The occupational safety action plan is a local document of the organization, which is approved by the employer. It consists of events planned in advance in a certain sequence that need to be implemented in the organization in order to bring labor protection into compliance with legal requirements.
Sample “Occupational Safety and Health Action Plan” List of Occupational Safety and Health Measures (from Order 181n)
How are occupational safety measures regulated?
Occupational safety measures are regulated by Order of the Ministry of Health and Social Development of Russia N 181n “On approval of the Standard List of measures annually implemented by the employer to improve working conditions and safety and reduce levels of occupational risks.”
Order 181n lists all possible labor protection measures, which is why they are called standard. Conventionally, they can be divided into organizational sanitary and technical.
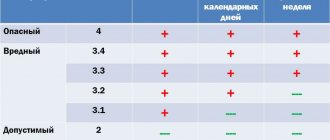
The title says “annually implemented,” although some of them do not need to be carried out anew each time (special assessments of working conditions and training are valid for more than a year).
The sequence of their execution is arranged in accordance with priority. Most often, only a small part of this list is sold. It all depends on the specifics. The more complex and dangerous the industry, the more of this list is necessary for implementation.
Therefore, a specific list of measures to improve working conditions and safety and reduce levels of occupational risks is determined by the employer based on the specifics of its activities.
It is important to note that the planning of occupational safety measures is provided for by standard regulation 438n dated August 19, 2016 for the implementation of the functioning of the occupational safety management system at the enterprise.
The most important occupational safety measures
Legal measures – provision of documentation, which includes regulations and local documentation on labor protection of the organization. This is the conclusion of individual employee contracts, lists, orders, regulations, etc.
Socio-economic measures - includes compensation to employees for accidents, compulsory insurance, payment of labor benefits to employees with whom the employment contract has been terminated, provision of benefits to employees working in hazardous work, etc.
Organizational and technical measures - creation of an occupational safety and health management system (OSMS).
Sanitary and hygienic measures – ensuring a reduction in the level of exposure to hazardous and harmful factors on enterprise employees, creating favorable working conditions.
Treatment and preventive measures - medical examinations and psychiatric examinations, provision of proper nutrition to workers involved in hazardous work.
Rehabilitation measures – ensuring the speedy restoration of working capacity of an employee who has had an accident or who has received an occupational disease.
How to develop an event plan for the year?
What need to do? First, analyze the expenses of previous years, make a list of all upcoming occupational safety measures, and calculate the cost estimate for these activities. Based on this information, develop and approve a labor safety action plan with management.
Sequencing:
1. Write down all possible activities that may be in your organization from Order 181n “Standard List of Activities”.
2. Ask the accounting department for the costs of the current year’s events in order to more accurately predict the events for the next year
3. Ask the HR department for a list of current employees and plans for hiring new ones in order to predict activities for them (training, briefings, medical examinations, etc.).
4. Talk to department heads. Find out what changes have taken place in the field of labor protection (workwear has worn out, pro-free allowances have increased, etc.). Find out what your plans are for next year (purchase of new equipment, adding new employees, etc.).
5. Familiarize yourself with the documents in which labor safety measures are implemented : professional assessments, special assessment cards, regulations of supervisory authorities, etc.
6. Make a final list of activities in order of importance. First, indicate the mandatory ones - training, preliminary and periodic medical examinations, special assessments, then the optional ones - purchasing a stand, new collective protective equipment, etc.
7. Make an estimate of labor protection costs:
- All organizations, with the exception of government ones, are required to spend at least 0.2 percent of the cost of producing their products on labor protection measures. (Article 226 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation). Therefore, ask the accounting department for the costs of production for the last year.
- Ask your planning department or accounting department about budget planning to find out how the budget is planned in your organization as a whole.
- Assess the cost of material assets that will have to be purchased, as well as the cost of services from third-party organizations in the field of labor protection. You should know how much personal protective equipment, fire extinguishers, safety devices, worker training, special assessments, etc. cost.
8. Develop and approve with management a plan of occupational safety measures based on the list of activities and cost estimates. According to standard provision 438n on OSMS, the plan should include:
- results of working conditions;
- list of events;
- responsible persons;
- the timing of each event and what results are expected.
It is necessary that the action plan be recorded on paper and approved by the employer. However, there is no approved form as such, so it is formed in free form. The main thing is that it is understandable and meets current needs. It may contain both the name of the event and the calculation of the financial component. It all depends on how work is organized within the organization.
The fine for the absence of a labor safety action plan ranges from 30 to 90 thousand, or suspension of the company’s activities for up to 90 days. (Article 5.27 of the Administrative Code)
Main stages of planning
The development of a plan for the implementation of new labor protection tools is guided by the following principles:
- perspective – focuses on solving the target problem;
- the leading link prefers a more effective event. For example, improve the qualifications of employees or slightly improve their working conditions;
- continuity of the process - the more aspects the plan covers, the greater the need for continuous development and improvement.
Planning includes the following procedure:
- Analysis of existing “problem areas”, description of goals and methods of achieving it.
- Collection of statistical information, its processing, development of ways to improve existing indicators.
- Checking the financial balance, establishing the amount for labor protection measures, distributing funds to solve the task.
- Vigilant monitoring of compliance with instructions; correction of some points of the expected result may be necessary.
- Further monitoring of the state of safety regulations, timely preventive strikes on emerging problem areas.
It is impossible to create an effective plan without initial data (information), these include:
- analysis of the state and trend of industrial injuries, the occurrence of diseases caused by work activity;
- results of inspections of workplaces for sanitary and technical conditions, certification of existing tools;
- report on the logistics of the site, lines, availability and quality of personal protective equipment for workers. Testing their knowledge of safety regulations, conducting briefings and advanced training courses;
- instructions from regulatory government bodies and independent labor protection services;
- proposals from heads of structural divisions and services, trade unions, individual appeals.
Elements and procedure for drawing up an action plan
It is most practical to develop a document in the form of a table, which consists of:
- List of activities carried out (type and purpose of the work carried out).
- The timing of the event and the regulated period for implementation.
- Indication of the responsible person or group in the form of an executive committee.
- The note indicates the successful completion of the planned action.
It is logical to provide an additional column to indicate financial costs. In addition to the list of general activities, the internal document is supplemented with specific features of the production in question.
Material support
Financing of occupational safety measures is consistent with existing standards. Additional investments are deducted from the profits of the enterprise in question. Sources of funds include:
- Multi-purpose investments (reconstruction of equipment, automation of industrial lines, machine tools).
- Bank lending is used to modernize existing technical means and technologies.
- Investment contributions.
- Sinking funds.
- Financing obtained from the calculation of production costs.
Occupational safety measures are an important tool for reducing the risk of injuries and occupational diseases.
Modernization of production and improvement of the quality of workplaces (with preliminary instruction) will increase the efficiency of employees and the quantity of products produced.
You will learn how you can reduce the costs of carrying out occupational safety measures in this video:
Example of a simplified occupational safety and health action plan for an accounting firm
When developing an occupational safety and health action plan, many factors must be taken into account. Let's start from the very beginning of the office. The organization has just registered. He rents an office and begins moving into it and recruiting staff.
The action plan might look like this:
1. Fire safety measures:
— preparation of an evacuation plan; — purchase of fire extinguishers; — maintaining related documentation; — purchasing signs and “Exit” signs in case of fire evacuation; — development of a fire safety training program; — appointment of those responsible for the premises.
According to the law, the owner is always responsible for the premises, but very often the landlord shifts part of the responsibility to the leasing organizations. The above is a list of the most common events that rental organizations face. Therefore, when choosing a room, you need to take this point into account.
If the owner of the premises is the employer himself, then care must be taken to ensure that the premises meet fire safety requirements (presence of warning systems, serviceability of fire hoses, unhindered access to emergency exits, and so on).
2. Organization of a preliminary medical examination for hired employees (if necessary), as well as psychiatric examinations and pre-departure medical examination (if necessary).
From May 24, 2021, such examinations were canceled for office employees, however, if the company has a driver, then such examinations are necessary for him (psychiatric and pre-trip). The same applies to other non-office specialties, if they are included in the organization’s staffing table.
3. Conducting a special assessment of working conditions.
— determination of the list of workplaces subject to SOUT; — concluding an agreement with a certified organization; — assistance to the organization in the process of conducting a special assessment; — submission of reports on the results of the implementation; — familiarization of employees with the results; — organization of events recommended based on the results of the special assessment.
Carrying out this event will allow us to determine working conditions. Including the materials of the special assessment of working conditions, based on its results, there will be a list of recommended measures that you can add to the plan for the next year (for example, replacing lamps with brighter ones, etc.). However, if everything is in order at the workplace, then there will be no activities in the SOUT materials.
4. Organization of the necessary training on labor protection for managers and employees of the organization (HSE, HSE, civil defense and emergency situations) in accordance with the internal structure of the organization.
In this case, you send for training the general director, heads of structural divisions and other responsible persons who will directly monitor compliance with labor protection requirements and, thanks to the training, will have the opportunity to conduct briefings.
5. Creation of local regulations and documents:
— OT management system; — orders appointing those responsible for various issues related to labor protection; — training programs; — labor protection instructions; — accounting journals; - other related documentation (here you can describe in detail what kind of documentation (that is, related to medical examinations, psychiatric examinations, operation of a company car, and so on).
Documentation is maintained depending on the specifics of the organization’s activities. The more complex and dangerous the industry, the more paperwork will need to be maintained. The list of documents is created based on the legislative act under which you are working.
6. Creation of jobs that meet labor protection requirements:
— the presence of grounding on all equipment used in work; — use only serviceable and certified equipment; — lighting sufficient to perform work duties; — purchasing or making warning signs (“Caution wet floor”, “Caution step”, etc. This will be individual in each case); — purchase of comfortable ergonomic furniture.
You should not skimp on your employees. A comfortable and safe workplace, where the employee will not have back, eye pain, etc., will do his job better.
7. Organization of work and rest schedule and comfortable working conditions:
— approval of the work schedule and regulated breaks; — organizing a place for storing and eating food (if the premises allow it, since eating is prohibited at work places); — availability of ventilation, heating and air conditioning systems to maintain optimal microclimate parameters; — purchase of coolers with drinking water and conclusion of an agreement with the organization for a constant supply of water; — purchase of household appliances for the dining room; — organization of a smoking area in accordance with fire safety requirements.
Creating conditions for comfortable rest will allow your employees to recover faster and thereby increase their ability to work.
8. Purchase of stands, visual materials, scientific and technical literature for conducting briefings.
This event will allow employees to focus their attention on important issues related to their safety.
9. Instructing employees in safety rules:
— carrying out all necessary briefings; — testing knowledge of labor protection requirements; — on-the-job training (if necessary); — maintaining documentation related to these activities.
The quality of this event determines how seriously employees will take the announced rules. If the event is held “formally for show,” then the attitude towards it will be appropriate. The task of an occupational safety specialist is to increase the self-discipline of employees in matters of compliance with safety requirements.
10. Monitoring compliance with workers’ labor rights
In accordance with the labor code. This includes compliance with the work and rest schedule, timely payment of labor, including payment for overtime and work on weekends and holidays. In some cases, the employer’s compliance with requirements related to the health of employees (short shifts, medical leave, work restrictions due to pregnancy, etc.)
11. Organization of compliance by employees with labor protection requirements and internal rules of the organization:
— taking action against employees who violate safety requirements; — carrying out measures aimed at preventing the recurrence of such situations.
12. Organization of investigations of workplace accidents in the event of employees being injured while performing their work duties.
This is roughly what the list looks like for 1 year of operation of a new organization. In the future, this list will only contain control over compliance with all activities and the timing of their implementation. This is necessary in order to organize repeated briefings, training, SOUT and other events that are periodic.
Thus, a labor protection specialist, based on information obtained in the course of his work, organizes labor protection and safety measures. It is worth noting that almost all of the activities listed in this article imply the correct management of document flow, one way or another related to the event being implemented.
Development of a labor safety action plan is one of the most important stages. Such a plan is usually drawn up for a year. In it, the specialist describes the organizational and technical measures for labor protection in order of their importance, thus setting priorities. At the same time, he sets tasks and distributes responsibility in order to be able to control the progress of the planned activities.
After the period for which the action plan was developed, the success of its implementation is summed up. A comparative analysis is carried out (pre-event/post-event) and a new plan is developed. Thus, each subsequent one increasingly improves the level of labor protection in the organization. Ultimately, all that remains is control over the frequency and maintenance of the functioning of labor protection.
Contents of the plan of organizational and technical measures [p.187]
All functional and production departments must have analytical work plans that provide for the content of the analysis and the frequency of its conduct. For example, in carrying out a technical and economic analysis at an enterprise, not only economic departments (economic planning, labor and wage organization, accounting, financial) should participate, but also technical departments in accordance with the functions they perform. Thus, the chief mechanic’s service must analyze the implementation of equipment repair schedules, checks and inspections, as well as equipment downtime for technical reasons, study the implementation of plans for organizational and technical measures to improve the state of the repair service and equipment operation, as well as installation, adjustment and commissioning schedules for new equipment, vehicles and various technological installations, etc. The heads of production departments (teams, sections and workshops) should also carry out a technical and economic analysis. This will allow for more economical use of labor, material and monetary resources and production capacity. Therefore, in order to conduct a technical and economic analysis at each enterprise, in accordance with the structure of the management apparatus and the regulation of the functions and rights of each of its links, a scheme for the distribution of responsibilities between them must be developed. At the same time, the division of functions between structural divisions should eliminate duplication and parallelism in their work, while ensuring at the same time the full implementation of tasks associated with conducting an in-depth, detailed technical and economic analysis. 91 [p.91]
In the process of implementing standards at an enterprise, it is necessary to compare the organizational and technical conditions adopted in the standards with those existing at the enterprise for this type of work, develop a plan of organizational and technical measures aimed at achieving the conditions provided for in the standards (introduction of advanced technology, equipment, technological equipment, organization of workplaces, workplace maintenance systems, etc.) comparison of the technological content provided for in the regulatory tables with the actual work performed on regulated operations; calculations of labor cost standards according to the standards being implemented. [p.40]
The plan of organizational and technical measures must be specific; it must indicate the content, purpose of the activities, who is responsible for them, the place of implementation, and sources of financing costs. The plan must also define economic efficiency and indicate the payback period for costs. [p.172]
The content of production meetings is very diverse. They participate in the development and discussion of draft plans; they listen to the heads of enterprises and workshops about current work and the results of economic activity for a certain period; they consider issues of organizing production, labor, wages; they discuss plans for organizational and technical measures, the introduction of new equipment, and proposals from innovators and inventors. [p.57]
The calendar plan is developed based on the plan of organizational and technical activities. Therefore, it is necessary to study its content, determine the proportion of measures aimed at increasing labor productivity, find out whether they are reflected in the calendar plan for replacing and revising standards, and whether measures for the scientific organization of labor are taken into account when developing the calendar plan. [p.55]
Based on notifications about changes in standards, enterprises monitor the implementation of the plan of organizational and technical measures. For these purposes, a statement or card is filled out, which contains the content of the implemented event, the value of the norm at the beginning of the reporting period and after the event, the planned and actual amount of changes in norms, conditional annual savings according to the plan and report. [p.147]
To reveal the content of fixed production assets (fixed capital), study their dynamics, structure, degree of wear and the possibility of restoring the working capacity of tools, assess the level of use of fixed production assets and transfer their value to finished products, various groups of technical and economic indicators will be considered below. allow not only to assess the actual state of the entire set of fixed production assets (fixed capital), but also to develop a plan of organizational and technical measures to identify and implement intra-production reserves that contribute to the growth of not only the efficiency of fixed production assets, but also production as a whole. [p.60]
The volume of repair work in physical terms is determined on the basis of maintenance schedules and technical inspections of equipment, data on the standard content and volume of repairs, reports on the actual operating time and condition of the equipment, orders from technological shops for the manufacture of non-standard equipment, plans for new equipment and organizational and technical measures. etc. [p.296]
Contents of scheduled preventive maintenance. The operability of equipment, its reliability and safety are ensured by scheduled preventive maintenance (PPR). The PPR system is a set of preventive, organizational and technical measures for the care, supervision, maintenance and repair of equipment, carried out according to a pre-drawn plan in order to prevent unexpected equipment failure. The PPR system applies to all types of equipment of main and auxiliary workshops, including means of transport and communications. [p.192]
Further detailing of plans, determination of a specific list of products to be produced in the planning period, labor and material resources required to implement the plan, development of organizational and technical measures to ensure the implementation of plans, bringing plan targets to the executors - all this represents the content of the economic and social planning of the enterprise. [p.217]
Upon completion of the development of a plan for increasing the economic efficiency of production, they begin to calculate the remaining sections of the technical industrial and financial plan, since their content and indicators directly follow from the production and sales plan and are justified by organizational and technical measures. [p.59]
Of particular importance is a systematic approach to assessing the activities of each link of the national economy. A comprehensive study of the results of economic activity, expressed in socio-economic indicators, and the rational use of resources is the content of economic analysis. It is aimed at assessing the validity of planned targets, the progress of their implementation, the study of production factors, the effectiveness of organizational and technical measures, production technology, etc. The systematic approach lies in the fact that the analysis is carried out not only for the past period, but also in the process of implementation ongoing monitoring of the activities of associations, enterprises, and their divisions in order to timely (during the work) identify emerging deviations in the formation of production and financial indicators from those established by the technical industrial and financial plan. Based on this analysis, proposals are developed to eliminate identified deficiencies and mobilize reserves. It is no less important to generalize the experience of leading enterprises for its wide dissemination, since often enterprises of the same profile, operating in the same conditions, have significant differences in the level of economic and financial activity. When assessing the implementation of planned tasks, it is necessary to identify the factors due to which the plan was fulfilled. Moreover, it is necessary to strictly distinguish between internal factors, depending on the work of a given team, and external factors - the degree of cooperation in specialization, changes in prices, product range, etc. [p.6]
Plan. technical development of the enterprise, including organizational and technical measures, is approved by the director of the enterprise. After the plan is approved, the activities listed in it are broken down into workshops, with the content, timing and order of implementation being brought to their attention. [p.172]
Submits for approval estimates for work and services performed by the estimate department for the maintenance of the department and service centers, reports on the implementation of self-supporting indicators and organizational and technical measures, proposals for changing prices based on market conditions and the state of demand for these products, information on the shipment of products to consumers, information on balances of finished products in the warehouses of the sales department, data on the supply of products, the amount of products not delivered under contracts for the reporting month and cumulative results from the beginning of the quarter (year); a report on the implementation of the supply plan, taking into account concluded contracts, information on the balances of finished products. [p.656]
Technical development. The content of the plan for technical development and use of achievements of science and technology is a system of technical, organizational and economic measures aimed at increasing the technical level and quality of construction, fulfilling planned targets for commissioning production capacities and construction projects, increasing labor productivity, profits and reducing the cost of construction - installation work. The main activities of the plan aimed at technical development are divided into the following areas of technical progress [p.98]
After developing five-year and annual plans, ministries and departments set tasks for construction and installation trusts, house-building plants and associations. Then, such primary construction organizations as construction and installation departments (CMU), mobile mechanized columns (PMK) and construction departments (CS), develop plans for the introduction of new equipment and organizational, technical and economic measures that are part of the construction financial plan. These plans are developed under the direction of the chief engineer. Initially, an approximate list of activities is compiled that defines the main directions of the plan, in which their brief content is given and the objects where they will be implemented are outlined. [p.161]
The first two factors fully depend on the activities of the construction and installation organization; they cover a complex of technical, organizational and economic measures that make up the content of plans for technical development and increasing production efficiency. Changes in the volume, structure and territorial location of construction and installation work do not directly depend on the activities of a given construction and installation organization (management, trust) and are external to it. But these factors are also subject to mandatory consideration when making summary calculations of labor productivity growth and reducing the cost of construction and installation work. [p.74]
The content of NOT includes mainly organizational measures related directly to the labor process and purposeful human activity. This is the difference between NOT and a technical development plan and organizational and economic measures. [p.187]
The purpose of developing an enterprise development strategy is to identify the main directions for its further development based on the maximum use of scientific, technical, production and personnel potential. Strategic planning typically involves developing long-term plans spanning 10 to 15 years. When developing long-term plans, the main directions in which the enterprise will develop are determined, the content and sequence of implementation of the most important organizational, economic and technical measures are established to ensure the achievement of the main goals. The stages of the strategic planning process for a market-oriented enterprise are presented in Fig. 11.19. As can be seen from the figure, the process of strategic planning of an enterprise begins with determining the purpose of the enterprise, its position in the business environment using a portfolio analysis of areas of activity. [p.332]
When carrying out analysis work, it is necessary to ensure that all organizational, technical, economic, social, etc. activities carried out at the enterprise are linked within the management system. In addition, attention should be paid to the level of automation of management functions. The analysis data should become the basis for revising, clarifying functions and tasks to improve product quality, and identifying those elements of the system that should be supplemented, reworked or developed again. Based on the results of the analysis, a report is usually drawn up and terms of reference are developed for improving the management system, which should include the following sections: basis for improvement; characteristics of the current system; purpose and objectives for improving the system; clarification of the composition and content of the functions of the system when improving it; structure of a product quality improvement plan (or program quality) timing of the formation of the project for an improved system; main regulatory and methodological sources; prospects for continuing work; additional instructions; annexes (lists of departments and persons with whom STP and other normative and technical documentation systems must be agreed upon). [p.472]
Organizational events, in turn, are planned. The content of the plan depends on the volume of work and the time for which it is designed. With long-term target and five-year planning, a plan for the technical development (technical orientation) of construction is drawn up for the ministry, main construction departments and trusts. Before the start of construction, a plan is developed for the general organizational and technical preparation of construction production and preparation for the construction of a complex of facilities in accordance with the construction organization project (COP). [p.145]
On the basis of these standards, production tasks (work orders) are drawn up, which stipulate the content and volume of work to be performed and represent the tasks of the national economic plan brought to the workplace. They are taken as the basis for calculating piece rates, which ensures the possibility of introducing the most effective remuneration systems into production. Without technically sound standards, it is impossible to correctly design the organization of production, determine the need for labor, staff units and teams of workers, establish calendar plans and rational methods of performing work. Technically sound standards are also of great importance for planning the cost of work (products), strengthening cost accounting, determining the effectiveness of technical and organizational measures, and organizing socialist competition. [p.72]
The plan for improving management, planning and organization of production is aimed at introducing progressive forms and methods of management that will help reduce the number of employees in the management apparatus, reduce the cost of its maintenance and increase production efficiency. It contains measures to disseminate progressive forms of production organization (concentration, specialization, cooperation, combination) in accordance with the characteristics of individual industries for mechanization, automation and rational organization of management processes based on the use of economic and mathematical methods, computers and office equipment for the development and implementation of automated control systems . This provides for measures to improve in-plant technical, economic and operational planning and organization of cost accounting, including a system of planned indicators, a system of economic incentives within the association, a system of self-supporting relationships within the association and with other organizations. This also includes measures to improve the organizational structure, methods and organization of the work of the apparatus management, mechanization and automation of engineering and managerial work. Includes measures to improve the system of accounting, control and office work, organization of preparation and technical control of production, organization of production in the main and auxiliary workshops of the enterprise, coordination of their activities, increase of the organizational level of production, improvement of the system of training and retraining of management personnel. [p.130]
Plan for technical development and production organization. Determine the technical, organizational, socio-economic and research activities necessary to fulfill tasks to increase product output, improve its quality, reduce production costs, increase labor productivity, profit and profitability of production. Consequently, the content of this section of the plan is tasks to increase the technical and organizational level of production. For each activity included in the plan, costs, implementation timeframes, economic efficiency, impact on other sections of the plan and sources of financing are calculated. Major repairs are also planned, since it ensures the restoration of fixed assets and their further use. [p.124]
Must know regulations, orders, orders of higher authorities, methodological, regulatory and other guidance materials on the organization of labor and production management, prospects for the technical and economic development of the enterprise, economics and organization of production, labor and management, the procedure for developing long-term and annual plans, NOT content of the main directions of the scientific organization labor and methods of conducting research work in these areas, methods for determining the economic efficiency of activities in the field of labor and labor, assessing the level of labor organization, production and management of the achievements of domestic and foreign enterprises and scientific institutions in the field of improving labor organization and production management, organizational technology, means of mechanization of information [p.62]
Job responsibilities. Ensures the implementation of work to improve the organization of labor, production management, forms and systems of wages, material and moral incentives for enterprise employees, and the organization of socialist competition. Heads the preparation of long-term and annual plans for labor and wages, drawing up sections of technical industrial financial plan NOTES, cost estimates for the maintenance of the management apparatus, developing tasks to reduce the labor intensity of products (works, services) and calendar plans for revising labor cost standards, determining the economic efficiency of implementing scientific measures labor organization. Analyzes the effectiveness of the application of existing forms and systems of remuneration, material and moral incentives, ensures the development of proposals for their improvement, as well as draft regulations on bonuses for employees of the enterprise. Manages work to study labor processes, organization and working conditions at the enterprise and identify reserves for growth of labor productivity, as well as the development of measures to improve the division and cooperation of labor, improve the use of working time, certify the rationalization of jobs, techniques and methods of labor, reduce the use of heavy labor physical labor, creation of favorable working conditions and other areas of NOT. Prepares proposals for the introduction and improvement of the efficiency of collective (team) forms of organization and remuneration, as well as for the use of centrally developed standard projects for organizing the labor of workers, employees and individual divisions of the enterprise. Organizes work on labor standardization, timely revision of standards, introduction of technically sound labor standards, improvement of standardization based on the application of intersectoral, sectoral and other progressive labor standards, expansion of the scope of labor standardization for temporary workers and employees. Provides control over the expenditure of wage funds and material incentives, compliance with the planned relationships between the growth rate of labor productivity and average wages, the correct application of wage forms and systems, tariff rates and prices, official salaries, the establishment of categories of workers and categories of specialists. Carries out work to improve organizational management structures, organize and mechanize the work of employees, develop regulations on structural divisions of the enterprise and job descriptions for employees, staffing schedules for employees in accordance with industry standard staffing levels, staffing standards and salary schemes and the established wage fund. Provides control over the rational use of wage funds, determining - [p.80]
Thus, the workshop monthly plan of organizational and technical activities is mainly aimed at ensuring the production of products in full accordance with the technical documentation. [p.39]
In accordance with these factors, measures of an organizational, technical, economic, social, administrative nature are developed, constituting the main content of current and long-term plans for improving production, and internal reserves for increasing labor productivity are determined. The point of calculating reserves is to comprehensively assess the level and changes in labor productivity for each factor. This calculation is called factorial. The effect achieved due to the influence of individual factors (measures) is defined as the difference between the number of workers that would be required for the planned year while maintaining the labor productivity achieved in the base period (i.e., the base number is multiplied by the growth rate of production volume), and planned number or as the difference in labor costs. [p.209]
Job responsibilities. Organizes the development and implementation of organizational and technical measures for comprehensive information protection at enterprises carrying out work the content of which is a state or commercial secret, ensures compliance with the work regime and maintains the confidentiality of documented information. Leads the development of projects of long-term and current work plans, compiling reports on their implementation. Manages the implementation of work on the organization, coordination, methodological guidance and control of their implementation on information security issues and the development of technical means of control, determines the prospects for their development. Ensures interaction and the necessary cooperation of co-executors of work on the organization and conduct of research and development, organizes and monitors the implementation of planned tasks, contractual obligations, as well as the timing, completeness and quality of work performed by co-contractors. Organizes work on concluding contracts for information security work, takes measures to ensure financing of work, including those carried out under contracts. Ensures the department's participation in the development of technical specifications for research and development carried out at the enterprise, formulates the goals and objectives of the work to create secure information technologies that meet the requirements of comprehensive information security. Organizes special research and control checks to identify unmasking signs and possible channels of information leakage, including through technical channels, [p.100]
The successful solution of the tasks facing the repair service to reduce costs, repair and maintenance of equipment is facilitated by the use of a system of planned preventive maintenance (PPR) of equipment, i.e. rational operation and scheduled repair of equipment. This system provides a set of organizational and technical measures for the care, supervision, maintenance and repair of equipment, carried out preventively according to a pre-developed plan in order to prevent progressive wear, prevent accidents and maintain equipment in working condition at maximum productivity. [p.192]
Contents and procedure for developing a plan to improve production efficiency. This section of the technical industrial finance plan determines the qualitative side of the enterprise’s production activities. It includes a complex of organizational, technical, economic planning and research activities. The development of measures to draw up a plan for increasing production efficiency is carried out systematically - throughout the entire year preceding the planned one. [p.240]