Relatives by law: close relatives according to the Family Code of the Russian Federation
Every person should be able to distinguish between these types of relationships. For the law, the completeness of citizens is not so important. Miscellaneous kinship Blood relatives are people who share one or more common ancestors. Accordingly, this includes children, grandchildren, brothers, sisters, grandmothers, grandfathers, aunts and uncles, and so on. Info There is, as already mentioned, acquired kinship. It arises as a result of some legally significant actions. This may include recognition of paternity/maternity, wedding or adoption. In Russia there is such a thing as incomplete kinship. Along with it there is a full-born. What it is? In the first case, citizens have one common ancestor, in the second - several. For example, children from the same mother but different fathers are half-siblings. A close relative is recognized by law without taking into account full blood. But they still mention her.
Full and half-blood relatives
The consensual type of relationship is the most common in the world. It is popularly known as “blooded”. In this case, the children have common biological parents. Such brothers and sisters have a common genotype, are similar in appearance, and can, in most cases, act as donors for each other if necessary.
Half-siblings are relatives who also have a genetic connection, but it is due to the presence of only one common parent, regardless of whether it is the father or the mother. Therefore, the likelihood of having common external traits or character types is significantly reduced compared to siblings.
For persons who are biological children of the same woman, but have different fathers, the term “half-born” was introduced. In the opposite case, when children are united by a common father, but they are born by different women, they are given the status of “half-blooded”.
Property and family law
Oddly enough, the legislation does not consider relatives as objects of family law. Consequently, they do not have the same privileges and responsibilities as relatives.
There are a number of nuances:
- Judges cannot be related to the defendants.
- Persons in property up to the fourth line cannot marry.
- Relatives may become objects of family law in the case when it comes to the payment of alimony by a stepdaughter/stepson to a stepfather or stepmother. However, each such case requires individual consideration.
In-laws - who are they?
This name is not given to blood relatives, but to those who join our family as a result of marriage.
For example, father-in-law and mother-in-law for a wife, father-in-law and mother-in-law for a husband, brothers or sisters of a significant other for their spouse. All these are in-laws.
By the way, the parents of the spouses (matchmakers) are also related to each other.
But as for godfathers, this is a very controversial issue. Are they related? There are two opinions.
Some classify them in this category as relatives acquired as a result of the church rite of baptism.
At the same time, others argue that nepotism is a special type of relationship, and it differs from property in that godfathers do not have common blood relatives.
It is noteworthy that quite often they take on the role of godparents not strangers, but someone from distant relatives (for example, a brother-in-law or brother-in-law). And in this case, a person can simultaneously be both a relative and a godfather.
How can people become relatives?
As mentioned above, strangers become in-laws when one of their close relatives gets married. Moreover, even if over time the spouses separate, their mothers, fathers, brothers, sisters and others continue to remain in a relationship.
However, if, for example, a woman got married a second time, her relatives will become relatives of her husband’s relatives. However, the relatives of the first spouse will have nothing to do with them.
By the way, if we consider nepotism a property, then the second way to enter into such a relationship is to participate in the baptism of a child. However, in this case, only the godparents and parents of the baby become in-laws. And in relation to the rest of the relatives, no changes occur.
Difference from relatives
Although property means a certain relationship, relatives are not relatives. Since the second category requires the presence of a common ancestor or a closer blood connection.
For example, a father and mother are relatives to their children because they are related by blood.
At the same time, the stepfather or stepmother is not related to the stepson or stepdaughter. Because they have no genetic connection. Therefore, despite the fact that they play the role of parents, both the stepfather and the stepmother are relatives in relation to the child.
Paradoxically, sometimes second parents can be more caring than a father or mother who refused to raise their child. However, the degree of care and other moral qualities do not affect the name of the relationship.
Full and half siblings of the testator: turn
Taking into account the related principle, the legislator has set clear priority positions, defining the principle of priority in inheritance. The law provides for only 8 priority groups. Their distribution in descending order corresponds to the priority of the heir in relation to others.
Heirs of the first stage after the death of the husband.
Read about inheritance rights here.
In accordance with Article 1142 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation, the first priority includes the parents/spouse/children of the testator.
Close relatives
The Family Code states that close relatives are parents and children, grandparents, as well as grandchildren and other relatives in the direct and ascending line - these are full or half brothers and sisters. They are highlighted separately, but nevertheless included in the general circle. Since this term is spelled out in an article related to certain obstacles that may prevent marriage, it also mentions adoptive parents and adopted children who are not allowed to marry each other.
But they are no longer considered relatives. Separate attention is given to the status of spouses. They cannot be related by blood, therefore a relationship arises between them. They also affect relatives of both spouses. However, husband and wife are only members of the family, which includes parents and children. Therefore, this unclear status of the father or mother causes some problems when it comes to other branches of law.
The right and order of inheritance of brothers and sisters
The law clearly defines the order of succession.
There are 8 queues according to the degree of relationship. Brothers and sisters are included in the first two lines. First of all, immediate family members are included - children, parents and spouses. This also includes children born out of wedlock, provided that the testator recognized himself as the father of such a child. Full and half brothers (sisters), grandparents, regardless of the line of kinship (maternal or paternal), belong to the second line of inheritance.
It is necessary to enter into an inheritance within 6 months from the date of death of the testator. The right of inheritance of each subsequent line occurs when the heirs of the previous line cannot exercise their rights. In practice this happens for several reasons:
- there are no relatives in the previous line;
- heirs of the first stage do not have rights to inherit;
- disinheritance;
- voluntary renunciation of the right of inheritance;
- other reasons provided for by law.
Distribution of property between heirs of the same degree of kinship occurs in equal shares. If one of the heirs died before the opening of the inheritance, then its part passes to his heirs and is distributed among them also in equal parts.
Close relatives under Art. 14 Family Code of the Russian Federation
Thus, the main sign of inherent relationships is the presence of a basis for their occurrence, namely, the presence of marriage. It is he who generates the relationship between relatives. Relatives are relatives of each spouse in relation to each other and in relation to the second spouse. The main difference from family ties is the lack of consanguinity among relatives.
The concept of in-laws came to the legislation of the Russian Federation from Roman law. Legal relations between relatives are not regulated by acts of family and civil legislation today, and therefore gaps in the law may arise, and this, accordingly, requires improvement and refinement.
Is it possible to change relationship status?
Relationships in each family are individual, but sometimes undergo changes due to various life situations. There are often situations when blood brothers and sisters, by coincidence, do not want to maintain contact with each other. But there are also opposite phenomena, when half-siblings become so close that they begin to consider themselves family.
Is it possible to change the relationship status in this case? This procedure is not possible, since the statuses that determine the relationship between brothers and sisters are not classified as “changing”, unlike the status of husband or wife. These statuses are determined solely on the basis of the birth facts of persons who are brothers and sisters. But this does not prevent them from treating each other like family.
Close relatives according to the civil code
Therefore, they cannot claim anything after a divorce. They are considered former relatives. When do you not have to pay taxes? The most important advantage that close kinship provides is tax breaks:
- when inheriting property, regardless of its size, you will not have to pay personal income tax (you will only have to pay a notary state fee in the amount of 0.3% of the value of the property);
- when receiving property under a gift agreement, close relatives are also exempt from income tax;
- for purchase and sale transactions, the seller (but not the buyer!) can apply for a tax deduction;
- The donor does not need to file a tax return.
In addition to close kinship, tax legislation includes the concept of “related persons.”
In-laws and relatives: what is the difference?
Attention It implies that there is a biological connection between people, which naturally arises between ancestors and descendants, as well as between individuals descended from the same ancestor. Adoption Despite the fact that the main and only characteristic of the biological closeness of people is blood relationship, in the legal sphere there are exceptions to this rule. In the modern world, the institution of adoption has become widely developed. This fact cannot but rejoice, because many single children have the opportunity to find new parents and get the opportunity for full social formation and development. An adopted child is a close relative in accordance with the RF IC, just like adoptive parents. Evidence As we have found out, it cannot be confidently stated that a biologically step-native person cannot fall under the category of “close relatives” under the Family Code of the Russian Federation.
Full and half siblings
The Civil Code of the Russian Federation speaks of the existence of legal significance in the course of inheritance for both direct and lateral family lines. Brothers/sisters are relatives assigned to the second group of the lateral line. They have equal rights of inheritance with relatives belonging to the direct line of the second kinship group.
Heirs belonging to the second group of inheritance have the opportunity to inherit only when there are no heirs of the first, as well as persons who can exercise their rights of inheritance according to the right of representation, for any kind of reason, or if these persons, in accordance with the provisions of paragraph. 2 p. 1 art. 1141 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation due to circumstances, they will not be called upon to inherit or will not be able to accept it.
If you want to find out how to solve your specific problem, please contact the online consultant form on the right. It's fast and free! Or call us at :
+7 Moscow, Moscow region
+7 St. Petersburg, Leningrad region
8 Federal number (free call for all regions of Russia)!
The concept of “close relatives”
Close relatives are direct blood ancestors and descendants along a vertical and horizontal line.
Along the vertical line, close relatives are children and parents, grandparents and grandchildren. Along the horizontal line, brothers and sisters are recognized, including half-siblings who have only one common parent.
The basis for identifying the legal category of close relatives is the principle of blood.
However, this is only a general definition of the concept. In practice, in different branches of law, the list of close relatives can vary significantly.
Despite the blood sign of identifying close relatives, the following are not included in this category:
- Great-grandparents;
- Great-grandchildren and great-granddaughters;
- Aunts and uncles;
- Nephews and nephews;
- Cousins or second cousins.
In addition, adoptive parents and adopted children may be recognized as close relatives in certain cases. There is no blood relationship between them, but their relationship replaces the parental one.
Husband and wife are also not recognized as close relatives . However, in specific issues of regulation of legal interests, they still have some rights. This applies, for example, to common property acquired during marriage, which is divided between them during the divorce process.
Common-law spouses are not recognized as relatives at all. The rights of common-law spouses are limited only by the possibility of presenting alimony for the maintenance of a child whose father is the common-law husband.
In addition, the legislation contains the concept of family members. It is used to a greater extent in housing law. It is considered that those who live in the same premises are considered members of the same family.
The degree of relationship here can be quite distant. These can be mothers-in-law, mothers-in-law, stepfathers and stepmothers.
Close relatives according to the Family Code of the Russian Federation
Who is a close relative under the law? The Family Code provides the most comprehensive description of close kinship.
In Art. 14 of the RF IC directly states that close relatives include the following categories of citizens:
- Children and their parents;
- Grandmothers and grandfathers;
- Grandsons and granddaughters;
- Full and half-sisters and brothers.
In family relationships, the degree of relationship is of great importance . So, for example, it is prohibited by law for persons who are related to marry.
Issues of eviction or settlement, as well as restrictions or deprivation of parental rights are resolved based on known family relationships.
Close relatives according to the Civil Code of the Russian Federation
According to the Civil Code of the Russian Federation, close relatives, in addition to those persons whom we have identified above, also include spouses who have legally consolidated their relationship.
After a divorce, a spouse can claim half of the joint property acquired during the marriage, even if all the property came into ownership thanks to her spouse.
In addition, a woman can, by law, apply to the court to order alimony payments for her maintenance until the age of their common child. That is, the ex-husband can pay money for both the child and his ex-wife if the latter proves in court her difficult financial situation.
Let's consider two more important categories of legal relations in civil law, within which close relatives have special privileges.
These include:
- Gift to a close relative. When donating property to a close relative, the transaction is exempt from taxation. Your mother will not have to pay tax if you give her your apartment as a gift.
- Inheritance to a close relative. Close relatives belong to the first and second categories of inheritance. If a deceased relative did not leave a will after death in which specific persons were indicated, his property will be divided among relatives who express this desire. Also, for inheritance, different rates of state duties are established depending on the degree of relationship. Thus, close relatives pay 0.3% of the value of the property, and other relatives pay 2 times more.
Close relatives according to the Criminal Procedure Code of the Russian Federation
In criminal law in 2021, the following relatives are recognized as close relatives:
- Children and parents;
- Husband and wife;
- Grandparents, grandchildren and granddaughters;
- Sisters and brothers;
- Adoptive parents and adopted children.
According to the Code of Criminal Procedure of the Russian Federation, a citizen may refuse to testify in court and during investigative actions against his close relatives.
The interrogation of a minor subject must always be carried out in the presence of his legal representative - a parent.
Also, the degree of relationship is important when obtaining permission to visit a convicted person in a correctional facility. In this case, legal spouses have equal rights with blood close relatives. But being common-law spouses, getting permission with a convicted person is much more difficult.
Inheritance for full and half-blood relatives
A process such as entering into inheritance represents a transfer of rights and obligations from one owner of property to another.
Such a process can be carried out after the death of the testator, both on the basis of the law and according to the will drawn up. In the second case, this right can be exercised by a person who is defined by such a document and this is not always the one who is related by blood ties to the deceased. However, the first case requires mandatory establishment of relationship. How this happens and what you need to know about this process is what we will talk about later in our article. Who can exercise this right?
So, the law determines that only those persons who are related by blood to a deceased person can claim rights and obligations in relation to his property. This takes into account not just the degree of relationship, but also situations where there is incomplete relationship. That is, when there are children or grandchildren of the testator on one of the lines - mother or father. To establish such data about potential successors, the notary must check the documents and include in the list those that meet the requirements:
- Having a relationship with the deceased. This is not just a biological, but also a legal connection based on the fact of origin between persons. It becomes legal in cases provided for by the norms of family law;
- In case of adoption of the testator;
- Upon adoption of the testator's child;
- When entering into a marriage with a person leaving property;
- In cases where there is property between the testator and the acquirer, which is provided for by law;
- Availability of the recipient's stay on full financial support (disability, illness, incapacity for work or minority);
As we see, acceptance of an inheritance cannot arise by law without the presence of such a factor as kinship.
What does the law say about queues?
The order of inheritance is formed by laws and depends on the close relationship of the successor to the deceased. The closest ones fall into the first degree - these are the child, wife or husband, as well as the parents of the deceased. More distant are considered to be sister and brother, as well as grandfather and grandmother, whom the law classifies as next in line. This involves relatives on both lines of kinship, both father and mother. Let's pay more attention to this point.
A brother and sister who have the same parents are considered full siblings. They both have the same father and the same mother. This also includes screwed brothers - boys who were born out of wedlock and were recognized. A similar division occurs in relation to sisters. This group also includes twins - children who were born to the same woman as a result of one pregnancy. Half-parents include those children who have only one common parent. These may be uterine children who were born by the same mother, but they came from different fathers. The second option is half-blooded, that is, those who are born from the same father, but have different mothers.
A separate category are children, who are usually called step-children. They are not blood relatives, but were raised in the same family. Such a connection is not related, but has a connection with her. The law does not classify this category as the second stage, unlike the previous ones. But if representatives of the first priority are absent, then both full and half-blood relatives can take advantage of their rights.
In this case, the inheritance is formalized in exactly this order. Sometimes difficult situations arise when you can prove your case not just with a notary if you have all the documents, but through the court. Both categories of citizens in such cases are not without the need to defend their interests.
Lost evidence, the impossibility of establishing kinship due to the loss of archival materials leads to such cases. It is in these cases that the court helps to accept the inheritance in a separate process. It is worth noting that this is not a simple matter and you cannot do it without the knowledge of specialists. The thing is that such an authority always requires not just filing an application, but searching for evidence. This is where you will need to conduct a whole investigation, obtain many certificates from government bodies, such as the registry office for special requests, so that as a result the party can prove its case. Often, to prove the degree of relationship, a medical examination is initiated, and the question of searching for medical papers and other options is raised. The involvement of witnesses is also a standard mechanism in such cases.
Thus, the fact of kinship is an important part of the inheritance process in our state and cannot be ignored. The help of a qualified lawyer will help you avoid mistakes in the legal process and resolve the case in your favor. Documents, filing petitions, requests, appealing decisions - all this will help you on the way to receiving an inheritance.
Close relatives according to the family code: features of legislation
Family law of the Russian Federation defines it as the presence of an ascending or descending direct direction (parent and child, adopted children, grandchild, grandparents, and blood ties with one of the child’s parents are required). There are also different types of consanguinity:
- One generation (for example, brother and sister).
- Adjacent generation (for example, parent and child).
- A generation later (for example, grandfather and grandson).
There are blood relationships between brother and sister, these include:
- Full kinship (this type implies common parents).
- Not full-blood relationship (this type means that the family only has a common mother or a common father).
2.
The Housing Code includes not only close relatives in accordance with the IC, but also spouses. The main reason for classifying all these people as family members is their cohabitation. Tax Code Tax legislation is consistent with family law and does not include husband and wife as close relatives.
At the same time, the Tax Code in its text uses not only this category, but also the term “family members”. This document fixes the rules that profits received as a result of transactions carried out between close relatives cannot be taxed, as well as income received as a gift between these people. Conclusions Thus, even in the legislation there is no consensus on the definition of the circle of persons included in close relatives.
However, according to family law, marriage is the basis for a special kind of legal relationship, which excludes the possibility of considering a husband and wife as in-laws. Questions and answers Natalya, 34 years old: Is it possible to marry someone in-law? Answer: According to current legislation, marriage with a relative up to the fourth line is impossible. Oleg, 25 years old: What relatives of my wife are related to me? Answer: In-laws include all the wife’s relatives who are related to her by blood. Among them: the wife's parents, brothers, sisters, the wife's grandparents, children from the wife's previous marriage, uncles and aunts, etc. Irina, 30 years old: In what legal act can you find the definition of in-laws? Answer: In the current legislation of the Russian Federation there is no specific definition of the concept of in-law.
Family ties, or Who is related to whom and by whom
— by category — Culture ᄂCulture
07 August 2013, 00:00 | Galina Zamyslova
In fairy tales, everything ends with a happy wedding, but in life everything just begins with it! Immediately after registering your marriage, you receive a complete set of new relatives along with your chosen one.
From this day on, you have two families that have merged into one and entered into complex family relationships. Once upon a time, the question did not even arise about who was being treated by whom, but today, alas, much has been forgotten and we cannot figure out even the closest relatives.
Let's go back a couple of centuries ago, when families were large, a patriarchal structure reigned, and even the most distant kinship was held in high esteem.
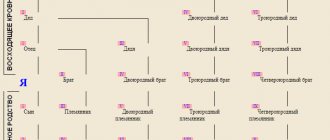
Blood relatives
With blood relatives, everything is more or less clear: mother, father, brother, sister, uncles and aunts, nephews, grandparents. This is if you don’t go deeper. And if you try to figure it out, you might think that all people in the family are brothers!
- Bratanich - brother's nephew
- Bro - cousin's wife
- Bratanna – brother’s daughter, brother’s niece
- Brother - cousin or distant relative
- Bratova - brother's wife
- Bratych - brother's son, brother's nephew
- Bro, brother - cousin
It's about the same with the sisters:
- Sister, sister, little sister - cousin
- Sister - cousin, daughter of mother's or father's sister
- Sister, sister, sister (ancient Russian) – son of mother’s sister (nephew by sister)
Do you know what to call your grandparents' brothers or sisters? Great Aunt - grandparent's sister (great aunt) and Great Uncle - grandparent's brother. And that’s not all - there are also cousins, second cousins and a whole series of great-great-great... .
You can even get confused among your grandchildren! Judge for yourself: a grandson and granddaughter are not only the son and daughter of a son or daughter, but also the children of nephews. You can get completely confused about your grandchildren and great-grandchildren:
- Great-brothers and sisters - second cousins
- Great-nephew (niece) - grandson (granddaughter) of a brother or sister
- Great-great-cousin (niece) is the grandson (granddaughter) of a cousin.
Next come grandsons, second cousins, etc. This is only blood relatives!
In-laws
Let's return to the wedding, after which the number of relatives grows at least twice - these are in-laws.
Do not marry anyone, but you will be provided with a mother-in-law and father-in-law (the parents of your husband), as well as a father-in-law for your chosen one! But they, in turn, acquire you as a relative.
Let's figure it out in order:
- Father-in-law and mother-in-law are the husband's parents for the young wife
- Father-in-law and mother-in-law are the wife's parents for the husband
- Matchmaker, matchmaker - parents of husband and wife in relation to each other
- Son-in-law - daughter's husband
- Daughter-in-law (aka daughter-in-law for father-in-law) – son’s wife
- Brother-in-law - husband's brother, yatrovka or intercourse - brother-in-law's wife
- Sister-in-law - husband's sister
- Sister-in-law - wife's sister
- Brother-in-law is the husband of his wife’s sister, brothers-in-law are men whose wives are sisters to each other
- Brother-in-law - wife's brother, shurich - brother-in-law's son
| Who is here: brothers-in-law, sisters-in-law, brothers-in-law, daughters-in-law, brothers-in-law? |
By the way, if, in addition to family ties, we also mention family relationships, then most often the father-in-law is more kind than the mother-in-law towards his daughter-in-law. With father-in-law and mother-in-law it can be anything - if the father-in-law is always a friend to the son-in-law, then mothers-in-law can be different - both in the form of an “old saw” and in the form of a best friend.
| Even “stars” and princesses have mothers-in-law! |
Close, but not family
It turns out that there are close relatives and close ones, but not relatives. Not very clear? Let's figure it out now!
If a husband or wife has children from previous marriages, they are considered half-siblings. At the same time, the mother’s husband is the stepfather, and the father’s wife is the stepmother. Not a natural son - a stepson, not a natural daughter - a stepdaughter. So it turns out that they seem to be close relatives, but not relatives.
The following are also considered close, but not relatives:
- Named daughter, named son – adopted children
- Named mother, named father - adoptive parents
If the newlyweds get married, then they still have imprisoned parents - an imprisoned mother and an imprisoned father, who replace their parents at the wedding ceremony.
When a child is baptized, the following are added to the number of close, but not relatives:
- Godfather and godfather are godfather and mother in relation to the godson’s parents and to each other
- Godmother - spiritual mother
- Godfather - spiritual father
- Godson - godson
- Goddaughter - goddaughter
- Godbrother (sister) – son (daughter) of the godfather
There was a custom of exchanging pectoral crosses and people who performed such a ritual by kissing three times also became close:
- Brother of the cross, brother of the cross
- Cross sister, brother-in-arms
It also happened that we had to look for a nurse for a child when the mother was unable to feed. The wet nurse became a milk mother, and her children and the child she nursed became milk brothers and sisters.
So many relatives around...
| Try to figure out who is getting to whom and by whom! |
Blood, in-laws or relatives - who is dearer?
Galina Zamyslova , etoya.ru
Spouses: relatives or in-laws?
When considering this topic, sooner or later you will definitely have to face the question: “Who are husband and wife to each other?” After all, they have no blood relationship (such marriages between close relatives are prohibited by the legislation of most countries of the world).
First of all, spouses are a family, and it is from this point of view that the law views them. However, in different areas the degree of their relationship is viewed differently.
Thus, in criminal law, a husband is not a relative of his wife, but a member of a joint family created with her. The Housing Code treats their relationship the same way.
But tax law considers spouses as close relatives, along with brothers and sisters, parents, and grandparents.
But in the Labor Code the name of the relationship between husband and wife is not precisely formulated. And then each employer chooses for himself whether to consider them close relatives or members of the same family.
Thus, it turns out that from whatever point of view one considers the relationship of the spouses, in any case they will not be considered in-laws. By the way, they cannot become godfathers either. The fact is that, according to church rules, godparents cannot marry. But those who have already joined cannot baptize together.
Half-brothers and half-siblings
When determining inheritance rights in the case of the presence of half- and half-brothers, as well as half-brothers and sisters, they are guided by civil law. Inheritance rights are designated as follows:
- half-brothers (sisters) have the right of inheritance in the absence of full-born (natural) children;
- a full sister or brother excludes the rights of half-bloods;
- half-brothers and sisters have the same rights;
- half-children acquire rights to inheritance earlier than first cousins.
However, in practice, there are many nuances when different categories of brothers and sisters enter into inheritance. Litigation can take years. Life circumstances in different families make the process of accepting an inheritance almost unique.
For example, citizen Sidorov enters into an inheritance according to the will of his own father. He is the only heir, but at the last moment he remembers his half-brother (maternal brother), who lives very poorly, and decides to share the inheritance with him. It turned out that it is impossible to divide the property, you can only write a waiver, but the waiver is written in favor of the full heirs in order, and the half-brother does not appear in this line, since he is not a relative of the testator.
Can marriages take place between relatives?
Another question that sometimes still has to be faced is: “Can persons in property enter into marriage?”
If in the case of blood relatives such a prohibition is understandable (degeneration of the breed and the occurrence of hereditary diseases), then in the case of in-laws it is rather a tribute to tradition.
Despite this, in many countries the law prohibits unions between people who are related to each other. However, this is not always justified. For example, if the husband's divorced mother fell in love with his wife's single father. Why don't they get married? Or, as is often shown in television series, the wife’s sister fell in love with her husband’s brother (a similar situation is described in Jane Austen’s novel “Emma”).
It's another matter if the stepfather is going to marry his stepdaughter. It really does look like incest, even though they're not technically related. But then the ban is really justified.
By the way, only in Orthodox countries is marriage between close relatives and in-laws up to the fourth line prohibited. Moreover, among Catholics and Protestants, such a ban applies only to close relatives and first-line relatives.