Are dynamic and static tests of PPE against falls from height carried out?
The frequency and scope of inspections of personal protective equipment against falls from heights is regulated by clause 123 of the Labor Safety Rules when working at height, approved by Order of the Ministry of Labor and Social Protection of November 16, 2020 No. 782n. According to this document, “dynamic and static tests of personal protective equipment against falls from a height are not carried out by operating organizations.”
Since 2015, all fall protection equipment is subject to mandatory certification for compliance with the requirements of the technical regulations of the Customs Union “On the safety of personal protective equipment.”
Group 3 for height - 990 rubles
Get your altitude certificate by taking the test online.
Go to course
Storage and care of PPE
Basic rules for caring for PPE:
- expenses entirely on the part of the company's management;
- Regular dry cleaning, washing, degassing, decontamination, disinfection and neutralization, and drying are required.
Basic rules for storing PPE:
- the use of premises that are specially equipped for storage: they must have the required temperature and moderate humidity;
- storage in a warehouse is included in the period during which they need to be used;
- it is possible to equip the premises with dryers, devices for disinfection, degassing, and decontamination;
- installation of special racks, boxes, cabinets with inscriptions in the warehouse;
- lack of direct rays of the sun;
- location of heating devices at a specified distance;
- protection from external damage.
Who assesses the significance of PPE defects caused by falls from a height?
During operation, personal protective equipment against falls from a height can wear out, deteriorate under the influence of unfavorable factors, fail if shock-absorbing mechanisms are activated, etc. By assessing the significance of defects and making a decision on the further use of personal protective equipment in accordance with clause 22 of the Intersectoral Rules for the Provision of Workers special clothing, special shoes and other personal protective equipment approved by order of the Ministry of Health and Social Development of Russia dated June 1, 2009 No. 290n are handled by an official authorized by the employer or a labor protection commission.
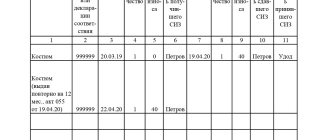
Based on the results of the inspection, be sure to fill out the corresponding columns of the PPE registration card or create a separate form. At the same time, clause 28 of the same rules places responsibility on the employee for timely notification of the employer about the malfunction of the PPE issued to him. Therefore, workers performing work at height should also know what, how and when to check.
Liability for failure to provide
The employer bears administrative responsibility for inadequate provision of PPE for employees under Part 1 of Art. 5.27.1 of the Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation, in the event of a repeated commission of a similar violation - in accordance with Part 5 of Art. 5.27.1 Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation.
If the employer did not provide workers with first class PPE (of simple design), did not repair it, did not replace it in a timely manner, liability will arise under Part 1 of Art. 5.27.1 Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation in the form of:
- Warnings
- Fine:
- for officials - from 2000 to 5000 rubles;
- for individual entrepreneurs - from 2000 to 5000 rubles;
- for a legal entity - from 50,000 to 80,000 rubles.
If the employer does not provide workers with PPE of the second class (complex design), liability will arise under Part 4 of Art. 5.27.1 of the Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation in the form of a fine:
- for an official - from 20,000 to 30,000 rubles;
- Individual entrepreneur - from 20,000 to 30,000 rubles;
- for a legal entity - from 100,000 to 150,000 rubles.
A repeated similar violation will entail liability in accordance with Part 5 of Art. 5.27.1 Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation in the form of:
- for an official - a fine of 30,000 to 40,000 rubles or disqualification for a period of one to three years;
- Individual entrepreneur - a fine of 30,000 to 40,000 rubles or administrative suspension of activities for up to 90 days;
- for a legal entity - from 10,000 to 200,000 rubles or administrative suspension of activities for up to 90 days.
Thus, the employer’s area of responsibility is the timely and full provision of certified PPE to employees, control over the correct use of them, as well as for their storage and care.
Competent person for PPE inspection
A competent person to check PPE against falls from a height is appointed by order of the organization and must have safety clearance group 3, the group is confirmed by a certificate that can be obtained after completing on-site or remote training in safe methods of working at height. In addition, the responsible employee must know:
- current requirements for periodic testing of PPE;
- recommendations and instructions from manufacturers of safety equipment.
He must be able to:
- determine and evaluate the significance of defects;
- establish the degree of wear of personal protective equipment;
- initiate maintenance and repair activities;
- draw up an act on the write-off of unsuitable insurance equipment and their elements.
To meet these requirements, the appointed person may require training, both introductory (before starting work) and continuing education (when commissioning new models of PPE, etc.).
What does it mean to provide PPE for enterprise employees?
PPE includes devices designed to protect various parts of an employee’s body while performing work duties and isolating the entire body from harmful substances. A worker cannot perform work without the personal protection provided as part of his position. Such devices must be used for their intended purpose and maintained in accordance with the instructions contained in the manufacturer's documentation accompanying each product.
Labor protection, personal protective equipment
On the other hand, they do not include:
- mandatory uniforms that are not specifically designed for the safety and health of the employee;
- PPE used by the military, police and other law enforcement agencies;
- equipment used by first aid and rescue services;
- Sports Equipment;
- mechanisms for self-defense;
- portable devices for detecting and signaling threats and violations of public order.
How often should fall protection PPE be fully inspected?
The frequency of complete inspections is determined by the manufacturer's instructions; as a rule, the interval between inspections does not exceed 12 months . However, a competent person has the right to establish more frequent checks - special ones, taking into account the conditions and intensity of use. Thus, a welder’s harness is more often at risk of melting, safety elements when used at a chemical plant or in a seaport are more susceptible to corrosion, etc.
At the same time, clause 124 of the Labor Safety Rules when working at height requires workers to conduct a thorough inspection of safety equipment before and after use . This is especially true for those equipment that are operated under the influence of aggressive environments, for example, a welder’s harness, etc.
Pre-operation check , carried out before each use (including the very first), includes:
- visual and tactile check of the condition and functionality of PPE;
- external inspection of anchor devices for the absence of mechanical damage, traces of corrosion and deformation;
- checking the presence of labels and expiration date of the product.
The expiration date of protective equipment, the rules for their storage, operation and disposal are established by the manufacturer and are indicated in the operational documentation (instructions) for the product.
Read more about the marking of personal protective equipment against falls from a height in the article.
Abstract on the topic “Personal protective equipment for the population”
The importance of personal protective equipment is currently very high. They help a person in various situations and industries of human production. Personal protective equipment is used to prevent or reduce human exposure to hazardous and harmful industrial and natural factors.
Attention!
If you need help with academic work, we recommend turning to professionals. More than 70,000 experts are ready to help you right now.
Cost calculation Guarantees Reviews
Content
Introduction Introduction 1. Respiratory protection 2. Skin protection 3. Medical protection Conclusion List of sources used
Introduction
The importance of personal protective equipment is currently very high. They help a person in various situations and industries of human production. Personal protective equipment is used to prevent or reduce human exposure to hazardous and harmful industrial and natural factors.
The intensive use of natural resources and environmental pollution, the widespread introduction of technology, mechanization and automation systems into all spheres of social and production activity, and the formation of market relations are accompanied by the emergence and wide spread of various natural, biological, man-made, environmental and other hazards.
The use of personal protective equipment (PPE) occupies one of the leading places in the complex of measures to protect the population in man-made emergencies or when exposed to weapons of mass destruction of a possible enemy.
Introduction
The relevance of the chosen topic is determined by the fact that PPE is necessary to protect the respiratory system when people are in an atmosphere of contaminated air with toxic, radioactive, hazardous chemical substances, biological agents, as well as to protect open areas of skin and clothing from contact with drops and aerosols of toxic and hazardous substances. chemically hazardous substances, radioactive dust and biological agents. In addition, personal protective equipment is also used to protect the human body from the effects of heat flows and smoke aerosols in fire conditions, and from production factors that negatively affect human health.
In the main part of this essay, I consider the classification of PPE by purpose. They are divided into personal respiratory protective equipment (RPP), skin protective equipment (SPP) and medical protective equipment. There is also a classification based on the principle of protective action: PPE of filtering and insulating types.
Need work? There is a solution!
More than 70,000 experts: teachers and associate professors of universities are ready to help you write your paper right now.
Cost calculation Guarantees Reviews
Personal respiratory protection includes industrially produced gas masks and respirators and simple protective equipment manufactured by the population, such as dust-proof fabric masks and cotton-gauze bandages.
Skin protection means include special protective clothing made from rubberized and other insulating fabrics, as well as household clothing made from polyethylene and other moisture- and dust-proof materials.
Goals and main objectives of this work:
- Study the classification of personal protective equipment for the population;
- Know how to properly use personal protective equipment in different conditions;
- Identify problems and the causes of their occurrence while providing the population with personal protective equipment;
- Find solutions to identified problems.
1. Respiratory protection
The most reliable means of protecting people's respiratory organs are gas masks. They are intended to protect the respiratory system, face and eyes of a person from harmful impurities in the air. According to the principle of operation, all gas masks are divided into filtering and insulating.
Filtering gas masks are the main means of personal respiratory protection. The principle of their protective action is based on preliminary purification (filtration) of the air inhaled by a person from various harmful impurities.
“Currently, in the country’s civil defense system for the adult population, filter gas masks GP-5, GP-5m and GP-4u are used: filter-absorbing box 1, front part 2 (for the gas mask GP-5 there is a helmet-mask, for the gas mask GP -4u - mask), bag for gas mask 3, connecting tube 4, box with anti-fog films 5, helmet-mask with membrane box, included in the GP-5m gas mask kit. For children - DP-6, DP-bm, PDF-7, PDF-d, PDF-sh, as well as a children’s protective camera (KZD-4).”
It should be borne in mind that filter gas masks do not protect against carbon monoxide, so an additional cartridge is used to protect against carbon monoxide
There are also insulating gas masks (IP-4, IP-5, IP-46, IP-46M). They are special means of protecting the respiratory system, eyes, and facial skin from all harmful impurities contained in the air. They are used when filter gas masks do not provide such protection, as well as in conditions of lack of oxygen in the air. The air necessary for breathing is enriched with oxygen in insulating gas masks. The gas mask consists of: a front part, a regenerative cartridge, a breathing bag, a frame and a bag.
100 rubles discount on your first order!
Promotion for new clients! Place an order or make a cost estimate and receive 100 rubles. The money will be credited to your account in your personal account.Find out the cost Guarantees Reviews
Respirators. “In the civil defense system, the R-2 respirator is most widely used. Respirators are used to protect the respiratory system from radioactive and ground dust and when operating in a secondary cloud of bacterial agents. The R-2 respirator is a filtering half-mask 1, equipped with two inhalation valves 2, one exhalation valve 3 (with a safety screen), a headband 5 consisting of elastic (stretchable) and non-stretchable straps, and a nose clip 4.”
If a lot of moisture appears while using the respirator, it is recommended to remove it for 1-2 minutes, remove the moisture, wipe the inner surface and put it on again.
“Anti-dust fabric mask PTM-1 and a cotton-gauze bandage are intended to protect the human respiratory system from radioactive dust and when operating in a secondary cloud of bacterial agents.” They do not protect against toxic substances. Masks and bandages are mainly made by the population itself. The mask consists of two main parts—the body and the mount.
Body 1 is made of 2-4 layers of fabric. There are 2 inspection holes cut out in it with glasses inserted into them. The mask is attached to the head with a strip of fabric 3 sewn to the side edges of the body. A tight fit of the mask to the head is ensured by elastic band 4 in the upper seam and ties in the lower fastening seam 6, as well as by transverse elastic 5 sewn to the upper corners of the mask body. The air is purified by the entire surface of the mask as it passes through the fabric during inhalation. Every worker, employee, and student can make a mask.
The mask is worn when there is a threat of contamination from radioactive dust. When leaving the contaminated area, decontaminate it as soon as possible: clean it (knock out radioactive dust), wash it in hot water with soap and rinse thoroughly, changing the water.
Cotton-gauze bandage. It is produced by the population independently. “This requires a piece of gauze measuring 100x50cm. A layer of cotton wool 1-2 cm thick, 30 cm long, 20 cm wide is applied to the gauze. The gauze is folded on both long sides and placed on the cotton wool. The ends are cut lengthwise at a distance of 30-35 cm so that two pairs of ties are formed. If necessary, cover the mouth and nose with a bandage; The upper ends are tied at the back of the head, and the lower ends at the crown b. Lumps of cotton wool are placed in narrow strips on both sides of the nose. Dust-proof goggles are used to protect the eyes.”
All respiratory protection equipment must be kept in good working order and ready for use at all times. Not only workers and employees of industrial enterprises related to hazardous substances, but also the population living near such facilities should know the specifics of using gas masks and the rules for handling them.
Order work from 200 rubles
If you need help with academic work, we recommend turning to professionals. More than 70,000 experts are ready to help you right now.
Cost calculation Guarantees Reviews
2. Skin protection
In conditions of nuclear, chemical and bacteriological (biological) contamination, there is an urgent need to protect the entire human body. According to their purpose, these funds are conventionally divided into special (service) and improvised.
Special skin protection products reliably protect people's skin from vapors and drops of toxic substances, radioactive substances and bacterial agents, completely protect against the effects of alpha particles and weaken the light radiation of a nuclear explosion. According to the principle of protective action, skin protection products can be insulating and filtering.
“Insulating skin protection products are made from rubberized fabric and are used when people spend a long time in contaminated areas, when performing decontamination, decontamination and disinfection work in lesions and infection zones. Insulating skin protection products are used only to protect formation personnel. Isolating protective equipment includes: light protective suit L-1, protective overalls, suit and general protective kit.”
Filtering skin protection means - a set of protective filter clothing (PFC). The main purpose of this kit is to protect human skin from the effects of toxic substances in a vapor state. “The kit also provides protection against radioactive dust and aerosolized bacterial agents. Ordinary clothing (underwear, tracksuits, etc.) can be a means of protection if it is soaked in a soap-oil emulsion (2.5 liters per set).”
The simplest means of skin protection serve as a mass means of protecting the entire population and are used in the absence of standard means. The simplest means of skin protection include regular clothing and shoes. Raincoats and capes made of vinyl chloride or rubberized fabric, coats made of drape, leather, and rough cloth protect well from radioactive dust and bacterial agents. “They can protect against droplet-liquid toxic substances for 5-10 minutes, wet clothing for 40-50 minutes. To protect your feet, it is recommended to use rubber boots, boots, felt boots with galoshes, shoes made of leather and leatherette with galoshes. Rubber, leather gloves, canvas mittens are used to protect hands, and a hood is used to protect the head and neck.
For greater sealing, a bib measuring 80X25 cm with ties for fastening around the neck is sewn to the jacket, and wedges are sewn to the slits of the trousers.”
Ordinary clothing treated with special impregnation can also protect against toxic fumes. “As impregnation, detergents OP-7, OP-10 or soap-oil emulsion are used.”
100 rubles discount on your first order!
Promotion for new clients! Place an order or make a cost estimate and receive 100 rubles. The money will be credited to your account in your personal account.Find out the cost Guarantees Reviews
With the simplest means of skin protection, you can overcome contaminated areas and leave areas where there has been a spill or release of hazardous substances. For a certain period of time, these means will protect the human body from direct contact with drops, aerosols and vapors of harmful and toxic substances, which can significantly reduce the likelihood of injury.
The importance of personal protective equipment for skin in modern conditions is difficult to overestimate. The likelihood of everyone getting into an emergency situation is very high. This is especially true for residents of large cities, where the sudden occurrence of emergencies (fires, releases of toxic, harmful substances, destruction of buildings as a result of an explosion, etc.) is not a rare occurrence. Therefore, the ability of everyone to use individual skin protection products in modern conditions is of particular importance.
3. Medical protection
“Individual first aid kit AI-2 is designed to provide self-help and mutual assistance for injuries and burns, as well as to prevent and reduce the effects of toxic substances, bacterial agents and ionizing radiation. Contains medicines, antidote and radioprotectors.
Nest of 1 individual first aid kit - a syringe tube with an analgesic. It should be used for fractures, extensive wounds and burns. To do this, the syringe tube is removed from the first aid kit. Take the ribbed rim with your left hand, and the body of the tube with your right hand and turn it clockwise all the way with an energetic rotational movement. Then remove the cap protecting the needle and, holding the syringe tube with the needle up, squeeze the air out of it until a drop of liquid appears at the tip of the needle. After this, without touching the needle with your hands, insert it into the soft tissue of the upper third of the thigh from the outside and squeeze out the contents of the syringe tube. Remove the needle without unclenching your fingers. In emergency cases, the injection can also be given through clothing.”
A means for preventing (weakening) damage from organophosphorus toxic substances (Taren - six tablets) is placed in slot 2 in a round red pencil case. It should be taken one tablet at a time when the signal “Chemical alarm!” If signs of poisoning increase, take another tablet. At the same time as taking the drug, you must wear a gas mask. It is recommended to take the drug again no earlier than after 5-6 hours.
Antibacterial agent No. 1 (tetracycline, hydrochloride) is placed in slot 5 in two identical tetrahedral containers without painting. “It should be taken in case of immediate threat or bacterial infection, as well as in case of wounds and burns. First, take the contents of one pencil case (5 tablets at once), wash it down with water, then after 6 hours take the contents of another pencil case (also 5 tablets).”
Antibacterial agent No. 2 (sulfadimethoxine - 15 tablets) is located in slot 3 in a large round pencil case without coloring. “It should be used when gastrointestinal disorders occur, which often occur after irradiation. On the first day, take 7 tablets at a time, and in the next two days - 4 tablets.”
“Radioprotective agent No. 1 (cystamine) is placed in slot 4 in two octagonal pink cases of 6 tablets each. This drug is taken when there is a threat of radiation - 6 tablets at a time. If there is a new threat of radiation, but not earlier than 4-5 hours after the first dose, it is recommended to take 6 more tablets.
100 rubles discount on your first order!
Promotion for new clients! Place an order or make a cost estimate and receive 100 rubles. The money will be credited to your account in your personal account.Find out the cost Guarantees Reviews
Radioprotective agent No. 2 (potassium iodide—10 tablets) is placed in slot 6 in a white tetrahedral pencil case. You need to take one tablet daily for 10 days after radioactive fallout, especially when consuming fresh, not canned milk. First of all, the drug is given to children one tablet at a time.
The antiemetic (etaperazine -6 tablets) is located in slot 7 in a round blue pencil case. “Immediately after irradiation, as well as if nausea occurs after a head injury, it is recommended to take one tablet.”
An individual anti-chemical package is designed to disinfect droplet-liquid toxic substances that have come into contact with open areas of the body and clothing. “The kit includes a bottle with a degassing solution, equipped with a screw cap, and four cotton-gauze swabs. All this is in a sealed bag. If droplet-liquid toxic substances get on open areas of the body and clothing, it is necessary to moisten the swabs with liquid from the bottle and wipe the contaminated areas of the skin and parts of clothing adjacent to the open areas of the skin with them.” The liquid in the bottle is poisonous and dangerous if it comes into contact with the eyes.
The individual dressing package consists of a bandage and two cotton-gauze pads. The end of the bandage, fixed pad 2, colored threads 3, movable pad 4, bandage 5, roll of bandage 6. The bag has a pin, the rules for using the bag are indicated on the cover.
The outer cover of the package, the inner surface of which is sterile, is used for applying sterile dressings.
The solution to the problem of life safety is to ensure normal (comfortable) conditions for people’s activities, to protect people and their environment (industrial, natural, domestic) from the influence of harmful factors exceeding regulatory permissible levels. An important part of this is medical personal protective equipment. Maintaining optimal conditions for human activity and rest creates the prerequisites for high performance and productivity.
Conclusion
Thus, having considered the theoretical aspects of this problem, it can be argued that ensuring human security is the most important thing in the world community.
Need work? There is a solution!
More than 70,000 experts: teachers and associate professors of universities are ready to help you write your paper right now.
Cost calculation Guarantees Reviews
The purpose of my work was to study the protective properties of personal protective equipment and the rules for their use. I theoretically examined the properties of medical protective equipment, breathing and skin PPE. Their main characteristics were identified.
I believe that in order to ensure complete safety of the population, it is necessary to eliminate the reasons for the failure to comply with the necessary protection. There are several reasons: remoteness of PPE storage sites, lack of transport to deliver them to the emergency area, problems with organizing the issuance of PPE to the population, etc. In addition, it is necessary to take into account the specifics of chemically hazardous objects. For example, in case of accidents with the release of nitrogen dioxide, dimethylamine ammonia into the atmosphere, civilian and military gas masks do not protect against these gases. It is necessary to use either an additional DPG-3 cartridge or special gas protection boxes. In addition, each region must take into account its own characteristics.
When a threat of enemy attack is declared, the entire population must be provided with personal protective equipment. The personnel of the formations, workers and employees receive personal protective equipment at their facilities, the population - in the housing office and public health department. If there is a shortage of gas masks at the site, they can be replaced with gas masks and respirators intended for industrial purposes. The rest of the population independently makes anti-dust fabric masks, cotton-gauze bandages and other simple means of respiratory protection, and to protect the skin they prepare various capes, raincoats, rubber shoes, rubber or leather gloves. Personal protective equipment should be stored in or near work areas.
Unfortunately, the likelihood of emergencies caused by industrial accidents increases every year. Their consequences are becoming more and more serious. For example, accidents at chemical plants entail poisoning with hazardous chemical substances (HAS) of varying severity. In this case, not only the personnel of the facility itself, but also the population living next to it may suffer. An effective measure aimed at reducing the consequences of emergencies at such enterprises is to provide people in the area of probable contamination with toxic substances with personal protective equipment for the respiratory system (RPP) and skin (PPE). This applies to workers and employees of the facility, and to non-military emergency rescue units, and to the population. Proper provision of the population with personal protective equipment has always been and remains the main task today.
List of sources used
1. Sibikin Yu. D. Occupational safety during installation, maintenance and repair of electrical equipment of enterprises. Directory - Moscow, KnoRus, 2011 - 288 p. 2. Vlasov I. D. Instructions for the use and testing of protective equipment - Moscow, DEAN, 2010 - 112 p. 3. Mankov V. D., Zagranichny S. F. Methodological recommendations for the study of “Instructions for the use and testing of protective equipment” - Moscow, NOU DPO “UMITTS “Electro Service”, Nestor-Istoria, 2007 - 128 p. 4. Mankov V. D., Zagranichny S. F. Protective equipment used in electrical installations. Design, testing, operation - St. Petersburg, NOU DPO "UMITC "Electro Service", Nestor-History, 2007 - 148 p. 5. Badaguev B. T. Personal protective equipment. Classification and quality control. Procedure for issuance and application. Storage and care. Accounting for personal protective equipment - St. Petersburg, Alfa-Press, 2010 - 160 p.
Stages of testing PPE against falls from a height
The manufacturer's instructions for use of personal protective equipment against falls from a height outline the basic requirements and stages of periodic inspections. In general, the full inspection algorithm consists of the following steps:
- analysis of documents - availability of certificates of conformity, operating instructions, markings;
- studying the history of operation of the safety equipment - PPE record card, forms based on the results of previous inspections;
- visual and tactile inspection of the product - the use of a magnifying glass, probe and other special tools is acceptable;
- function check;
- documenting the results of the inspection;
- formulation of recommendations.
If one of the following criteria is met, personal protective equipment against falls from a height is subject to immediate rejection and removal from service. Otherwise, the likelihood of an accident, investigation and bringing the perpetrators to justice increases. Rejection criteria:
- a violation of safe operation requirements was detected during pre-operation or periodic inspection;
- the product was used to stop a fall;
- the product was not used for its intended purpose;
- manufacturer's markings are missing or unreadable;
- the history of use of PPE against falls from height is unknown;
- the service life or storage period has expired;
- the product has been subject to repairs that were not authorized by the manufacturer;
- doubts have arisen about the integrity, completeness or compatibility of PPE.
Checking the harness
When visually inspecting the harness, pay attention to the condition of the following elements:
- Strengthening tapes and textile attachment points:
- cuts;
- wear;
- reflow;
- marks;
- chemical pollution;
- weak areas;
- tears;
- Power firmware threads:
- circumcised;
- worn out;
- tattered;
- elongated;
- Failure indicators;
- Metal attachment points and adjustment buckles:
- deformation;
- marks;
- wear;
- corrosion;
- Comfort elements:
- travel limiters;
- firmware of protective components;
- protective covering;
- soft pads;
- unloading loops, etc.
During functional tests the following is checked:
- installation of tape in buckles;
- functioning of quick-release buckles FAST;
- operation of the adjusting buckles.
Checking slings
When visually inspecting the slings, pay close attention to the condition of the following elements:
- Shock Absorber Band:
- a cut;
- wear;
- burned areas;
- marks;
- chemical pollution;
- weak areas;
- Threads in the seams of the shock absorber, tape base of the sling body, power sewing:
- circumcised;
- worn out;
- tattered;
- elongated;
- with traces of chemical exposure;
- Rope sling base:
- cuts;
- wear;
- rigidity;
- fraying;
- bloating;
- traces of exposure to high temperatures;
- chemical pollution;
- hernias;
- Cable base of steel sling:
- cuts;
- wear;
- chemical exposure;
- traces of corrosion;
- folds;
- twists;
- Sealing loops;
- Protective thimbles:
- Availability;
- deformation;
- Connecting elements (body, bolt, locking mechanism, axles, rivets) and length adjustment mechanism:
- Availability;
- corrosion;
- deformation;
- marks;
- cracks;
- wear;
- Protective covers:
- Availability;
- wear.
When checking the performance characteristics, special attention is paid to the operation of the locking mechanism and the efficiency of the return spring of the connecting carabiners, as well as to the proper functioning of the lanyard length adjustment mechanisms.
Group 3 for height - 990 rubles
Take the exam online at our training center.
Find out more
Checking ropes
When visually inspecting ropes, pay attention to the appearance of defects in the following functional elements:
- Braid:
- cuts;
- wear;
- rigidity;
- fraying;
- bloating;
- traces of exposure to high temperatures;
- marks;
- chemical exposure;
- core opening;
- hernias;
- Seam threads in stitched ends:
- circumcised;
- worn out;
- tattered;
- elongated;
- with traces of chemical exposure;
- Nodes:
- form;
- wear.
The rope core is subject to tactile inspection - palpation, during which the presence of the following defects is noted:
- hard places;
- soft spots;
- bends and twists;
- hernias;
- lack of braid.
Checking the clamps
When visually inspecting the clamp, the inspector’s attention is focused on the condition of the following elements:
- Body and clamp lever, locking mechanism, connecting elements (body, bolt, locking mechanism, axles, rivets):
- Availability;
- corrosion;
- deformation;
- marks;
- cracks;
- wear;
- Shock Absorber Band:
- a cut;
- wear;
- burned areas;
- marks;
- chemical pollution;
- weak areas;
- Power sewing threads:
- circumcised;
- worn out;
- tattered;
- elongated;
- with traces of chemical exposure;
- Flexible anchor line:
- cuts;
- wear;
- rigidity;
- fraying;
- bloating;
- traces of exposure to high temperatures;
- chemical exposure;
- hernias;
- Protective thimbles and covers:
- Availability;
- deformation.
Functional tests are used to check:
- operation of the locking mechanism;
- return spring efficiency;
- movement along the anchor line;
- stop when exposed to load.
Checking connecting links
When visually inspecting connecting links, pay attention to the presence of cracks, marks, signs of wear, deformation and corrosion. Functionally check the operation of the carabiner latch and return spring.
Checking descenders
Release devices are inspected for cracks, marks, signs of wear, deformation and corrosion. They functionally check the ability to move and brake, evaluate the operation of spring mechanisms, ease of opening and closing.
Checking block videos
When visually inspecting the block rollers, pay attention to the presence of cracks, marks, signs of wear, deformation and corrosion. They functionally check freedom of rotation, evaluate the operation of spring mechanisms, ease of opening and closing.
Checking retractor type locking devices
A visual inspection of retractor-type locking devices is carried out according to the same parameters as the inspection of lanyards and safety harnesses. During functional tests, attention is paid to the ability of the tape to freely extend and retract, as well as to stop when a sudden load is applied.
Checking helmets
When visually inspecting the helmet, pay attention to the presence of cracks, marks, melting, and traces of chemical exposure. The performance test is aimed at assessing the operation of the adjustment mechanisms of the head, neck and chin straps.