Hello! In this article we will talk about salary supplements.
Today you will learn:
- What categories of citizens are entitled to salary bonuses and what types of them exist;
- How do allowances differ from surcharges?
- What are incentive payments and much more.
Everyone knows that even if a person is officially employed, this is not a guarantee that he will be given all the required additional payments. Therefore, today we will figure out what the employer is obliged to pay extra for and what additional payments and allowances employees have every right to.
Content
- Components of remuneration
- The legislator's word
- Allowances and surcharges: the difference between concepts
- Types of salary supplements
- Bonuses paid regardless of the will of the employer
- Additional payments to wages
- Who can count on bonuses and additional payments?
- An example of calculating allowances and surcharges
- Additional payments considered controversial
- Documentation that sets out the payment procedure
- Under what conditions are payments made?
- Employer's responsibility for payments
The legislator's word
Remuneration is a kind of instrument, thanks to which the labor costs of all employees are compensated. The legislation provides for measures that are designed not only to protect the rights of workers, but also to establish a salary level that will correspond to real labor costs.
So, the law establishes:
- Based on Article 133 of the Labor Code, any employer does not have the right to set employees a salary that is lower than the minimum wage. Its size is determined by federal and regional legislation;
- Article 143 of the same Code says that the salary is set taking into account the tariff structure, or the tariff schedule, or categories;
- If the working conditions at an enterprise or organization deviate from the standard ones, then employees have the right to compensation for all additional labor costs, as specified in Articles 146 - 154 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation;
- The employer has the right to set the amount of incentive payments;
- The Labor Code obliges the employer to calculate and pay wages.
Design methods
- If the payments are not permanent, but are one-time, management simply issues an order for additional payment, indicating the amount. The employee can familiarize himself with the order and receive the due amount along with his salary.
- Sometimes the conditions for additional payments are included in the employment contract, where the conditions for receiving them are also indicated. Subsequently, the employer will not be able to change the amount of payments.
- The conditions for receiving additional payments are specified in great detail in collective agreements. It is referred to in the employment contract.
- All conditions for receiving payments are prescribed in a local act, for example, “Regulations on allowances and additional payments.”
- The latter are accepted after agreement with the employee representative (trade union organization).
That is, the amount of compensation payments under local acts can be changed upward, in favor of the employee.
If there is no such representative, the manager makes the decision independently. At the same time, there is a lower limit for the amount of additional payments and bonuses of a compensatory nature (for difficult and especially difficult working conditions and for work with a character deviating from the normal one).
This means that the employer does not have the right to charge additional payments less than the norm .
There are two lists compiled at the legislative level that determine the standards for allowances. These are lists of jobs with difficult (dangerous, harmful) and especially difficult (dangerous, harmful) working conditions. They include more than 200 items.
Incentive allowances can be reflected both in local acts and in collective agreements.
They must be reflected in the text of the employment contract (or mentioned with reference to a local act), since they are part of the salary.
The amount of payments can be fixed, indicating the exact amount, or set as a percentage of the salary or tariff rate. In cases where the employee has retained his average earnings (annual leave, business trips, sick leave), these types of payments are not suspended.
If an employee needs to accrue additional payments for several reasons, and their amounts are determined as a percentage of the salary, then the salary in its pure form is taken as the basis, without taking into account the already accrued allowance.
How to get maternity leave if you don’t work - a detailed guide! Correct calculation of sick leave is very important. Our detailed article was written by professionals specifically for this topic.
How to resolve the issue of sick leave pay after your dismissal - read here.
Allowances and surcharges: the difference between concepts
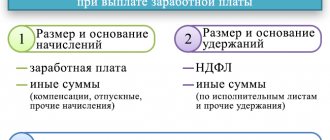
In order to motivate employees, employers can pay not only the wages required by law, but also funds in the form of bonuses or other material incentives. And the state, in turn, obliges managers to pay additional payments when certain cases occur.
Now let's look at these points in more detail. What is a surcharge?
An additional payment is a type of payment that is in the nature of compensation, as it is assigned in the case when an employee worked on holidays, combined his work with the responsibilities of a colleague, that is, performed an increased amount of work.
An allowance is a type of payment that is intended to stimulate an employee so that he wants to further grow and develop in his profession. Examples include bonuses for long continuous work experience, length of service, academic degrees, and so on.
As for the general features, there is one: both payments increase the employee’s remuneration.
And their differences are as follows:
- Additional payments are mandatory, allowances are not;
- An additional payment is compensation, and an allowance is an incentive payment;
- The bonus emphasizes the importance of the employee, and the additional payment is designed to compensate for difficult working conditions.
Bonuses are paid at the initiative and desire of the manager!
Special working conditions - what are they?
In order not to violate the law, managers must clearly understand who works in the enterprise under special conditions and who works under normal conditions. After all, higher pay is provided for the former.
- Operation under normal conditions has the following characteristics:
- working day duration – 8 hours;
- Day shift;
- working week – 40 hours;
- weather conditions are normal;
- work at your place of residence, and not in a remote area; full compliance with sanitary standards.
It turns out that failure to comply with these requirements makes working conditions special.
. True, receiving a higher salary on an ongoing basis is possible if such factors operate regularly. That is, the work week is longer than normal, as is the length of the shift; the employee can work the night shift.
If we rely specifically on labor legislation, we can understand that special conditions are accompanied by the emergence of some unfavorable factors. These may be working conditions at the enterprise or climatic conditions. In fact, such employees work in harmful, dangerous and abnormal conditions. In Art. 149 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation also contains a list of conditions that are not considered normal, but are only temporary in nature.
These include:
- -work on weekends and holidays;
- -increasing the length of the working day (for example, work needs to be completed by a certain deadline, which is why the employee has to stay late);
- -work on the night shift;
- -internal part-time work.
In this case, we are not talking about increasing the rate. A person usually receives additional payment for additional functionality or hours worked.
Types of salary supplements
For clarity, we present this information in the form of a table.
Table 1. Types and characteristics of allowances.
| No. | Type of allowance | a brief description of |
| 1 | For providing mentoring | They pay “old-timers” of enterprises for training young specialists |
| 2 | For high professional qualifications | Only highly qualified specialists are paid |
| 3 | Personal allowances | Paid in the event that a valuable employee needs to be kept at his place of work, but it is not possible to promote him in position or increase his salary |
| 4 | For having an academic degree or title | Employees who have defended their master's and doctoral dissertations, etc. |
| 5 | If you have access to state secrets | Employees of individual structures, diplomatic services |
| 6 | For knowledge of foreign languages | Often found in enterprises that produce products for export |
Such payments are established at any time, as a measure to encourage any achievements of employees (there are companies that make such payments for participation in corporate sports competitions, for those who do not go on sick leave for a long period of time, etc.).
Before canceling such payments, employees must be warned about this!
Next, we will consider the types of allowances that are mandatory.
Different types of personal allowances
The type of allowance can be determined by various factors:
- Basis for accrual - the employer has the right to assign a personal allowance:
- for experience;
- for skill level;
- for a certain intensity of work;
- for professional excellence;
- for performing tasks of special importance and/or urgency;
- for “bonus” skills and abilities, for example, knowledge of a foreign language;
- for an academic degree in a specialized field;
- for work under conditions of official secrecy, etc.
- Duration of validity of the provisions on the allowance - these payments can be established either permanently or temporarily:
- for a month;
- per quarter;
- for a year;
- indefinitely.
- The amount of the premium can be determined in different ways:
- a fixed amount is fixed in local documents;
- the amount of the bonus is calculated in a certain way, for example, as a percentage of the salary or average salary;
- determination of the size by the labor participation rate: the monthly amount allocated for allowances will be distributed differently within the group of workers.
NOTE! Despite the fact that the amount for personal allowances is not limited by law, they should not be set in an amount exceeding the monthly salary. Large premiums are difficult to justify in court in the event of any disputes; there is a high probability that they will be recognized as part of mandatory payments. Practice shows that the maximum amount of a personal bonus should not be more than 50% of the salary, and the optimal amount is 10-20%.
Bonuses paid regardless of the will of the employer
As Article 149 of the Labor Code says, the employer is obliged to pay for:
- For working conditions that are harmful, dangerous or difficult;
- For work in harsh climate conditions (if an employee spends the entire working day on the street, he has the right to receive this payment);
- For work at night (if the schedule is not shift);
- If the employee performs work that requires a high level of knowledge and skills;
- If an employee combines several positions at once.
The above list is the main one; there may be additional items, but they are already determined by the employment contract. But there is a nuance that needs to be paid attention to while the employment contract has not yet been signed, then it will be very difficult to appeal: the employer can indicate in the employment contract a list of works that the employee is obliged to perform. In this situation, the employee cannot demand additional payment.
The feasibility of assigning personal allowances
In what cases may an employer need a personal allowance mechanism? When might it be necessary to make remuneration special for a specific employee or group of employees? The following options are possible:
- the employer wants to highlight the successes of a particular employee;
- there is a desire to reward an employee for having outstanding or unique knowledge and skills;
- It is undesirable to change the existing system of rates and salaries, but at the same time there is a need for additional incentives for workers.
Question: When calculating vacation pay, should I take into account the bonus paid to the employee by March 8, the personal bonus to the salary and the one-time charge for mentoring? View answer
Additional payments to wages
Additional payments, as well as allowances, play an important role in the personnel remuneration system. We will also consider their types in table form.
Table 2. Types and characteristics of surcharges.
| No. | Type of surcharge | a brief description of |
| 1 | For an increased production rate | They are paid most often to workers who are paid on piecework. Mandatory condition: high quality of manufactured products |
| 2 | One-time additional payments | The so-called “lifting” for young professionals |
| 3 | For traveling or rotational work | Paid to those who work on a “shift” basis |
| 4 | For overtime work | If required by production needs (there is an order from the manager and written consent of the employee). If the employee carried out such activities on his own initiative, there will be no additional payment |
| 5 | For work at night | Night time is considered to be the period from 10 pm to 6 am. |
| 6 | For work of a harmful or dangerous nature | Paid to miners, emergency workers, nuclear power plant workers, etc. |
| 7 | For going to work on holidays and weekends | In this case, payment is made in double amount; exit is carried out on the basis of an order from the manager with the written consent of the employee. The additional payment will be calculated depending on the form of remuneration |
| 8 | For combining professions | Example: paid for performing the duties of a janitor and plumber in an institution or enterprise |
| 9 | For transportation of dangerous goods | It is usually paid in the railway transport, road transport, etc. industries. |
| 10 | Regional coefficient | Depends on the region of the country, as well as on natural and climatic working conditions |
How is an allowance different from a surcharge?
There is no clear position on the issue of distinguishing between the concepts of “surcharge” and “addition”. Russian legislation does not regulate this issue and does not distinguish these terms in any way. Thus, when designating this payment, you need to use exactly the name that is found in local regulations or is more often found in practice and is applicable to a specific case.
But in some literature these concepts are differentiated as follows: the bonus is stimulating in nature, and the additional payment is compensatory for working in difficult conditions.
Who can count on bonuses and additional payments?
Not all categories of workers can count on the establishment of bonuses and additional payments.
These payments are not eligible:
- For those who work under a civil contract;
- Workers under a contract;
- Those with whom an agency agreement has been concluded.
This is explained by the fact that legal relations with such persons are regulated by the Civil Code, and not the Labor Code.
Those citizens who are hired on the basis of employment contracts, even those concluded for a certain period or who are part-time workers, have the right to receive all the specified monetary payments.
Payment procedure and rules
Who is entitled to payments, that is, the subject composition, the employer determines independently (in the case of compensation payments - in accordance with the requirements of current legislation).
Some standard grounds and payment conditions for bonuses can be identified:
- Terms (payments can be indefinite, periodic, one-time).
- Conditions for their payment (fulfillment of sales plan, budget, sales volume).
- Requirements for the employee (no disciplinary sanctions, minimum period of work in the company).
- Requirements for the preparation of supporting documentation (supporting documents, approval process, source of financing, forms of orders and instructions).
Payments to certain categories of workers (for example, those working in the regions of the Far North and localities equivalent to them, employees of educational and medical institutions, etc.) are regulated by separate chapters of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, federal laws, laws of constituent entities of the Federation and other legislative acts.
In this case, the procedure established by the employer cannot worsen the employee’s position in comparison with that established by law.
An example of calculating allowances and surcharges
In order for the understanding to become as complete as possible, let us consider the payment of allowances and additional payments using a specific example .
In a kindergarten, an employee is both a laborer and an electrician. It turns out that he combines 2 positions. As a general worker, his salary is 12,000 rubles. For the duties of an electrician, the management pays him an additional amount that does not depend on the salary - 10,000 rubles (as stated in his employment contract). Based on the results of his work, the amount of his bonus is 4,000 rubles.
The monthly payment calculation will look like this: 12000+10000+4000=26000 rubles. In our example, the allowance and bonus are accrued not as a percentage, but as a fixed amount. But these indicators can also be calculated depending on the salary, that is, as a percentage.
Incentive payments
All types of incentive payments are made from the enterprise's funds received as a result of its activities in the form of income.
- On the one hand, the more efficient the operation of the enterprise, the more funds can be allocated and distributed among employees in the form of incentives.
- On the other hand, the more an employer encourages (motivates) its employees, the more interested they will be in the success of the enterprise.
That is why payments are called incentive payments. These include:
- regular bonuses, when the salary distribution system is based on bonuses, and their size is determined as a percentage of the salary (or tariff rate). They participate in determining average earnings;
- one-time individual bonuses that reward an employee for some achievement. Such bonuses are paid or not at the discretion of the manager and are not taken into account when calculating average earnings;
- remunerations related to the main wage payment system.
- thirteenth salary;
- Long service benefits, calculated depending on salary, are paid once a month, yearly, or quarterly;
- incentive bonuses and additional payments established by law. These are bonuses for titles, ranks, degrees, classes;
- bonuses and additional payments paid at the discretion of management for professionalism and labor achievements.
Incentive payments to social workers:
- To teachers. According to the new point system. They depend on the progress of students and extracurricular activities (preparing students for various olympiads, competitions and competitions). The teacher has evaluation sheets that reflect the students’ performance, work results, and remuneration. Such sheets serve as the basis for the calculation of incentive bonuses when distributing payments from the general fund.
- Librarians. Allowances for degrees and awards, or additional payments for working with readers, for issuing subscriptions, building the library fund and its efficiency.
- For cultural workers. Regular and one-time additional payments depend on receipt of bonuses, success, achievements and length of service.
- For preschool employees. 60% of the institution’s bonus fund is supposed to be distributed among educators and teachers, the remaining 40% is distributed among the rest of its employees.
- To health workers. Doctors and mid-level medical personnel and junior personnel of ambulance teams. The size of payments depends on the volume of services for the population and their quality and can reach up to 80% of the salary. Recently, incentives have been paid to health workers who are willing to move to rural areas.
Not all healthcare workers are entitled to incentive payments . For example, the director, if he does not practice medicine at the same time, cannot receive them.
Also, employees of medical institutions who receive an allowance for high-tech care, and medical staff who receive subsidies as part of the national project “Health” do not receive additional payments.
For example:
Vasiliev V.V. worked as an obstetrician-gynecologist for 11 years. The management gave him an incentive bonus in the amount of 10% of his salary, which amounted to 7,000 rubles. In 2007, Vasiliev became a participant in the national project “Health,” for which he received 3,000 rubles in addition to his salary. From this time on, the incentive bonus is no longer paid.
Additional payments considered controversial
In this part of the conversation we will pay attention to budgetary enterprises and institutions. It is no secret that their employees receive their salaries from budget funds.
In this regard, the Federal Service for Financial and Budgetary Supervision has questions regarding several types of additional payments, namely:
- Additional payment for working with computer and office equipment;
- Additional payment for combining positions.
When certain control measures were carried out, Rosfinnadzor employees considered that before assigning these types of additional payments, it was necessary to conduct a full certification of workplaces, otherwise their payment would be unlawful.
Let us note that often enterprises and institutions do not agree with this position, and when going to court, judges take their side.
Wages calculated at tariff rates, piece rates, official salaries Payment of bonuses to workers, specialists, employees for improving business results.
Encouraging the winners of socialist competition Additional payments and bonuses for professional excellence, high achievements in work, performing particularly important work, combining professions (positions), etc. Other payments (payments based on regional coefficients, vacation pay, etc.) [p.129] For the purposes of To stimulate the professional skills of workers and strengthen their material interest and responsibility for the quality of products (works) and the fulfillment of production tasks, it is planned to introduce differentiated bonuses for professional skills for workers of the III category in the amount of the tariff rate. Bonuses can be paid for mastering new professions and performing related functions. [p.192] Premiums for professional skills are established specifically based on the results of certification of workers in accordance with the Regulations on Professional Skills in effect at the enterprise. [p.18]
Employees who perform at the same enterprise, along with their main work stipulated by an employment agreement (contract), additional work in another profession (position) or the duties of a temporarily absent employee without release from their main job, are paid additionally for combining professions (positions) or performing the duties of a temporarily absent employee (Article 151 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation). Additional payments for combining professions (positions) can be established for the employee along with an allowance for professional skill or high qualifications. [p.233]
Within each form of remuneration, different remuneration systems may be used. Thus, there are simple time-based and time-bonus wage systems. The latter provides for the addition of bonuses for production results, bonuses for professional skills, combination of professions and positions, etc. to the basic salary for time worked. [p.90]
Additional payments and allowances for professional skills, combination of professions [p.115]
These bonuses are not paid for the month in which cases of defects or deterioration in product quality are detected. In case of production of low-quality products, failure to fulfill planned (standardized) tasks, established norms of labor costs, allowances for professional skills are completely canceled (11, sub-clause a, clause 8). [p.630]
The practice of leading enterprises shows that it is best to consistently increase premiums for professional excellence in steps of 4% (55, 1987, N7Q 1, p. 76). [p.631]
Workers who have monthly salaries in exchange for tariff rates should not be given an additional bonus for professional skills (55, 1987, No. 1, p. 77). [p.631]
To tariff rates, differentiated bonuses are introduced for the professional skills of workers for workers of the III category - up to 12%, IV category - up to 16%, V category - up to 20% and VI category up to 24% of the corresponding tariff rate. Establishing bonuses for skill is one of the elements of perfect-[p.122]
During the transition to new conditions of remuneration, incentives for highly qualified labor are strengthened, compensation for work in unfavorable conditions is determined, which motivates workers to produce high-quality products. The use of bonuses for workers for professional skills, including supervisory workers, is of great importance. For workers in the main production, bonuses for professional skills are established primarily for the high quality of products, strict adherence to technological discipline, systematic fulfillment of planned tasks and production standards. Bonuses are established by saving the wage fund in the amount of up to 12% of the tariff rate for workers of the III category and up to 24% for workers of the VI and subsequent categories. [p.116]
It is important to note that the mechanism of financial liability for poor quality of work is being significantly strengthened. If the quality of work deteriorates, or systematic violations of technological discipline occur, not only will additional payments and bonuses for professional skill and excellence be cancelled, but the qualification category may also be lowered. Such a measure should significantly expand the arsenal of incentives for the quality of labor and products. [p.135]
Allowances for professional excellence. In order to stimulate the improvement of the professional skills of workers and strengthen their material interest and responsibility for the quality of products (works) and the fulfillment of production tasks, enterprise managers, in agreement with the trade union committee, have been given the right to introduce differentiated bonuses to tariff rates for professional skills for 3rd category workers in up to 12%, 4th category - up to 16, 5th category - up to 20, 6th and higher categories - up to 24% of the corresponding tariff rate. The issue of establishing premiums for professional skills is decided directly by the enterprise in relation to the organization of work, the workplace and the role of the employee in the production process. Criteria for assessing professional skills can be stable provision of high quality of products and work performed, strict adherence to technological discipline, systematic exceeding of planned targets and production standards, performance of work of particular complexity, mastering new professions and related functions. [p.68]
In order to increase responsibility for product quality, it is stipulated that in those months when a worker commits a defect, he is not paid bonuses for professional skills. In the case of systematic production of low-quality products and failure to meet production targets or labor cost standards, allowances are canceled completely. [p.69]
Allowances for professional skill are of an individual nature and therefore are not included in the calculation of piece rates and in the overall team earnings, but are paid personally to those workers to whom they are assigned. [p.69]
For workers employed in particularly critical work for at least 1 year, gradually increasing (taking into account continuous work experience) bonuses for professional skills are introduced in the amount of 4, 8, 12% of the tariff rate. Moreover, premiums are added to the tariff rate taking into account these additional payments. [p.256]
Additional payments for work at night and overtime, for work on holidays, up to average earnings, for team leadership, allowances for professional skill, for work with a personal brand (when individual team members have the right to work with a personal brand), payment for time performance of state or public duties and others are carried out in the prescribed manner and are not included in the team earnings. The award for the title of Best in Profession, based on the results of socialist competition, for rationalization and invention, and other one-time individual awards are also not included in the total earnings of the brigade. [p.107]
Additional positions are being introduced for specialists and managers. Thus, instead of two engineering positions (engineer and senior engineer), four are being introduced with greater differentiation between minimum and maximum salaries for beginners and more qualified specialists. In addition to tariffs and salaries, a system of surcharges is being widely developed; enterprises independently determine the specific amounts of surcharges depending on the severity and harmfulness of working conditions at specific workplaces based on the results of their certification. Premiums for professional skills are also being introduced. These bonuses will apply only to those workers who ensure high quality products, master new professions and perform related functions. If workers are married, these bonuses are cancelled. [p.15]
Allowances for professional skills are introduced by the administration of the enterprise with the participation of the foreman and are formalized by order or directive. [p.425]
Allowances for professional excellence. To increase the material interest of workers in improving their professional skills, bonuses are established in addition to their earnings, which can be introduced at enterprises and production associations. [p.209]
Allowances for professional excellence are paid to skilled workers who have worked at the enterprise for at least a year, and are increased no more than once a year. [p.210]
In case of production of low-quality products, failure to fulfill planned (standardized) tasks, or established norms of labor costs, allowances for professional skills are canceled completely. [p.127]
In most cases, remuneration is made according to a time-bonus system. Due to the increasing complexity of production and the increasing labor intensity of service functions (mainly technical), there is an increase in the number of support and service workers, and their wage fund increases to an even greater extent due to the introduction of various kinds of allowances to the basic tariffs (increasing the maximum size of bonuses, allowances for professional skills, etc.). The presence of this large, sluggish wage fund greatly reduces the efficiency achieved in the main production. [p.252]
In connection with the equipping of enterprises with highly mechanized and increasingly productive equipment and machines, the complication of economic relations and increased responsibility for work results, the requirements for the professional skills and qualifications of workers are increasing. Taking into account the experience of the manufacturing industries in logistics, it was allowed to apply bonuses for the professional skills of workers. They were paid, as a rule, with high quality of work, systematic fulfillment of production standards and standardized tasks, strict adherence to technological, production and labor discipline, mastery and performance of work in related operations, professions and specialties. [p.90]
The need for bonuses for professional skills was determined by the insufficient flexibility of tariff rates in relation to specific conditions for stimulating labor. Thus, the step between the sizes of tariff rates for related qualification categories is equal to 12-20% of the tariff rate. However, if, under specific conditions, a transfer to a higher tariff rate is not justified and it is advisable to set a salary level intermediate between two tariff rates, then you can use an increase of 4, 8 and 12% of the rate. The allowance is also used in cases where, in accordance with the Unified Tariff and Qualification Reference Book (UTKS), a higher category of work is not provided for or they are already charged at the maximum sixth category. [p.90]
The material and technical support system did not set conditions for the payment of bonuses for professional skills that were previously used in manufacturing industries, such as its strictly phased establishment for a specific employee (4, 8, 12% of the tariff rate); continuous work experience at the enterprise; increase in the size of the bonus no more than once once a year, work at this enterprise for at least one year. [p.90]
Additional payments and allowances for professional skills, combination of professions and other incentive payments [p.61]
When opening certificate cards for workers and calculating their wages, it is advisable for the accounting department to systematically check whether the application of the established tariff rates corresponds to the assigned worker qualification categories and the current conditions of remuneration at the enterprise, whether bonuses for professional skills, additional payments for working conditions, combination of professions are legally established etc., since they serve as the basis for correct payment of labor and economical spending of the wage fund. [p.80]
At enterprises operating in new economic conditions, bonuses for professional skills amount to workers of the 3rd category - up to 12%, 4th category - up to 16%, 5th category - up to 20%, 6th category - up to 24% tariff rate. [p.293]
Improving self-supporting relations is closely connected with the further development of the initiative of work collectives, the creation of a system of motives and incentives that encourage all workers to have a creative attitude towards work and the most efficient use of production resources. Collective contracting and other effective forms of organizing and stimulating labor are most consistent with the new economic mechanism. The brigade form of organizing and stimulating labor becomes the main one. Production teams, as a rule, switch to cost accounting. Teams are given greater rights; they themselves determine the size of bonuses and earnings, taking into account the real contribution of each team member to the overall results of work, establish bonuses and additional payments for professional skills and combining professions, and recommend changing the employee’s rank in the prescribed manner. [p.333]
Hourly wage rates for workers engaged in heavy and hazardous work, as well as in steeplejack work with hazardous working conditions, are increased by 12%, and for work with particularly difficult and hazardous working conditions - up to 24%. For certain professions of workers of the VI category, engaged in the management of powerful and particularly complex machines and mechanisms, their repair and maintenance, hourly tariff rates can be increased to 140 kopecks. An important element of the wage organization system is additions to tariff rates for professional skills up to 12% - for III category up to 16% - for IV up to 20% - for V up to 24% - for VI. In case of failure to complete tasks and low quality of work, allowances are canceled. In order to ensure the effective development of the national economy, increasing coefficients in the amount of 1.15-2.0 have been introduced to wages in the regions of the Far North, Far East and areas equivalent to these regions. [p.267]
ADDITIONAL SALARY - various payments in addition to the basic salary, bonuses, additional payments for work at progressive rates, for deviations from normal working conditions, payment for full-day and intra-shift downtime, additional payments to foremen, allowances for professional skill, payments according to regional coefficients, northern allowances and etc. In recent years, in the Russian Federation, compensation payments introduced to public sector employees in connection with inflation processes have been included as components of wages. [p.76]
The situation is no better with the differentiation of workers' pay. On the one hand, the proportion of workers receiving bonuses for professional skills, additional payments for combining professions, functions, etc. has been sharply reduced. On the other hand, the possibility of establishing out-of-grade tariff rates has not actually been used. Given the acute need in mechanical engineering to secure highly qualified personnel, the number of workers assigned to the VII and VIII categories is about 0.1%. There is a high proportion of temporary workers whose qualification level is lowered by 1 - 2 points. [p.151]
The Decree of the Central Committee of the CPSU, the Council of Ministers of the USSR and the All-Russian Central Council of Trade Unions of September 17, 1986 provided for differentiated additional payments to tariff rates for unfavorable conditions and labor intensity, and bonuses for professional skills. [p.66]
Allowances for professional skills were introduced in accordance with the post. The Central Committee of the CPSU, the Council of Ministers of the USSR and the All-Russian Central Council of Trade Unions dated September 17, 1986 No. 1115 (SP USSR. 1986. No. 34. Art. 179) in order to stimulate the improvement of the professional skills of workers and strengthen their material interest and responsibility for the quality of products (works) ) and fulfillment of production tasks. [p.148]
Production associations (enterprises) are given the right to pay, at the expense of savings in the wage fund obtained in comparison with the planned wage fund, bonuses for professional skills to qualified workers engaged in particularly responsible work. The allowances are 4, 8 and 12% of the tariff rate of the assigned category within the inter-category difference. The following are established for their payment: [p.424]
Allowance for professional excellence. In order to accelerate the growth of labor productivity and reduce staff turnover, stimulate the improvement of the professional skills of workers, strengthen their material interest and responsibility for the quality of products (work) and the fulfillment of production tasks, the resolution of the Central Committee of the CPSU, the Council of Ministers of the USSR and the All-Russian Central Council of Trade Unions On Improvement [p.126]
Documentation that sets out the payment procedure
- Collective agreement;
- Regulations on remuneration;
- Regulations on bonus payments to employees;
- Employment contract (may contain a reference to a collective agreement);
- Staffing table;
- Order from the manager (if the payment is a one-time payment and not permanent).
Under what conditions are payments made?
Any allowances and additional payments must first of all be contained in the pay slip of each employee.
There are a number of rules that the head of an enterprise or institution must adhere to:
- Each employee must have a task, for the successful solution of which he receives encouragement. But the task must first of all be solvable, and not a dead end. Simply put, any employee should have the opportunity to achieve good results;
- If we are talking about a bonus, then the amount should arouse interest, that is, be significant. It is unlikely that an employee will refuse smoking breaks for a bonus of 200 rubles;
- Employees should be aware that it is possible to receive certain incentives and additional payments. It is best to notify about this by drawing up an annex to the employment contract. Each newly arrived employee will be immediately familiar with this.
If the manager is ready to encourage his employees and pay them extra for something, then these recommendations will be quite feasible.
Employer's responsibility for payments
The employer is not required to report to employees for the amount of incentive payments. If, due to a difficult economic situation, crisis, or other circumstances, the bonus portion of wages is cancelled, a written warning to employees is sufficient.
The only violation here will be that the employer ignored the procedure for warning employees, nothing more.
In general, if you properly motivate employees, you can achieve truly high results and performance. For this purpose, the employer should use incentive measures that stimulate payments. This will not only increase labor productivity, but will also have the best impact on product quality.
Supplement for professional skills to salary
Sometimes employers consider it necessary to pay their employees additional funds in addition to their salaries in order to reward them for good work or to compensate them in some way. The very name of the bonus indicates that it is not assigned to everyone, but only to specific employees based on certain indicators.
Let us clarify on what basis a personal allowance can be established, which categories of workers are not entitled to it at all, how to properly formalize it, and, if necessary, cancel it.
The essence of a personal allowance
An employee can receive not only a “bare” salary, but also additional payments, including those assigned in addition to wages.
The Labor Code does not have a precise definition of a bonus. The bonus included in the salary, reflected in the employment contract or additional agreement to it, is common to all personnel when certain conditions occur, for example, for work in certain climatic zones, for shift work, etc. Such bonuses are not considered personal.
If the employer is not obliged to assign a bonus, but he does it for individual employees on an individual basis, reflecting the conditions of the appointment in a special Regulation, collective agreement or other local act, such payment will be a personal bonus . The right to assign such payments by the employer is granted by Art. 135 Labor Code of the Russian Federation.
The feasibility of assigning personal allowances
In what cases may an employer need a personal allowance mechanism? When might it be necessary to make remuneration special for a specific employee or group of employees? The following options are possible:
- the employer wants to highlight the successes of a particular employee;
- there is a desire to reward an employee for having outstanding or unique knowledge and skills;
- It is undesirable to change the existing system of rates and salaries, but at the same time there is a need for additional incentives for workers.
Different types of personal allowances
The type of allowance can be determined by various factors:
- Basis for accrual - the employer has the right to assign a personal allowance:
- for experience;
- for skill level;
- for a certain intensity of work;
- for professional excellence;
- for performing tasks of special importance and/or urgency;
- for “bonus” skills and abilities, for example, knowledge of a foreign language;
- for an academic degree in a specialized field;
- for work under conditions of official secrecy, etc.
- Duration of validity of the provisions on the allowance - these payments can be established either permanently or temporarily:
- for a month;
- per quarter;
- for a year;
- indefinitely.
- The amount of the premium can be determined in different ways:
- a fixed amount is fixed in local documents;
- the amount of the bonus is calculated in a certain way, for example, as a percentage of the salary or average salary;
- determination of the size by the labor participation rate: the monthly amount allocated for allowances will be distributed differently within the group of workers.
NOTE! Despite the fact that the amount for personal allowances is not limited by law, they should not be set in an amount exceeding the monthly salary.
Large premiums are difficult to justify in court in the event of any disputes; there is a high probability that they will be recognized as part of mandatory payments.
Practice shows that the maximum amount of a personal bonus should not be more than 50% of the salary, and the optimal amount is 10-20%.
Who gets a personal allowance and who doesn’t?
Additional personal benefits can be assigned to any full-time employee of the organization, since they are added to his salary, often calculated as a percentage of his salary. At the same time, the registration of an employee on the staff does not have much significance; the following may qualify for a personal allowance:
- an employee who has entered into a regular employment contract;
- "conscript";
- part-time worker.
It is not customary to assign personal bonus payments to the following categories of workers:
- freelancers;
- workers working under a contract;
- who have concluded civil contracts.
Registration of a personal allowance
The employer is not obliged to include the terms of the personal bonus in the employment contract, since this is an incentive payment.
But since this is still part of the remuneration, it must be documented.
To do this, you need to regulate the personal bonus in a collective agreement or in the Regulations on remuneration and be sure to refer to this document in the text of the employment agreement (Article 57 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
IMPORTANT! If the employer does not include provisions on the bonus in local documents, paying it without registration, he is not threatened with legislative liability. The only thing that can serve as a disadvantage for the employer in such a situation is that unreasonable payments cannot be attributed to expenses that reduce the tax base.
Petition and order for personal allowance
How else can you arrange the payment of a personal allowance, if not through a separate document? This may be necessary when the nature of the payments is not systematic, but one-time or calculated for a certain period.
In this case, it is advisable to draw up a memo (petition) from immediate management to a higher one who has the authority to assign a bonus. This could be the general director, financial director, head of the personnel department, chief accountant, etc.
In the text of the note, in addition to the mandatory details of business documents, you should indicate:
- arguments justifying the assignment of a bonus to a specific employee or their group;
- the expected amount of additional payment;
- at what expense is the premium supposed to be assigned (for example, from the wage fund or by increasing profits from sales, etc.);
- validity period of additional payments.
Read more: Appointment of Deputy General Director of LLC
ATTENTION! It is not customary to formalize permanent allowances using memos. After the expiration of the specified period, you can again apply for a supplement. With this kind of document you can request the appointment, increase, decrease, extension or cancellation of a personal payment.
The compiled memo, signed by management, will become the basis for preparing an order for the calculation of the allowance. The execution of this order can be in any form.
It is important to correctly motivate the appointment of additional payments, since their feasibility from a production or economic point of view is a guarantee that these costs are included in the cost of production, which is very strictly checked by tax authorities.
After issuing an order to assign an allowance, the employee must be familiar with it, which is confirmed by a personal visa (this procedure is common for any orders).
Cancellation of personal allowance
Like setting, canceling or changing a personal allowance occurs by order of management.
ATTENTION! The employer is not obliged to inform staff about the reasons for assigning personal allowances and their amounts, but if he plans to stop these payments, it is better to warn about this in advance.
Important nuances of personal increases
It is important to regulate all financial issues correctly and take into account all legislative subtleties. When assigning personal increases, the employer must take into account certain circumstances:
- A correctly executed personal allowance in accounting is treated as “labor expenses”.
- The bonus is calculated simultaneously with the salary.
- This payment is included in the calculation of average earnings necessary for calculating, for example, vacation pay (Resolution of the Government of the Russian Federation No. 922 of December 24, 2007, as amended on October 15, 2014).
- If the deadline specified in the bonus regulations is violated, when the payment is unreasonably and unexpectedly terminated earlier for the employee, the employee has the right to demand additional accrual of the bonus and payment of late fees.
- If the head of a structural unit does not send a memo on time, personal payments will be stopped, because this document is the basis for issuing an order to accrue funds.
- If an employee receiving a personal allowance is transferred to another position, the right to the allowance is not retained unless it is provided for by the provisions of the new position.
- A change in the leadership of an organization may lead to changes in the provisions on personal allowances.
- A personal allowance must be reflected in the staffing table, indicating the numbers of orders for its accrual.
8.1.1.1. Allowances for workers for professional skills are established with the aim of stimulating the improvement of their professional skills and increasing material interest and responsibility for the fulfillment of production tasks.
8.1.1.2. Allowances for professional skills are of an individual nature , associated with the qualifications and personal business qualities of the worker, are established by qualified workers, whose professions are charged by category, and are designed to stimulate growth in labor productivity, increase production efficiency and quality of work.
8.1.1.3. who are not paid according to occupational categories, bonuses for professional skills are not established.
8.1.1.4. In accordance with paragraph 2 of the General Provisions of the ETKS, approved by Resolution of the Ministry of Labor and Social Protection dated March 30, 2007 No. 34, labor starting from the 3rd category is considered qualified
Allowances for professional skills are established for workers who are assigned a tariff category of at least third.
8.1.1.5. Indicators (criteria) for assessing professional skills include:
— stable, high-quality performance of work for at least 3 months (no defects in work, achievement of a high level of quality, no accidents or failures in serviced equipment due to the fault of personnel, etc.);
— availability of permits necessary for independent work;
— systematic achievement of higher indicators in labor compared to the average indicators of workers of the same profession (the degree of labor contribution to overall results, fulfillment of given load schedules and operating modes of equipment, fulfillment and overfulfillment of standardized tasks, etc.);
— periodic performance of work of a higher category than assigned, work on complex equipment;
- performing related operations or combining professions (the ability to work in several professions (specialties), confirmed by past work experience or documents on the mastery of these professions (specialties)), expanding the service area, if additional payments are not established for workers for these indicators;
— the behavior (ability) of an employee in extreme, critical situations to make an effective decision to prevent serious production failures and possible accidents, etc.;
— the ability to share existing work experience and work skills with other employees of the organization;
Read more: The second form of security clearance for traveling abroad
— absence of overexpenditure of used material assets against established standards, saving of material and technical resources, optimal expenditure of funds;
— advanced techniques and methods of work that are in demand at the enterprise, participation in rationalization work, revision of existing and implementation of more progressive labor standards;
— confirmation of a high work culture and the desire to improve and spread it (strict adherence to production and labor discipline).
8.1.1.6.
Specific criteria for professional excellence for each specific profession are established on the basis of tariff and qualification requirements, work instructions, documents on the technical operation of electrical and heat control installations, equipment, main structures of power plants, electrical and thermal networks, legislative and regulatory acts.
8.1.1.7. Workers receiving a bonus for professional excellence must have high business qualities, ensure the highest levels of productivity and quality of work, master advanced techniques and methods of work, and have a high level of professional training.
8.1.1.8.
Allowances are established for workers who have worked in their profession for at least 3 months, consistently ensure high quality of products and work performed, and have no violations of safety rules (H&S), rules of operation of power plants and networks (PTE), fire safety rules ( PPB), production and labor discipline for three months
.
8.1.1.9. The amounts of bonuses for professional skills are established differentially depending on the category assigned to the employee and specific indicators of the quality of his work as a percentage of the worker’s tariff rate:
| 3rd category | 12 % |
| 4th category | 16 % |
| 5th category | 20 % |
| 6th category | 24 % |
| 7th category | 28 % |
| 8th category | 32 % |
8.1.1.10. By decision of the director of the branch individual highly qualified workers are charged according to categories (starting from the fifth), for whom tariff rates are established based on the tariff coefficients of the corresponding tariff categories in the range of 2.03-2.48 inclusive (clause 4.4.7 and table 1 of Appendix 9 of the Regulations), the premium for professional skills is 32 percent.
Source: https://kalibr20.ru/urkons/nadbavka-za-professionalnoe-masterstvo-k-okladu/