Basic rules for daily work according to the Labor Code
Most often, the daily work mode is used, which means that work shifts are scheduled at intervals of two or three days. Then there is a violation of the provisions enshrined in legal acts on the length of the working week.
This period should not exceed forty hours per week. For this reason, when a company uses 24-hour work, a requirement is established to use a summarized procedure for recording hours worked. These provisions are spelled out in the provisions of Article 104 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation.
This rule provides that if it is impossible to comply with the reflected working time standards for a specific period, the company management is charged with monitoring the hours worked by a specific person. As a result, the resulting value cannot be greater than the value enshrined in legislative acts.
Accounting for working hours during daily work hours
Daily work involves a significant excess of the normal duration of work. Therefore, the rules on summarized recording of working time are used (Article 104 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
You can learn more about the procedure for recording working time from the corresponding article.
The starting point is one of the periods:
Subscribe to our newsletter
Yandex.Zen VKontakte Telegram
- month;
- quarter;
- year.
The time worked by the employee should not exceed the maximum duration for the period taken as a basis. Accordingly, if, with a 24-hour work schedule based on the “every other day” principle, the duration of work in 7 days exceeds the established 40 hours, the work schedule must be drawn up so that in the selected accounting period (for example, a month) the duration of working hours remains normal.
To understand how a schedule is drawn up when recording working hours in total, you can read the information from the article on this topic. As a result, overtime in one time period is compensated by rest in another.
The concept of daily work
Daily work should be understood as the fulfillment by a citizen of the obligations of the position, which is associated with the occupation of a certain position. This execution occurs within 24 hours. There are no prohibitions in the provisions of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation regarding this regime. However, when work is established during the day, the following provisions must be taken into account:
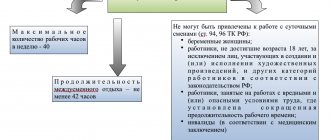
- In a week, a citizen must work no more than forty hours, which is prescribed in the provisions of Article 91 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation (there are exceptional situations that provide for the possibility of reflecting a shorter period of work).
- During the week, a citizen must be provided with a continuous period of rest (its minimum duration is forty-two hours, which is prescribed in the provisions of Article 110 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
- It is not always permissible to attract a citizen to work on a daily basis; the reason is restrictions due to the health or other characteristics of the employee (for example, this applies to minors and those with a disabled status).
It is also worth taking into account that the provisions of the law do not allow the use of labor of certain groups of citizens when establishing the regime in question. The list can be found in Article 96 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation.
Standard hours for a shift work schedule according to the Labor Code of the Russian Federation
Shift work schedule - Labor Code - standard hours - HR and accounting specialists often think about this when introducing new work modes in the company. Creating a correct shift work schedule is not an easy task, the solution of which requires a comprehensive analysis of both the provisions of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation and numerous by-laws.
In accordance with Art. 91 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, the normal working time is no more than 40 hours per week. Mandatory reduced working hours are regulated for people working in hazardous working conditions, minors, and also due to unsatisfactory health conditions. These standards apply to all existing work and rest regimes.
Standard working hours
In the course of establishing the duration of work, which involves performing duties every three days, it is quite difficult to comply with the standards for the duration of the working day defined in the legislation. The reason for this is that a citizen is obliged to remain in the performance of functions on the basis of a daily schedule. Then the company decides to use summary accounting of hours worked.
The period for fulfilling the obligation to work cannot be longer than that specified in the standards. It is stipulated that the accounting period cannot be more than 12 months. If we are talking about performing duties in dangerous or harmful conditions, then this period is reduced to three months.
The group to which a particular employee is assigned influences the number of hours that person can work. If he works less than a full week or day, the hourly standard will be reduced accordingly. An order developed by the Ministry of Health in 2009 provides a procedure according to which the standard working period is calculated.
Standard hours for a shift work schedule
- Daily, if the working day is constant;
- Weekly, if the length of the working day changes, but the working week remains unchanged;
- Summarized, if the schedule includes rotating weekends.
- For calculations, a standard week is used, in which there are 5 working days and 2 weekends.
- The length of the working week should be divided by 5 and multiplied by the number of working days in a month, excluding rest time. The number of working days in one month can be found independently or calculated using the production calendar.
- When determining labor standards, it is necessary to remove the period when the employee did not work (sick leave, went to study).
- If it is necessary to count hours not for a month, but for a period. Then the labor standard for the month is initially determined, then they are added up on a monthly basis depending on the duration of the reporting period
We recommend reading: If you did not receive child benefit until you were 18 years old
Employee rest during a 24-hour shift
An important point in this case is that a shift schedule is established for employees. This means that general weekends such as Sunday and Saturday, provided that a shift falls on them, will not count as days off. At the same time, the peculiarity is that the daily schedule can be used not only in relation to shift work. This can also be done using a flexible schedule. This is stated in the provisions of Article 102 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation.
The legislation allows for shifts lasting 24 hours. Such a schedule indicates that the citizen performs the duties of his position during the day, without leaving work. This period includes both daytime and nighttime. This schedule has significant differences from the schedule of those workers who work in a 5-day work week.
When such a schedule is established, the employee will rest during the days following the shift. In addition, rest periods are also set during the shift. When establishing rest, the provisions of labor legislation must be taken into account. It says that the duration of rest between shifts should be 2 times longer than the shift itself.
Standard hours for a shift work schedule in 2021 in three days
- Work week. It may consist of five days (Saturday and Sunday are days off), or six, but its duration should normally be 40 hours, or with a shortened time period - 24, 35 or 36.
- Change. The concept of a work shift includes the time after which workers engaged in the same labor process replace each other. It happens during the day and at night. When working in shifts, sometimes such a nuance arises as the inability to reduce the duration of the shift when it is provided for (for example, on a holiday). Then this time is considered overtime and is paid in accordance with overtime standards or compensated by providing time off. Payment for the night shift (from to ) occurs at an increased rate, which is approved by the employer.
- Working day. The time during the day during which work is performed. Normally equal to 8 hours.
- Accounting period. Time worked for a calendar period (for example, a quarter or a month, but not more than a year). This period allows you to compare the hours with the standards established by law. This is a unique form of control over the RV norm.
- Occupancy limit. Employment limit established by law. An example would be a part-time job. The number of hours worked in this case cannot exceed half of the daily wage rate per month. With a 40-hour work week in October 2021, part-time work should not take more than 84 hours.
This type of schedule is classified as either shift work or flexible work. In this case, the standard of 40 hours per week cannot be met. Therefore, hours exceeding the norm will be considered overtime, and their number will be determined at the end of the accounting period.
The right to sleep on a given schedule
It is necessary to take into account the provisions of Articles 106 and 107 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, which state that the time spent by an employee on rest and eating is not considered a break. For this reason, a citizen does not have the right to use this period of time at his own discretion. If the organization cannot arrange a break for the person to eat or rest, then this time is subject to payment.
Remuneration for daily work schedule
When an organization uses a shift or daily schedule, this has special features when calculating wages. Including:
- it is necessary to pay for the hours during which the citizen performed his labor duties in fact (this is the rate or salary for the position held)
- work that takes place at night must be paid at an increased rate, which is prescribed in the provisions of Article 154 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation
- if a shift falls on a holiday or weekend, then it must be paid at a double rate, however, the exception is situations when a citizen is given time off for a day worked
- hours worked in excess of the norm (in this case, the first couple of hours are paid in double amount, the rest of the time - in double amount)
It is important to take into account that changes to the above provisions can be made through the development of acts of local significance. At the same time, it is unacceptable to reduce the norms established by law.
Establishing a shift work schedule in an organization has certain features. This is how actual hours worked are calculated and how hours worked overtime must also be taken into account. The management of the organization needs to take into account some features:
- it is necessary to keep records of the overtime that takes place for each employee, which is prescribed in Article 99 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation
- A citizen can be involved in overtime work for no more than 120 hours (this value is set for an annual period)
- work on a weekend or holiday cannot be classified as overtime work
In order to establish the exact amount to be paid to the employee, it is necessary to carry out settlement transactions at the end of the accounting period.
Salary
First, let us recall that wages are established by an employment contract in accordance with the current employer’s remuneration systems, which include:
- the size of tariff rates, salaries (official salaries);
- additional payments and allowances of a compensatory nature, including for work in conditions deviating from normal;
- systems of additional payments and bonuses of an incentive nature;
- bonus systems, –
- and are established by collective agreements, agreements, local regulations in accordance with labor legislation and other regulations.
Why is it important? Because the employer needs to decide on the procedure for calculating wages when recording working hours in total.
Since the number of working hours for employees with summarized accounting of working hours for the accounting period (quarter, half-year, year) will differ in different months, it is best to calculate wages in each month based on the number of hours worked.
You may ask: what about the salary? If you pay a certain amount, you don’t need to count anything else. Yes, some employers believe that this is the easiest option. However, the salary when accounting for working time is summarized serves as the basis for calculating the rate per hour of work. This means that the accrued wages will reflect the difference in the number of shifts worked by employees of the same qualifications for the same month.
There are two options for calculating the hourly rate based on salary:
1. The calculation is made taking into account the standard working hours for a given month according to the production calendar. In this case, the hourly tariff rate will be different in different months of the accounting period.
Example 1
Let's calculate the hourly tariff rate for June 2021, if the employee's salary is 30,000 rubles.
According to the production calendar, the standard working hours for a 40-hour workweek in July 2021 is 168. Accordingly, the hourly tariff rate in July will be 178.57 rubles/hour (30,000 rubles / 168 hours). In August 2021, with a higher standard number of working hours, the hourly rate will be lower - 163.04 rubles / hour (30,000 rubles / 184 hours).
If the shift falls on a non-working holiday, how do I pay?
The employee works on a “every three days” schedule. One of his shifts falls on a non-working holiday. Does he have the right to receive another day of rest and pay in a single amount for work on this day? If he has, then who will work on his day of rest, because other shift workers have worked out their hours.
On the one hand, in this case, the employee is obliged to go to work according to the shift schedule (there is no requirement to ask for his consent). On the other hand, this day remains a non-working holiday for him.
Since Article 112 of the Labor Code, which establishes non-working holidays, applies to all employees, regardless of what mode they work under.
Consequently, payment for work on a non-working holiday (even if work on this day according to the shift schedule is included in the monthly norm of his working time) must be made in an increased amount.
Now let's look at how work on a holiday can be compensated. According to Article 153 of the Labor Code, the employer is obliged to pay for this day at least double the amount.
However, if an employee expresses his desire (instead of double pay) to receive another day of rest for work on a holiday, then such a day (within a period agreed with the employer) can be provided to him (please note that payment for work on a holiday must be be produced in a single size).
As follows from the above-mentioned rule of law, the employer has the right to provide another day of rest (at the employee’s request) as compensation for working on a holiday, but is not obliged. If it is possible to replace an employee on his day of rest, then, as a rule, the employee’s application must be satisfied.
Specific amounts of payment for work on a non-working holiday may be established by a collective agreement, a local regulatory act adopted taking into account the opinion of the representative body of employees, or an employment contract.
As practice shows, in a situation where an employee can be involved in work on a holiday only with his consent, the issue of compensation is resolved taking into account his wishes (before actually going to work). Otherwise, he may refuse to work on a generally accepted holiday.
If an employee was sick during his shift, when should he return to work?
An employee working on a “two days every other” shift schedule was on sick leave during his shifts (September 1 and 2). Should he go to work the day after the sick leave ends (that is, September 3)?
No, you shouldn't. The employee must begin work on the next scheduled shift. In the situation under consideration (when working on a shift schedule: two days of work, then two days off), he must go to work on September 5.
It should be borne in mind that he is not required to work sick days. These days are excluded from the norm of his working hours.
Night work according to the Labor Code
Legislative acts reflect the categories of citizens who are allowed to work after 10 p.m. The Labor Code indicates that night time is the period from 22 to 06 hours. Night mode affects the normal functioning of the body. For this reason, the law introduces restrictions on the conduct of labor activities during the period of time under review. Including, they cannot work at night:
- citizens under the age of majority
- women who are pregnant
At the same time, it is indicated that some persons may be involved in night work, provided that they agree with this. This requires consent in writing. These categories include:
- women with children under three years of age
- one parent who raises a child under five years of age
- persons acting as guardians
- citizens with disabilities and those raising disabled children
The listed citizens have the right to give consent to work at night. The management of the organization is responsible for familiarizing employees with this provision of the employment agreement. Familiarization is carried out against signature, provided that night shifts take place constantly. When night shifts are established on a one-time basis, it is necessary to obtain consent from employees each time.
When a citizen is hired, initially you need to find out the possibility of working on the night shift, if it is available at production. In this case, you need to obtain a certificate from the employee indicating the possibility of working at night. The format of this act is reflected in the Order developed by the Ministry of Health.
Payment for night hours
When a person’s work schedule is established every other day, this indicates that part of such a shift falls at night. It may also be that a citizen works at night on holidays or non-working days. Then you need to understand how payment for such days is made.
It is established by law that when performing work duties at night, payment is made in an increased amount. This rule is spelled out in the provisions of Article 154 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation. The minimum amount of increase in this situation has been established. It is 1/5 of what you earn on a normal day.
In an individual case, provisions for increased pay at night should be reflected in the collective agreement. Also, this information can be included in local standards, which are adopted taking into account the opinion of the organization’s trade union.
To understand the amount of payment, you need to give a specific example. Citizen Petrov works on a 24/7 basis. At the same time, his salary is 35 thousand rubles. There are 2 rest periods during the work shift, each equal to an hour. The surcharge is 25%.
The standards for hours worked are based on the fact that the work week is 40 hours. It is necessary to calculate the level of earnings for September, provided that this month Petrov worked all the shifts noted in the schedule. It turns out that in September the citizen worked 7 shifts of 22 hours and another 14 hours, for a total of 168. Of these, 58 were night hours. The calculation is based on the following indicators:
- hourly rate is 208.3 rubles
- surcharge for night work: 208.3 *25%*58= 3020.8 rubles
Based on the total for September, Petrov will receive 35,000 + 3020.8 = 38020.8 rubles.
Work during non-working hours or holidays is paid using a double tariff.
If a citizen has overtime work during the month worked, then payment is made at an increased rate. At the same time, the legislator sets the minimum amount of payment. The first couple of hours you need to pay 1.5 times the amount. The rest of the time is paid at double rates.