Basic provisions
The acquisition of education by all minors, without exception, is enshrined in the Constitution of the Russian Federation. The law does not provide a single valid reason for waiving this right.
The following factors are not taken into account:
- health status;
- language;
- religion;
- floor;
- beliefs;
- race;
- location;
- social status;
- nationality;
- origin and any other reasons.
Refusal to provide educational services cannot be justified by the health of a minor. Any student must be provided with the program that is recommended by the psychological, medical and pedagogical commission. If a student is unable to attend school, he is transferred to one of the following forms of education:
- Home-based. Teachers visit the child at his place of residence.
- Parental. Mom and dad themselves provide the minor with the knowledge provided for in the school curriculum. The student takes exams on a general basis.
- Remote. The child is provided with the necessary equipment to participate in learning at a distance from the teacher.
Children have the right to receive free education:
- preschool (preschool);
- general (primary, basic, secondary);
- secondary vocational;
- 1 higher education on a competitive basis.
Important! Refusal to enroll in a school can only be due to lack of places in classes. In this case, the child’s legal representative has the right to contact any other educational organization.
School Board of Trustees
Our school has a board of trustees. “Thanks to” his efforts, the school can no longer be called free. Every month they take considerable sums from us for certain needs. Is this legal?
The law allows parents of students to participate in the management of the school. The charter of an educational institution may permit the organization of boards of trustees at the school. This is one of the types of school self-government and one of the effective ways for parents and legal representatives of the child to influence the course of the educational process. In practice, such bodies deal with organizational and auxiliary issues.
Most often, it is the boards of trustees who collect money from the parents of students. In this case, it should be noted that such contributions must be exclusively voluntary.
Of course, the financial support of today's schools, especially state schools, most often leaves much to be desired, but still this is not a reason for systematic extortion. Therefore, the board of trustees can organize the renovation of the school, rather than collect money for it and give it to the school management. This so-called targeted financing is much more effective than banal contributions. The financial activities of councils must be completely transparent. You have every right to find out how your donated funds were spent.
Scroll
The child’s right to education includes a set of legitimate interests of minors.
However, all of them must be observed simultaneously. Among them:
- Respectful attitude towards the child and parents on the part of teachers and school administration.
- Free education.
- Specialized program for children with special needs.
- The choice of educational organization is at the discretion of the child and parents.
- The right to change educational institutions.
- Free use of school library materials.
- Ensuring the safety of students while gaining knowledge.
- Participation in socially useful work activities, taking into account the opinions of the child and parents.
- Equality of all children before the teacher.
- Obtaining knowledge from teachers and help from specialists (psychologists, social educators).
Who will catch up?
My son was sick almost the entire quarter. Is he required to take homework and midterm tests that he missed due to illness?
The law says that each student must master a certain amount of knowledge - an educational program for a certain educational level. If a child is often sick, parents have the right to choose an acceptable form of individual education for him, including at home. In any case, the state educational standard must be met. What gives the school the right to require the student to complete those tasks that he missed due to illness. Of course, he won't be forced to do all the missed homework. But he is obliged to pass a certain minimum. In practice, such issues are resolved individually by each teacher.
Legislative norms
The peculiarity of this right is the mandatory nature of its implementation. Therefore, it is regulated by a large number of regulations.
Basic documents establishing the right of minor residents of the Russian Federation to education:
- Convention on the Rights of the Child;
- Constitution of the Russian Federation;
- Family code;
- education law 2012.
Important! If a minor does not wish to receive an education, responsibility rests with his legal representatives.
If a child is a poor student, makes many absences for unexcused reasons, or exhibits bad behavior during classes or during recess, the issue of his upbringing may be raised at a meeting of the Commission on Minors’ Affairs and the Protection of Their Rights (KDNiZP). Parents are subject to liability measures provided for in Article 5.35 of the Code of Administrative Offenses.
What is written in the school charter?
I had a conflict with the administration of the school where my son studies. Without going into details, I can say that it is related to the construction of the program. The director began to refer to the charter, but I did not see it. Before enrollment, no one warned us that some new programs would be “tested” on children
.
Article 16 of the Education Law states: the school must familiarize the parents of the future student with its constituent documents
and other materials regulating the educational process. First of all, parents should pay attention to the charter of the educational institution. It stipulates how, in what order, children are admitted to school, the duration of study, the procedure for assessing knowledge, and how additional services are paid for. The charter of the school must not contradict the Law on Education and other regulations governing the education process. If a contradiction is still observed, then parents can challenge all illegal provisions (for example, on holding entrance exams when enrolling in 1st grade) in court or administrative proceedings.
The organization of the educational process at school is based on a curriculum developed independently by the school in accordance with the sample curriculum, and is regulated by the class schedule. Study loads of students should not exceed the maximum permissible loads determined by the school charter based on recommendations agreed with health authorities
. The duration of the school year in grades 1 lasts 30 weeks, in grades 2-11(12) - at least 34 weeks. The duration of vacations is set at least 30 calendar days during the academic year, and at least 8 weeks in the summer. For students in the first grades, additional week-long holidays are established throughout the year. The annual academic calendar is developed and approved by the school independently.
Types of violation of the right to education
Like any other right, the legitimate interests of students encounter obstacles to their implementation. Violators can only be persons responsible for its proper implementation. Among them:
- legal representatives;
- teachers;
- officials of an educational institution.
Specialized bodies must take all measures to restore the violated right. Let's take a closer look.
Parents/Guardians
Legal representatives are the guarantor of the realization of the right to education. They are responsible for mistakes made by minors during the learning process. However, in certain situations they may be violators, for example:
- lack of equipped space in the apartment for preparing homework;
- refusal to provide the minor with clothing and school supplies;
- ban on attending school;
- lack of control over class attendance and academic performance.
Parents must provide a place for the minor to prepare homework. You don’t need any special equipment for this; a desk is enough. Preparing homework on the windowsill, kitchen table and other places not intended for such activities is unacceptable.
Mom and dad are required to provide the child with basic necessities (clothing, shoes) and school supplies. The minor must attend school wearing clothing that fits him and is appropriate for the season. If parents do not have the financial ability to provide their child with a school uniform, notebooks, pens, etc., they must apply for financial assistance to the social welfare department at their place of residence.
Important! To receive financial support, permanent registration is required.
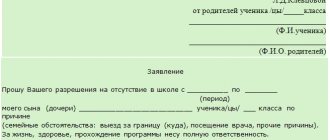
Legal representatives do not have the right to prevent a child from attending school without a good reason. This can only happen in the event of illness or an unforeseen situation in the family. Parents are required to notify the class teacher of forced absences from classes.
Teachers
Teachers may also violate children's educational rights. Although teaching lessons is their professional activity, personal hostility often develops between the student and the teacher, thus violating the principle of equality of children.
Interpersonal conflicts between students are not uncommon, especially during adolescence. Ensuring the safety of the child from illegal actions of other minors is the responsibility of the teacher. Such facts cannot be ignored.
In this case, the teacher cannot use physical force on children. The conflict should be resolved through conversation, involving parents, the school principal and/or the police.
Officials
A common violation on the part of school administration is denial of enrollment without a valid reason. The only reason can be the lack of free places in the required class.
Another possible violation is the collection of funds for educational literature, class needs, repairs and other purposes financed from the regional budget. Such actions are grounds for attracting the prosecutor's office.
Obstacles to transfer to another educational institution during the school year also violate the rights of the child. A minor may choose a school at his own discretion with the consent of his parents, without taking into account the opinion of the school administration.
Safety
My son's classmate was injured in a labor class. He even had to undergo surgery on his hand. Is the school responsible for such incidents?
According to Art. 32 of the Education Law, the school is responsible for the life and health of the student during the educational process. In any situation, the school must compensate for the costs of treatment and care for the child. As practice shows, schools do not hide the facts of injuries during school and, upon request, issue relevant certificates, which are the basis for claims for damages. If the school administration refuses to issue such a document, then the fact of injury can be confirmed by witness testimony or a medical report obtained from any medical institution.
In conclusion, I would like to note that laws related to education in our country require urgent reform in accordance with the conditions of a market economy. So today, Russian certificates of complete secondary education are not recognized in many European countries. Teenagers have to complete their studies for a year and a half in order to have the opportunity to study at foreign universities. In addition, the level of fundamental classical school education that was maintained during the Soviet era cannot be reduced. If we add to this the experience that the school education system has accumulated over the past ten years, then we can get the most acceptable option for the education system.
Gayane Mirzoyan, lawyer at the legal bureau “On Sretenka” Article from the magazine
Protection of educational rights
Children's right to education also means that disabled children, orphans and minors from poor families should not be discriminated against by teachers, school administration and other students. It is education that gives them a chance for habilitation in society, socialization and professional guidance for later life.
Ensuring the protection of the educational interests of minors, as well as other constitutional rights, is entrusted to a wide range of citizens and state and municipal bodies. Among them:
- parents;
- other legal representatives;
- officials of educational organizations;
- teachers;
- district education department;
- commission on affairs of minors and protection of their rights;
- regional ministry;
- government of a constituent entity of the Russian Federation;
- prosecutor's office;
- court.
Protection of the right to education is of a declarative nature. The legal representative of the minor must file a complaint about the violation of the child’s interests. When handling, you must follow the sequence. A one-time complaint to all authorities rarely gives a good result.
But if the goal of the legal representative is to cause harm to the violator, contacting the media will give a more effective result. The video shown in the news will become the basis for inspection of the educational institution by all authorities simultaneously. However, it will be difficult for the child to continue studying in this organization in the future. Therefore, the best option is a consistent solution to the problem.
The Constitution established the right to compulsory general education for all residents of the country. It is ensured and protected by both legal representatives and specialized bodies. Despite the fact that the field of knowledge has its own difficulties, Russia has provided the most accessible training for its citizens.
What should parents of a child whose rights have been violated do?
What to do if teachers or school administration violate a child’s rights?
In no case should the offense be ignored: any of the listed violations can traumatize the fragile child’s psyche, and the consequences of this trauma will have a negative impact in the future. Parents of a child whose rights have been violated must:
- Submit a written complaint to the school principal. In the document, indicate the surname, name and patronymic of the applicant, state the essence of the violation and demand that the problem be eliminated.
- If the management's complaint does not bring results, send a similar statement to the education department.
- If the violation of rights is flagrant and contrary to the law (for example, endless monetary extortions), a complaint must be sent to the prosecutor’s office.
What rights and responsibilities do students have?
Let's start with responsibilities. General rules of behavior within the walls of an educational institution prohibit schoolchildren from insulting the honor and dignity of other students and teaching staff, using obscene gestures and expressions, and smoking on the premises. In addition, schoolchildren are required to respect property rights and take care of school property and personal belongings of other students. In case of damage to someone else's property, compensation for damage is assigned to the parents or legal representatives of the child.
In general, the responsibilities of schoolchildren boil down to getting an education themselves, not interfering with the educational process, and not interfering with the learning of other students.
Schoolchildren's rights
Students of secondary schools have the following rights:
- free education in accordance with current standards established at the state level;
- independently choose a general educational institution and form of education: studying at school or at home, taking a course according to an accelerated program;
- maintaining personal dignity without discrimination on any grounds;
- decent learning conditions: warm classrooms, quality food, etc.;
- free expression of thoughts and beliefs, provided that this occurs in a correct form;
- learn in a timely manner about the conduct of tests and examinations;
- take a school curriculum in your native language;
- receive grades in each discipline in accordance with the knowledge acquired, without prejudice on the part of the teacher;
- attend extracurricular activities;
- take part in cultural events;
- get free access to any school resources necessary for the educational process, for example, library books;
- rest between classes, weekends and holidays.
Important! Schoolchildren retain the rights to freedom of speech, press, conscience and information. In March 2021
a legislative innovation has appeared that makes it possible to provide free meals to children studying in primary school, starting from September 1, 2020 - taking into account the transition period - until September 1, 2023. In accordance with the new law, primary school students will be provided with free hot meals (hot dish and drink) at least once a day. Starting in 2021, those schools that have canteens equipped to provide hot meals and the necessary kitchen equipment will begin implementation.
In March 2021, a legislative innovation appeared that makes it possible to provide free meals to children studying in primary school, starting from September 1, 2020 - taking into account the transition period - until September 1, 2023. In accordance with the new law, primary school students will be provided free hot meals (hot dish and drink) at least once a day. Starting in 2021, implementation will begin for those schools that have canteens equipped to provide hot meals and the necessary kitchen equipment.
The school charter is a set of internal rules governing the work of educational institutions. This regulatory document is drawn up in accordance with paragraphs of Article 25 of Federal Law No. 273-FZ.
In particular, the charter must contain the following information:
- information about the type of educational institution;
- information about the founders;
- information about educational programs and areas of study;
- organizational structure and division of powers.
Important! The general education organization must create conditions for familiarizing students, parents and teaching staff with this charter
Guarantees for minor workers and their legislative regulation
Guarantees for minor workers are established in labor legislation. This includes a shortened working day, a ban on working under certain conditions, as well as a mandatory medical examination, for which the future employee does not have to pay.
In addition to enshrining these conditions in the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, protection of the powers of this category of persons in the State Labor Inspectorate is provided. In addition, if your powers are violated, you can write a corresponding statement to the prosecutor's office. Practice shows that most controversial issues can be resolved before going to court, since it is simply not profitable for the employer to bear such expenses, and the court often sides with teenagers. However, if the problem cannot be resolved through pre-trial settlement, you can file a statement of claim in court.
Thus, the legal regulation of the activities of minor employees is somewhat different from the regulation of the labor of adult citizens
When applying for a particular position, it is important to study your rights and responsibilities, and also carefully read the form that you are asked to sign
General rules of student conduct:
Student behavior in class:
1. Do not be distracted yourself and do not distract other students from classes, as this violates the right of other students to receive the necessary knowledge.
2. It is recommended to stand up when a teacher or any adult enters the classroom, greeting them, and if you want to answer or ask a question to the teacher, raise your hand.
3. Recess time is the personal time of each student, which he can spend at his own discretion without disturbing others.
During breaks: the student must clean up his workplace; prepare everything you need for the next lesson; leave the office if the teacher asks; obey the requirements of the floor attendants; do not interfere with other students' rest.
Student behavior in the cafeteria:
1. Treat the dining room property with care.
2. When eating in the dining room, adhere to good manners and eat while sitting.
3. Clean up after yourself after eating, put back chairs,
4. Do not come to the dining room in outerwear,
5. Do not take food out of the dining room. The student can bring breakfast with him from home, buy pastries, juices and other products at the school buffet.
School duty officers (carried out by students in grades 7-11) are required to:
1. Attend the meeting held by the administrator on duty and the class teacher at 7 o’clock. 55 min;
2. Students will be checked for replacement shoes upon entering the school;
3. Help younger schoolchildren change clothes;
4. Maintain order in the locker room, assist in maintaining discipline during breaks;
5. Maintain cleanliness in assigned areas; At the end of lessons, remove the trash and hand over the territory to the administrator on duty or the class teacher.
6. Officers on duty are prohibited from using physical force, as well as humiliating students, even if they violate the rules of conduct. If necessary, contact the duty administrator or class teacher.
Requirements for the appearance of students:
1. Students in grades 5-11 come to school in business casual clothing. Boys wear suits (jacket, shirt with tie or turtleneck). Girls - a dark-colored skirt, blouse or turtleneck,
2. It is not permissible to wear clothes that are too revealing.
3. Bright, provocative items of clothing and jewelry are not allowed.
4. It is recommended not to wear excessive makeup, extreme hair color, or wear a lot of jewelry during classes.
5. A manicure is recommended - classic, light, non-provocative tones.
6. It is not permissible to wear clothing that emphasizes belonging to any youth or social movement.
7. At school, students must wear removable shoes.
8. Students are not allowed to attend lessons (except for physical education) in sportswear.
9. It is not allowed to wear outerwear at school, without special reasons.