Safety training is an integral part of any production facility. Before starting work, the employee must study the safety and labor protection instructions and sign in a special journal. The form of the TB familiarization log must comply with GOST 12.0.004.90. After the journal is completely filled out, it should be handed over to the archive, where it should be stored without any time limits.
Any employer, especially at hazardous production facilities, is required to have a safety briefing log. Otherwise, he risks receiving a large fine, and in some cases, including those related to harm to the health or death of an employee, and a prison term.
Logging control
Even if there are no new entries, the status of the journal should be checked by the head of the department every day . This is the first stage of verification. The next step is a check of the log by the head of the health and safety department, carried out at least once a month , where he must make a note about the presence or absence of violations. Such a check is carried out once a quarter by the general director or chief engineer of the organization.
This is the last stage of control. In the case of a small organization, the second and third levels of control are carried out by special control structures. If they do not do their job, then the director has nothing to worry about, since his task is reduced to only the first step.
You can see the rules and an example of filling out a fire extinguisher log book in this article.
Information on how to obtain a TIN for an individual via the Internet is here.
Types of briefings
Federal Law No. 181 provides for 4 types of mandatory safety training. Each employer must carry them out throughout the entire cooperation with an individual employee:
- Introductory. This briefing is intended to explain to the newly hired employee how he should behave at the enterprise or workplace. The subtleties of production are explained to him.
- Repeated. Conducted every 6 months. The calculation date is the date of hiring. Can be done collectively.
- Target. Instruction is carried out before the employee begins to perform work that involves risks to health and even life. Like the introductory one, it must be carried out individually.
- Unscheduled. Such instruction is carried out when new equipment appears in production or a non-standard technological process is introduced.
The latter type of briefing can also be carried out after confirmation of a violation of safety requirements, resulting in an accident. The initiator of an unscheduled briefing may be regulatory authorities that have identified violations. This training must be carried out if changes have been made to labor protection legislation.
In fact, there may be many more safety magazines. This could be a log of instructions on electrical safety, fire safety, or first aid to victims. It all depends on the specifics of the enterprise.
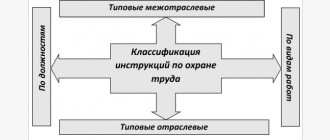
The classification of briefings is covered in Resolution of the Ministry of Labor and Ministry of Education No. 1/29 of January 13, 2003.
Who is responsible for compiling and maintaining the journal?
The necessary forms, which must be uniform for all divisions of the enterprise, are kept by the health and safety engineer or any other employee who has been entrusted with this responsibility by the relevant order of the organization. The employee of the organization who is responsible for on-the-job training should obtain the log from the HSE engineer. As a rule, such an employee is the workshop manager or site foreman.
All pages are numbered, stitched and certified with the seal and signature of the employee or head of the organization responsible for its maintenance. Basically, most organizations order daily safety training magazines from printing houses.
Rules for filling out the journal
GOST number “12.004-90” is a kind of regulation governing the rules for compiling a log of briefings on labor protection. According to current legislation, this log must be maintained continuously. In addition to the required parameters, each company can indicate additional information in accordance with the scope of production. As practice shows, most managers of large companies order the production of magazines from local printing houses. In order to avoid possible confusion associated with incorrect provision of information, experts recommend using a separate journal for each briefing. According to GOST rules, each TB journal must be:
- stitched;
- numbered;
- sealed with a company seal;
- endorsed by the signature of the General Director.
During the lecture, each employee must be familiar with the instructions on his job responsibilities. The lecturer’s task is to explain key points and answer questions that arise during the lecture. After the briefing, a short examination test is carried out, the data of which is recorded in a special journal.
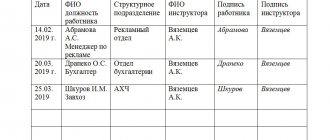
Let's look at what a sample of filling out a safety log looks like. On the title page of this document a mark is placed on the name of the enterprise and structural unit. After this, the name of the journal is indicated. Next, indicate the lines “Started” and “Ended”, where you need to record the period during which the journal was used.
In the part of the journal where the table is located, you must indicate the date of the lecture, as well as make a note about the person being instructed. In this column you need to enter the employee’s last name, first name, patronymic and year of birth. Next, his specialty is indicated, as well as the name of the structural unit where the employee carries out his work activities. After the briefing, the lecturer and the instructed person sign in a specially designated field.
In the event that an enterprise uses a mandatory form of internship, the official keeping the accounting log is responsible for filling out special columns indicating the number of work shifts. For unscheduled instruction, in the line with additional information you need to make a note about the reasons for the lecture. In some cases, the administration of the enterprise needs to use not only log books, but also personal cards of employees, where a mark is placed on the completion of the lecture.
Any employer, especially at hazardous production facilities, is required to have a safety briefing log
Types of safety training
Depending on when it is carried out, as well as the focus of familiarization with work in hazardous conditions, it is divided into the following types:
- introductory, mainly carried out when hiring a new employee or changing the type of activity of an employee;
- target;
- extraordinary;
- repeated, the most common type of instruction;
- introduction of safety rules in the workplace.
When performing an extraordinary inspection, a corresponding entry is made in the journal, which indicates the need for it.
After such familiarization, as in the case of primary and secondary, the instructed employee is required to sign.
With targeted instruction, which is carried out according to the work order, the employee receives permission to perform the necessary work. This type of job introduction includes:
- performing various works of a one-time nature;
- eliminating the consequences of various types of accidents;
- carrying out major events in which most of the organization’s employees are involved;
- in cases where work requires a permit or special permit.
List of required occupational safety magazines at the enterprise
The following documents must be kept:
- magazine for conducting introductory briefings;
- documents on other types of briefings: repeated and targeted;
- on the issuance of personal protective equipment;
- registration of a special assessment of working conditions;
- registration of occupational diseases and accidents;
- inspection of lifting devices;
- accounting for slings and lifting mechanisms;
- magazine on cleaning dust collectors and ventilation systems;
- a journal that records the assessment of employees' occupational safety knowledge;
- maintaining 1st and 2nd stages of control.
Registration of the TB briefing log
The cover of the magazine contains the following information:
- Name of the organization;
- the name of the unit in which the instruction is directly carried out;
- two dates that correspond to the beginning of filling out the journal and the end of all entries in it.
This log should display the following information:
- date of completion, indicated in the format dd,mm.yy;
- year of birth of the instructed employee;
- his full name;
- position held in the organization;
- the profession of an employee of the organization, and in the case of a posted employee, his main place of work and identification details are indicated;
- name and number of the instructions that are used in this case;
- FULL NAME. the employee conducting the training;
- personal signatures of the person being instructed and the person instructing;
- work experience in a new place;
- in case of an extraordinary briefing, the reason for it is indicated;
- number of shifts;
- FULL NAME. the person who issued permission to perform certain work at this enterprise;
- the position held by the employee eligible for introduction;
- date of issue of the permit;
- personal signatures of the person who received the permit and the person who issued it.
safety training log
The log is kept on A4 sheets , where the data to be filled out is located in a line. If necessary, one entry can occupy several lines. In the empty spaces left after filling, it is necessary to make dashes. Any commission checking the journal maintenance may make a remark in their absence.
Duties of the parties
All employees, regardless of position, have job responsibilities to ensure safety . If a specialist performs dangerous work, he must know and be able to fulfill the requirements established by regulations . His responsibility includes timely training on TB , after which he must confirm his knowledge. This is reflected in the magazine.
The head of the enterprise is responsible for monitoring the implementation of activities for the successful conduct of instruction. He must provide conditions for internships, not allow unprepared people to work, test knowledge, warn employees about possible risks when performing certain tasks, and provide them with the necessary protective equipment.
Responsibilities of employee and employer
Both the head of the organization and its employees have some job responsibilities related to the safe conduct of work, including instructions on them. The employee is obliged:
- comply with all requirements when conducting hazardous work established by a number of regulations and other documents;
- undergo timely training on the safe performance of the required types of work, which must be reflected in the necessary journal entry;
- in addition, he must undergo training at his workplace;
- confirm your knowledge in the field of occupational safety and health in the prescribed manner.
At the same time, the head of the enterprise must also fulfill a number of requirements, such as:
- carry out all necessary activities for conducting safety training;
- take all measures to complete the internship at the workplace;
- provide all necessary information regarding safety when performing all types of work at this enterprise;
- do not allow dangerous types of work to be performed by people who have not been familiarized with and have not signed the safety log;
- promptly check your employees for knowledge of the rules and regulations when performing hazardous types of work;
- inform your employees in advance about the possible risk to their health when performing certain work, and also provide them with all the necessary protective equipment.
Recently, much attention has been paid to the conditions for safe work in production. This is due to an increase in the number of accidents. If the safety journal is not kept correctly, and even more so if it is absent, any inspection by the relevant inspectorates, including the labor safety inspectorate, can have unpleasant consequences. Therefore, it is necessary to conduct all types of training on time and make appropriate notes in the journal.
Penalties
Officials who do not know how to fill out a safety log can use the occupational health and safety log . Please note that the absence of this document may result in penalties from regulatory authorities. This fact may be regarded as failure to conduct training lectures, which will entail an administrative fine in the amount of 110 to 130 thousand rubles. In relation to officials, the amount of penalties can vary from 15 to 25 thousand rubles.
In case of repeated violation, the fine will be from 100 to 200 thousand rubles. It is important to note that in this case, regulatory authorities can stop the operation of the enterprise for three months. In case of repeated violation, a penalty in the form of fines in the amount of 35 to 40 thousand rubles is imposed on officials. An official may also be suspended from his/her position for a period of up to three years.