Failure to provide leave under prohibition
Employees of the organization working under employment contracts have the right to annual paid leave. Moreover, this right is available not only to core employees, but also to part-time workers, seasonal workers, conscripts, etc. (Part 2 of Article 287, 291, 295, Part 4 of Article 310, Part 2 of Article 312.4 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
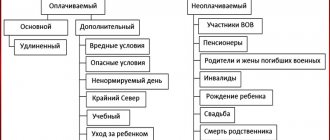
Some employees have the right to extended and additional leave (for more information, see “We provide extended leave”, “We provide additional leave”).
The right to leave must be exercised, therefore the current legislation establishes, in particular, a ban on non-provision of leave (Part 4 of Article 124 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation):
- for two consecutive years;
- employees under the age of 18;
- employees engaged in work with harmful or dangerous working conditions.
Let's summarize
- Vacation is not only a sacred, but also an employee’s right to rest, enshrined in the Labor Code.
- If an employee has not been on vacation for more than two years in a row, you will be fined.
- Unused vacation days accumulate and their price increases along with the employee's salary.
- Monitoring whether your employees go on vacation on time and whether they use it fully is the task of the person who keeps personnel records at the enterprise.
By the way, we specialize in Accounting services
More details
Check to see if you have accumulated any such surprises during your work? And share this article with your friends so that they can also check the situation in their companies.
Sanctions for violation of laws
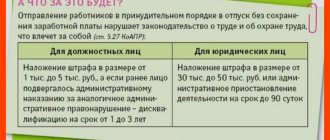
To ensure that the ban is not unfounded, administrative liability has been established for failure to provide leave. For a violation committed for the first time, the fine will be (Part 1 of Article 5.27 of the Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation):
- for officials – from 1,000 to 5,000 rubles;
- for individual entrepreneurs – from 1,000 to 5,000 rubles;
- for an organization – from 30,000 to 50,000 rubles.
For a repeated violation, the fine will be increased, and officials of the organization may face disqualification (Part 4 of Article 5.27 of the Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation):
- for officials – from 10,000 to 20,000 rubles. or disqualification for a period of 1 to 3 years;
- for individual entrepreneurs – from 10,000 to 20,000 rubles;
- for an organization – from 50,000 to 70,000 rubles.
General rules
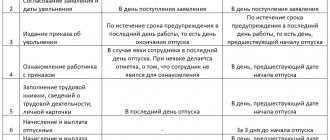
In order to take into account all legal norms and restrictions and avoid punishment for the lack of a vacation schedule, the personnel service plans in advance the work and rest schedule for the next year and puts everything into the T-7 form or its equivalent, developed and approved by the LNA. The schedule for the next year is approved no later than 2 weeks before its start.
IMPORTANT!
Employers - individuals, registered or unregistered as individual entrepreneurs, have the right not to draw up a work and rest schedule, but to define it in a written agreement (Article 305 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation). In this situation, there will be no fines, but provided that there is a replacement for it.
All employees have the right to rest, regardless of whether they have a permanent or fixed-term contract. The vacation of employees hired under fixed-term contracts rolling over to the next calendar year is planned in accordance with the general procedure (Article 123 of the Labor Code). Part-time workers, both internal and external, are also included in the annual schedule, and their absence in the plans will result in a penalty comparable to a fine for the lack of a vacation schedule in general.
Where do the firewood come from?
It would seem how the state labor inspectorate learns about the violation committed. In practice, two scenarios are possible:
- employee complaint;
- scheduled or unscheduled inspection of the organization (part 1 of article 353, part 2 of article 360 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
Currently, small businesses (organizations and individual entrepreneurs) are exempt from scheduled inspections due to a moratorium on inspections valid until December 31, 2021 (Part 1, Article 26.1 of the Federal Law of December 26, 2008 No. 294-FZ).
Read also
01.01.2018
Leave procedure
The legal basis for regulating the relationship between a citizen and an organization is the provisions of labor legislation and various orders issued by representatives of the Ministry of Labor.
The State Labor Inspectorate performs functions related to the compliance of all organizations with the provisions of labor legislation. If a violation occurs, the norms of the Code of Administrative Offenses apply.
Before deciding when and what sanctions are applied, you need to understand which of the employees and at what time can demand leave . An employee has the right to claim rest time after he has worked for the company for at least six months. Only continuous working time is taken into account. When there is an agreement with the management, it will be possible to go on vacation earlier than the specified time.
In subsequent periods, a schedule is formed that reflects the sequence of vacations. The company compiles it every year. It has been established that such an act must be approved by order of the organization’s management, and each citizen becomes familiar with it against signature. From now on, the schedule is considered as a mandatory type of document, and not only employees, but also management must comply with it.
It is worth considering that there are employees who have the right to use rest time as they wish. Including:
- citizens who are minors;
- female representatives before or after taking leave associated with expecting a baby;
- men whose wife is on leave due to childbirth and pregnancy;
- citizens who lived on the territory of Chernobyl.
It is stipulated that the minimum vacation value is 28 days. Only calendar days will be taken into account. It is also worth pointing out the possibility of dividing such a period into several parts. In this case, it is necessary to take into account the provisions of the law indicating that one of the parts of such rest time cannot be less than a couple of weeks.
In addition, there are groups of citizens who have the right to use an additional period for rest.
Is it necessary to compile
Necessarily.
The right to rest annually for at least 28 calendar days is guaranteed to employees by labor legislation (Article 115 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation). The vacation schedule is mandatory for both the employer and the employee and determines the sequence in which vacation days are granted. The employer approves it with the approval of the trade union (Article 123 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation). All organizations are required to draw up the document; fines and employer liability for the lack of a vacation schedule are provided for representatives of all forms of ownership.
For individual employers, the algorithm for providing rest to employees is established by agreement of the parties (Article 305 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation). Rostrud in letter No. 3683-6-1 dated December 20, 2011 recommends that an individual formalize it in writing if there are a large number of employees, although administrative legislation also establishes liability in the form of fines. Individual entrepreneurs have the same status as legal employers and are required to create a vacation schedule. The exception is those who, in accordance with the law, are classified as small businesses (Article 4 of Law N209-FZ of July 24, 2007).
Healthy:
- how to fill out and approve the vacation schedule;
- How to write an approval order.
What can you be fined for?
There are several possible grounds for imposing sanctions:
- failure to draw up a vacation schedule or approve it later than the deadline;
- failure to familiarize employees with the schedule;
- ignoring the opinion of the trade union.
Let's look at each of these violations.
Lack of vacation schedule or late approval
The employer's argument that the company employs only a few employees will not be accepted by the State Tax Inspectorate and the court. It will not be evidence that the employee did not object to the lack of a schedule and submitted annual leave applications.
If the schedule is approved in violation of the deadline (in 2021 - after December 17), then the sanctions will be the same as for its absence. It does not matter how long it is overdue: one day or six months.
Failure to familiarize employees with the schedule
Very often, the State Tax Inspectorate fines organizations and individual entrepreneurs for the fact that their employees were not familiar with the vacation schedule. At the moment, the question of whether the employer is obliged to familiarize his staff with this document is controversial. The courts did not have a single point of view:
- The first point of view is that the vacation schedule is a local regulatory act, and the employer is obliged to familiarize all its full-time employees with it (Part 2 of Article 22 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
The absence of a special column on familiarization in the schedule does not relieve the employer of the obligation to familiarize his employees with documents directly related to their work activities (JSC IC for Civil Cases of the Armed Forces of the Republic of Sakha (Yakutia) dated November 11, 2015 in case No. 33-4270/2, JSC Investigative Committee for Administrative Cases of the Chelyabinsk Regional Court dated February 24, 2014 in case No. 11-1778/2014).
- The second point of view is Art. 123 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation does not provide for the obligation of the employer to familiarize its employees with the vacation schedule.
The nuances of drawing up a vacation schedule and responsibility for non-compliance with it
“Budgetary healthcare institutions: accounting and taxation”, 2008, N 11
The nuances of drawing up a vacation schedule and responsibility for non-compliance with it
According to Part 2 of Art. 123 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, the vacation schedule is mandatory for both the employer and the employee. Representatives of the labor inspectorate may well classify the absence of a schedule under certain conditions as a violation of labor legislation. Therefore, in order to avoid troubles, the employer needs to take care of drawing up a vacation schedule in a timely manner. We hope this article will help you with this.
Sequence of vacations
The requirement to draw up a vacation schedule is mandatory for all employers. It must be approved by the employer no later than two weeks before the start of the calendar year, that is, before December 16. Its unified form N T-7 is determined by Resolution of the State Statistics Committee of Russia dated 01/05/2004 N 1 “On approval of unified forms of primary accounting documentation for recording labor and its payment.” To avoid conflict with employees, it is necessary to collect statements from them in advance in order to find out their wishes about the period and time of vacation. Then, based on this information, a vacation schedule is drawn up, taking into account all wishes. Labor legislation does not establish the obligation of employees to communicate their desire for a convenient time to grant them leave before drawing up a schedule. Therefore, if the employee did not inform the employer of his desire for a convenient vacation time before drawing up the vacation schedule, this does not give the employer grounds for refusing to grant the employee vacation at the time specified by him. It is also necessary to take into account that, by law, certain categories of employees must enjoy certain benefits and privileges.
So, according to the requirements of Art. 123 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, certain categories of employees, in cases provided for by the Labor Code of the Russian Federation and other federal laws, are granted annual paid leave at their request at a time convenient for them. The right to choose the period of time for the upcoming next vacation is enjoyed by:
- husbands while their wives are on maternity leave, regardless of the time of their continuous work in this organization (Article 123 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation);
- women before maternity leave or immediately after it, or at the end of parental leave (Article 260 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation);
— citizens under the age of 18 (Article 267 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation);
- persons working part-time (Article 286 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation). Leave for this category of citizens is granted simultaneously with leave at their main place of work;
- disabled people and war veterans, combat veterans (Federal Law of January 12, 1995 N 5-FZ “On Veterans”);
- Heroes of the Soviet Union and the Russian Federation, full holders of the Order of Glory (Article 8 of the Law of the Russian Federation N 4301-1 <1>);
- Heroes of Socialist Labor and full holders of the Order of Labor Glory (Article 6 of the Federal Law of 01/09/1997 N 5-FZ “On the provision of social guarantees to the Heroes of Socialist Labor and full holders of the Order of Labor Glory”);
- citizens who received or suffered radiation sickness and other diseases associated with radiation exposure as a result of the Chernobyl disaster or with work to eliminate its consequences, disabled people as a result of the Chernobyl disaster, participants in the liquidation of the disaster at the Chernobyl nuclear power plant (Articles 14, 15 of the Law of the Russian Federation N 1244 -1 <2>);
— persons awarded the sign “Honorary Donor of Russia” (Article 11 of the Law of the Russian Federation N 5142-1 <3>);
- citizens who received the total (accumulated) effective dose of radiation (Federal Law No. 2-FZ <4>);
- spouses of military personnel - simultaneously with the husband’s leave (Article 11 of Federal Law N 76-FZ <5>).
———————————
<1> Law of the Russian Federation of January 15, 1993 N 4301-1 “On the status of Heroes of the Soviet Union, Heroes of the Russian Federation and full holders of the Order of Glory.”
<2> Law of the Russian Federation of May 15, 1991 N 1244-1 “On the social protection of citizens exposed to radiation as a result of the disaster at the Chernobyl nuclear power plant.”
<3> Law of the Russian Federation of 06/09/1993 N 5142-1 “On the donation of blood and its components.”
<4> Federal Law of January 10, 2002 N 2-FZ “On social guarantees for citizens exposed to radiation as a result of nuclear tests at the Semipalatinsk test site.”
<5> Federal Law of May 27, 1998 N 76-FZ “On the status of military personnel.”
Note. In accordance with Art. 423 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, the above Laws are applied insofar as they do not contradict the labor legislation of the Russian Federation, which came into force on February 1, 2002.
In addition, Art. 263 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation provides for the provision of annual additional paid leave at a convenient time:
- an employee who has two or more children under the age of 14;
- an employee who has a disabled child under 18 years of age;
- a single mother raising a child under 14 years of age;
- a father raising a child under 14 years of age without a mother.
The listed categories of employees have the right to extraordinary provision of leave if this is established by the collective agreement of the organization.
Rules for scheduling vacations
When drawing up a vacation schedule, you need to make sure that it reflects all types of vacations to which employees of your organization are entitled. We are talking about both basic vacations (normal and extended duration) and additional ones. If employees have unused “remainders” from vacations for previous years, then they must be taken into account, since the vacation schedule is designed for one calendar year. In this case, the vacation schedule should indicate the actual number of vacation days that fall in a given calendar year. In the event of temporary disability of an employee, annual paid leave must be extended or postponed to another period determined by the employer taking into account the wishes of the employee. If an employee falls ill while on annual leave, his leave is extended or postponed to another period without fail, and the employee himself chooses, and the employer is obliged to take into account his wishes. When the vacation is extended by the number of days of incapacity, the employee’s vacation continues without interruption. In this case, the employee who has issued a sick leave must notify the employer about this in advance, before the end of the annual leave, and the employer issues an order to extend the leave. If the employee wishes to postpone the remainder of the vacation to another time, the employer is obliged to do so. The remainder of the leave must be used by the employee no later than 12 months after the end of the working year for which it is granted.
Every organization has employees whose going on vacation is accompanied by additional procedures; this mainly concerns financially responsible persons. Before leaving the organization for almost a whole month, the cashier or warehouse worker must transfer the valuables entrusted to him according to the act. For example, according to the schedule, the warehouseman's vacation is scheduled for July 4, 2008, which means that no later than June 21, 2008, an order must be issued to conduct an inventory at the warehouse for the temporary replacement of the financially responsible person.
The schedule is signed by the head of the personnel service and approved by the head of the organization or a person authorized by him, taking into account the opinion of the elected body of the primary trade union organization. If the organization’s employees are members of a trade union, then the vacation schedule must be agreed upon with its elected body - the trade union committee in the manner prescribed by Art. 372 Labor Code of the Russian Federation. The trade union committee must document the agreement on the schedule with an extract from the minutes of the meeting.
According to Part 3 of Art. 123 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, the employee must be notified of the start time of the vacation no later than two weeks before its start. In order to fulfill this requirement, individual organizations introduce additional column 11 “I have read the schedule. Date of. Signature" or "Notified of the start time of the vacation. Date of. Signature". The right to enter additional details into the approved unified forms of primary accounting documentation (except for forms for recording cash transactions) is granted to organizations by the Resolution of the State Statistics Committee of Russia dated March 24, 1999 “On approval of the Procedure for using unified forms of primary accounting documentation.” However, changes made must be formalized by the relevant local act of the organization. You don’t have to enter an additional column about notifying employees about the start time of vacations, but limit yourself to drawing up a familiarization sheet, which will be an appendix to the vacation schedule.
Postponement of the vacation period and correction of the schedule
As for the period for transferring the unused part of the vacation, the right to determine it is given to the employer, taking into account production interests. However, he is obliged to find out the employee’s wishes. Disagreements may arise between the employee and the administration of the institution when drawing up a vacation schedule (for example, the start time of the vacation established in the schedule does not suit the employee). In this case, the employee may ask the management of the organization or the authorized trade union body to postpone this date. The administration also has this opportunity if it does not agree with the start date of the vacation. In other words, both parties can make changes to the already approved vacation schedule.
In cases where the vacation period is postponed to another time with the consent of the employee and the head of the structural unit, changes are made to the vacation schedule with the permission of the person who approved the schedule or the person authorized by him. To do this, the employee needs to write a statement, and the manager issues an order to the institution indicating the reasons for postponing the vacation with the following content: In connection with the application (position, full name) dated (date) with a request to postpone the start of the main vacation, I order:
1. Satisfy the request for full name. on postponing the start date of the main vacation for 2008 from 09/01/2008 to 10/04/2008 without changing its duration.
2. Make appropriate changes to the vacation schedule for 2008 dated 12/09/2007.
Not only on the basis of Art. 123 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, we can conclude that drawing up a vacation schedule is the responsibility of the employer and employees. For profit tax purposes, institutions are required to draw up a vacation schedule in order to reasonably take into account as part of labor costs any accruals to employees in cash and (or) in kind, in particular such as incentive and compensation allowances related to working hours or working conditions; bonuses and one-time incentive payments; expenses stipulated by the norms of the legislation of the Russian Federation, labor agreements (contracts) and (or) collective agreements associated with the maintenance of these employees (clause 1 of Article 255 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
Let us remind you that according to Art. 252 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, expenses are recognized as justified and documented expenses incurred by the taxpayer. At the same time, documented costs, in particular, mean costs confirmed by documents drawn up in accordance with the legislation of the Russian Federation.
If a new employee is hired during the year, two options are possible: the first is to make additions to the vacation schedule, the second is not to adjust the document, because a newly hired employee has the right to vacation six months from the start of work and when planning for the next calendar year, he will already get to the schedule.
In accordance with Part 2 of Art. 123 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, the approved schedule is mandatory for both the employer and the employee. In addition, paragraph 17 of the Rules on regular and additional holidays, approved by the People's Commissariat of Labor of the USSR on April 30, 1930 N 169 (which, according to Article 423 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, are applied to the extent that does not contradict the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, which entered into force on February 1, 2002), states: that the employer has the right to require the employee to submit documents proving the impossibility of using vacation within the previously agreed upon time frame. According to Art. 124 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, the transfer of leave is possible only in case of temporary disability, as noted earlier, as well as the performance of state duties during leave, if the law provides for exemption from work (for example, military training), in other cases provided for by law and internal regulations of the institution .
Fines and liability for non-compliance with the vacation schedule
As mentioned earlier, the employer’s availability of a vacation schedule is a mandatory legal requirement regarding the procedure for granting vacations. In practice, for various reasons, vacation schedules are violated (for example, due to production needs or at the request of the employee himself). The objective side of this administrative offense is represented by actions (inactions) that violate labor legislation. In this case, the labor inspectorate may hold the organization administratively liable for violating labor laws. In accordance with Art. 5.27 of the Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation, violation of labor legislation entails the imposition of an administrative fine on officials in the amount of 5 to 50 times the minimum wage; for legal entities - from 300 to 500 times the minimum wage or administrative suspension of activities for up to 90 days.
If no changes have been made to the vacation schedule by the person responsible for its preparation, the employer can use the provisions of Chapter. 30 Labor Code of the Russian Federation. The basis for bringing to disciplinary liability is a disciplinary offense, that is, the failure or improper performance by an employee, through his fault, of the labor duties assigned to him. Taking disciplinary action is an employer's right, not an obligation. In addition, the employer retains the right to choose the measure of liability or refuse to impose a penalty (Article 192 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
If there are few employees, a vacation schedule is usually not drawn up. The employee submits an application and can often go on leave the next day. In such a situation, several violations arise at once. The employee will not be able to go on vacation the next day after submitting the application, since according to Art. 136 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation is required to receive vacation pay no later than three days before leaving. That is, the order to grant leave, as well as accounting documents, must be issued in advance. There are no separate sanctions for non-compliance or lack of schedule. However, the absence of a document, as well as late payment of vacation pay, will be regarded by the labor inspectorate as a violation of labor legislation. A possible fine for an entrepreneur is from 1000 to 5000 rubles. or suspension of activities for up to 90 days (Article 5.27 of the Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation). The labor inspectorate has the right to fine an entrepreneur for violations of labor legislation.
Recently, cases have become more frequent when an employee does not want to go on vacation, wanting to earn extra money for his own employer. The employer is also interested in this. Today, the Labor Code of the Russian Federation does not allow the employer to legally leave an employee at work during vacation and replace the mandatory part of the vacation (28 days) with monetary compensation. As a result, employers and employees resort to all sorts of tricks. For example, an employee is registered as being on vacation, but he continues to work (he receives a salary for this time as a bonus, for example), or during the employee’s vacation, a fictitious employee is hired, but in fact the same employee is working, contract agreements are drawn up with the employee, etc. Annual paid leave is provided to employees to recuperate during their work activities after certain periods. Moreover, the evolution of labor legislation shows that the duration of continuous annual leave is constantly increasing. One can understand the desire of workers to earn extra money from their vacations, including in the same organization where they constantly work, as well as the desire of employers to use the labor of employees without actually providing the latter with vacations. In this case, various methods are used, but for the most part they are a gross violation of labor laws, even if applied on the basis of mutual consent. Labor legislation provides various legal opportunities for additional work and improvement of financial situation, such as part-time work (both external and internal), part-time work, and overtime work.
N. Gridina
Journal expert
“Budgetary healthcare institutions:
accounting and taxation"
Signed for seal
28.10.2008