Have you ever encountered a situation where, after a long search, you found a new employee, discussed working conditions with him, reached an agreement, signed an employment contract and never saw him again - the “new guy” for some reason was unable to begin his duties or at all changed your mind about working in your company?
Most of us will simply break the employment contract and will not communicate with such a person in the future. Of course, it is possible to destroy the contract. But be careful not to create additional problems for yourself. If the failed new employee still has a copy of the contract signed by you, he can demand payments from the company, for example, for sick leave. To avoid creating an unpleasant situation, cancel your employment contract. It is legal! How to do it?
Internal documents
Before signing an employment contract, the new employee must be familiarized with the company’s personnel documents. Not all, of course, but only those that relate to the organization of work at the enterprise, remuneration, schedule, and so on.
In most companies, the employee is asked to read: a collective agreement, internal labor regulations, regulations on labor protection, regulations on remuneration, trade secrets, and job descriptions. The employee must familiarize himself with other internal documents that are adopted by the organization and are directly related to the duties that the new employee will perform.
If the company is small and belongs to micro-enterprises, there may not be such personnel documents as internal regulations, regulations on wages and bonuses. There are enough employment contracts that include all the terms of cooperation.
After reading, the employee must confirm in writing that he has read the documents. If there are few papers, the employee can sign each document that he has studied. If there are more than three papers, it makes sense to keep a separate book for employees to familiarize themselves with the company’s internal documents. Then the specialist must sign either opposite the title of each document or at the bottom of the list of all papers that he has studied.
Employment contract: formality or necessity?
Oleg Snezhko
At many Russian enterprises, labor relations are still formalized today as in the “good old days” - in the form of a statement from an employee with a resolution from the manager or the person replacing him. However, according to Article 16 of the Labor Code, it is the employment contract that is the basis for the emergence of labor relations and the issuance of an order for employment.
In accordance with the law, an employment contract is drawn up in two copies and contains conditions (material and other) that allow the employee to accurately understand his rights and obligations related to the performance of certain functions.
The essential terms of the employment contract are enshrined in Article 57 of the Labor Code. These include, in particular: place of work, date of employment, position and specialty, profession indicating qualifications or specific job function, rights and obligations of the parties, etc.
It is important to specify the working hours and payment terms in the employment contract. Often, the manager does not indicate a specific rate, but only makes reference to the relevant act (“payment according to the staffing table”, “in accordance with the regulations on remuneration”, etc.). This can lead to violations, so when concluding a contract, the employee must clarify the amount of both the salary and all incentive bonuses. A written employment contract limits the possibility of arbitrariness on the part of the enterprise administration: the documented nature and conditions of work allow a person to know exactly where and how much he should work. If there is a need for overtime work, then it will be performed for an additional fee (compensation).
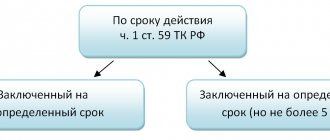
The law prohibits the conclusion of fixed-term employment contracts. At the same time, Article 59 of the Labor Code contains a fairly wide list of cases in which these agreements are legal. Thus, a situation has arisen where, on the one hand, employees are given the right not to sign fixed-term employment contracts, and on the other hand, the employer actively uses every opportunity to conclude such. The principle of “both ours and yours”, applied in this case by the legislator, infringes on the rights of the employee and upsets the balance of interests of the parties to the social partnership. In addition, if the court establishes the multiple conclusion of a fixed-term employment contract to perform the same labor function, it has the right to recognize the employment contract as concluded for an indefinite period (resolution of the Plenum of the RF Armed Forces of March 17, 2004).
The advantage of a written contract is that it acts as a kind of evidence in the event of any disputes and, in addition, serves as a source of information both for the employee (who, for example, needs to study any of the points in more detail), and for the employer, the court , labor inspectorates, etc.
Unfortunately, employment contracts have not yet become common practice. Referring to the fact that the Labor Code allows actual admission to work to be considered the basis for the emergence of an employment relationship, employers are in no hurry to develop standard contracts. Relatively recently, another negative trend has emerged - to replace the employment contract with a civil law one. In this way, employers are trying to escape their obligations to employees provided for by labor legislation.
It is important to note that an employment contract always involves the personal performance of a certain function within the framework of a specialty (qualification, position) in compliance with internal labor regulations (the labor process is important). As for the civil contract, it provides, first of all, for the performance of work, the provision of a service (the result of the work is important). By the way, according to the Labor Code, if a controversial situation arises, the court has the right to oblige the employer to apply the norms of labor, rather than civil, legislation to such an agreement.
Many commercial organizations, having great independence in the field of regulation of wages, working hours, and other working conditions, are trying to worsen the situation of personnel in violation of current legislation. However, if the employment contract includes conditions that reduce the level of rights and guarantees of the employee, they cannot be applied (part two of Article 9 of the Labor Code). If the administration of the enterprise refuses to conclude an agreement for an employee (the employer must communicate the reason in writing), he has the right to seek help from the relevant authorities (labor inspectorate, prosecutor's office, court). Article 64 of the Labor Code prohibits unjustified refusal to conclude an employment contract.
We sign the contract
When all issues have been agreed upon, you need to receive a job application, after which you can sign an employment contract.
According to the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, drawing up a written work contract is the responsibility of the company. You cannot limit yourself to just applying for a job.
An employment contract is the main document that confirms the employment relationship between an employee and a company. What must be indicated in the employment contract: last name, first name, patronymic of the employee, his tax identification number, company name or full name of the individual entrepreneur - employer, details of identification documents (for example, passport number, where, when and by whom it was issued) , full name and position of the person who signed the employment contract on the part of the employer, place and date of conclusion of the contract, place of work.
In addition, the employment contract must indicate the employee’s position and the functions that he will perform. For example, work in a position in accordance with the staffing table or profession, specialty indicating qualifications, or a specific type of work assigned to the employee. Do not forget to indicate the start date of work, the duration of the contract, terms of payment, work and rest hours, compensation for hazardous work, if such is provided in your company, the condition of compulsory social insurance and SNILS.
You will find a complete list of everything that needs to be included in an employment contract in Article 57 of the Labor Code.
What is an employment contract?
Form and meaning of the employment contract
An employment contract is a voluntary, mutual agreement between two parties, describing their mutual responsibilities and rights. According to the contract, the employer undertakes to provide the employee with the tasks and working conditions described in this contract. The employee, in turn, guarantees independent, responsible and high-quality performance of his duties.
The procedure for concluding and executing an employment contract involves the written confirmation of the agreed obligations. Only in this case do the parties to the contract claim to protect their rights in court.
Important!
According to Art. 67 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, an employment contract is concluded exclusively in writing, in two copies. The employer is obliged to formalize the employment relationship with the employee within three days after the actual admission to work.
It is the employment agreement that describes the conditions under which the employee performs his duties. For the employee, this is a guarantee of timely payments, sick leave or vacation. Refusal to comply with the norms established by law leads to administrative liability.
Legal assistance with drawing up an employment contract:
Rules and stages of the procedure for drawing up an employment contract
The Labor Code of the Russian Federation does not contain a strict sample employment agreement. In accordance with Art. 57, the document must contain:
- name of the company and full name of the employee applying for the position;
- position and type of work (main or part-time);
- date of actual employment;
- end date of service when applying for a fixed-term employment contract;
- mutual rights and obligations;
- the amount of salary, bonus, condition of payment of allowances;
- schedule;
- the procedure for payment and the amount of monetary compensation in the event of an industrial injury or harm to the physical health of an employee.
Important!
The employer is required to include each of the listed points in the agreement. Otherwise, the contract may be declared invalid.
Registration of employment under an employment contract is carried out in three main stages:
- The employee provides an identity card, TIN and SNILS to the employer. If the job requires special physical skills or the work is harmful to health, the employee will be required to undergo a preliminary medical examination. The candidate must agree to this procedure. If a citizen enters an official position for the first time and cannot provide a work book, the employer is responsible for processing it.
- Issuing an employment agreement, familiarizing the employee with it and signing the contract. The agreement comes into legal force from the moment the relevant document is signed or the employee is actually admitted to the place of work.
- Issuing an order to hire an employee. The terms and conditions of the document must comply with the terms described in the employment agreement. The employer enters the necessary information into the employee’s work book and provides a copy of the employment order.
Important!
according to Art. 69 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, the employer undertakes to familiarize the employee with labor and safety rules, company regulations, and other regulations. The employee confirms his awareness with a personal signature.
First work day
The employee must begin his duties on the day that you define in the employment contract as the start of work. This is usually the day when the contract is signed by both the employee and the company representative. It may be another day if there are special requirements of federal law regarding the position for which the employee is hired. But this is a rare case.
It is also possible in the contract, by agreement of the parties, to determine and enter a specific day for the start of work after the day the contract is signed.
note
If an employee does not show up for work on the first day, you have the right to cancel the employment contract in accordance with Part 4 of Article 61 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation. You should not be interested in the reason why the new employee was absent. Whether he got sick, overslept, changed his mind - it doesn’t matter.
If the first day of work is not specified, the employee must go to work on the next working day after the contract came into force, that is, signed. This rule is defined in parts 2, 3 of Article 61 of the Labor Code.
After signing the contract, employment is formalized by order of the director, which is issued on the basis of the concluded employment contract in accordance with Article 68 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation.
The new guy didn't show up for work
If an employee does not show up for work on the first day, you have the right to cancel the employment contract in accordance with Part 4 of Article 61 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation. You should not be interested in the reason why the new employee was absent.
You can cancel the contract, and the employee has no rights to demand that he be hired or compensated for anything. To cancel the contract, issue an order; it can be drawn up, for example, as shown in sample document 1.
After this, send the employee a notice that he must come for a work book or send consent to have his work book sent by mail. The notification letter can be drawn up, for example, as shown in sample document 2.