it will be easier to form an impression of a new person, as well as obtain additional information about sources of income, connections, professional network, as well as other information that facilitates control.
Federal Law No. 79-FZ “On the State Civil Service of the Russian Federation” dated July 27, 2004, in Part 3 of Article 42, reveals the procedure for all actions with the personal files of this category of employees.
Neither the Labor Code nor other regulations of the Russian Federation contain a mandatory requirement to maintain personnel documentation exclusively through personal files created for each employee. Therefore, such registration of personnel data is not at all mandatory or even recommended.
IMPORTANT! The laws of the Russian Federation do not prohibit legal entities or individual entrepreneurs from maintaining personal affairs for their employees.
If the management of an organization or individual entrepreneur has decided to make it mandatory to fill out personal files, this must be enshrined in the accounting policy by prescribing the procedure in internal regulations. As a rule, it is the case that they use the regulations developed for civil servants.
Despite the fact that no requirements define or limit the composition of a personal file and the procedure for maintaining it, the practice of this branch of office work shows the undoubted convenience for the manager of this form of storing personal information. It is for this reason that the ubiquity of personal files in the personnel service has formed the myth of their obligatory nature.
The positive effect of introducing personal personnel records is obvious:
- timely recording of all employee documentation;
- tracking career dynamics;
- recording data on possible benefits;
- assessment of prospects for professional growth;
- safety and orderliness of personal documentation;
- prompt access to the entire range of personnel information.