According to the law, after the death of the testator, inherited property can pass from one owner to another either by law or by will. In the event that the testator did not leave a will, inheritance occurs according to the law, as well as in a number of other cases determined by the Civil Code.
Other cases should be understood as situations where the will is declared invalid, the heir has the right to allocate a compulsory share.
Rights to inheritance are formed after the death of the owner of the property. In addition, an inheritance case can be opened even if a citizen is declared dead in court.
Right to inheritance
Inheritance is the process of transferring property from one person to another after death, as well as the transfer of obligations that are not inextricably linked with it.
The right to inheritance is guaranteed constitutionally and is one of the fundamental rights of a citizen.
The right to transfer property assets is inextricably linked with the right of private property and the right of each owner to dispose of the property belonging to him at his own discretion. Including in case of death.
As for those persons to whom the law guarantees the right to inheritance, they can exercise this right by accepting the property that remains after the death of the testator. The law protects the interests of minor children and other disabled heirs.
In addition, blood relatives of varying degrees of kinship have the right to claim inheritance.
The exercise and registration of inheritance rights can take place according to the law, in the prescribed manner, if the will of the testator has not been changed, by drawing up a will.
A feature of legal relations in the field of inheritance is that the right to receive an inheritance arises in the presence and totality of legal facts. These include the death of the testator, the actual acceptance of the property by the heir, the presence of certain family ties (if we are talking about inheritance by law).
If there is a will, this document is added to all of the above.
To learn more about the rights to property and how it can be realized, read the article “Inheritance Law”.
Who can be the heir
Let's find out who can be the heir: people, animals, legal entities? Since we live in a country with strong traditional foundations and family values, the transfer of property to animals is not encouraged.
According to Russian laws, only the following can be considered heirs:
- people regardless of gender, age, citizenship, nationality;
- legal entities: institutions, enterprises, organizations, as well as the state or municipalities.
You can, of course, leave an apartment to a cat by drawing up a closed will, but in this part, upon the claim of interested parties, the document will most likely be declared invalid.
Depending on the pattern of inheritance, it is possible to determine who the heirs are.
If the last will of the deceased is formalized in the proper form and he gave orders regarding the accumulated property, then those indicated in the document will inherit.
Simply put, a will determines who else has the right to inherit. And it doesn’t have to be relatives or close people, it can be anyone: a nurse from a medical institution or a favorite city.
If there are no instructions on the division of property, then relatives will become the new owners, depending on the degree of relationship.
The legislator considers children, parents and the surviving husband or wife to be closest. The rest (siblings, uncles, aunts, grandparents) will be ranked up to the eighth stage.
Procedure for entering into inheritance
To enter into inheritance rights, the recipient of the property must accept it. For this purpose, the legislation establishes a certain procedure. In accordance with Article 1152 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation dated November 26, 2001 No. 146-FZ, property assigned to the heir is considered to belong to him not from the moment of actual registration or entry into rights, but from the moment the inheritance is opened.
The procedure for entering into an inheritance and the subsequent registration of inheritance rights can be carried out on the basis of law and/or a will. Including in a situation where the owner did not leave a written order for all of his property available at the time of death. Then the inheritance procedure by law extends to those property rights that were not covered by the will.
The inheritance may include the property of the deceased person, which was in his or her possession at the time of death. Including movable and immovable, securities, corporate, as well as other ownership rights and obligations.
Acceptance of property from a relative after his death occurs after the opening of the inheritance. In this case, persons interested in receiving assets submit an application for their inheritance rights to the notary who opened and conducts this case.
To enter into inheritance rights you must:
- Collect a package of documents (general - about the testator and title documents - about the property).
- Find out whether there is a will in relation to the inherited property (in case of inheritance by law).
- Contact the notary at the place of opening of the inheritance within six months with an application for acceptance or refusal of the inheritance.
- At the end of the specified period, receive a certificate in accordance with which to register the property in your own name (in whole or in part established by law or by will).
Receiving an inheritance by law
Art. 1141 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation provides for the right to receive property in the order of priority established by law. In accordance with it, the heirs of the distant line cannot claim to receive property from a deceased relative until the persons in the closest line exercise their right to it.
If none of the heirs accepted or all refused to accept, then the property is recognized as escheated and becomes the property of the state.
Read more about the specifics of acquiring and exercising the rights of each of them in the article “Entering inheritance by law.”
Receiving an inheritance by will
If, according to the law, only relatives can claim to receive property, then according to the will, the one who is indicated in the text of the document by the testator himself can become the new owner. To receive an inheritance, the notary will need to present the will.
The current legislation and courts take into account the will of the deceased, so challenging it can be extremely problematic and this is only possible if there are strong arguments.
More information about the procedure for receiving an inheritance on the basis of a document drawn up on the disposal of property can be found in the article “Entering an inheritance under a will.”
Preemptive right of inheritance
Effect of paragraph 1 of Art. 1168 refers to property that is considered indivisible. Therefore, the property right to receive it should be highlighted. According to the law, such a right belongs to citizens who, on a general basis, owned property together with the deceased citizen.
The second category of heirs by law includes citizens who have the right to a thing recognized as indivisible (in the event that the persons called to inherit were not the owners of common property), taking into account the fact that these citizens used the property on an ongoing basis.
To understand all these legal subtleties, you need to understand what it means to “use” a thing, while the law does not say anything in what period it was used, or the number of persons. That is, the successor could dispose of it as a sole user or together with other citizens.
Example. The father owned a boat, which was used by both father and son. Most often they swam on it to fish. At the same time, the father taught his son the rules of using the boat, taught him how to operate it and repair it. After the father died, the son uses the boat for its intended purpose. Therefore, in the event of distribution of this property, it is the son who will have a priority right to it. That is, he has a better chance of getting the boat than other heirs who, like him, did not have ownership rights to it.
At the same time, the legislator isolated the rule in paragraph 3 of Art. 1168 of the Civil Code, which introduces a special procedure for situations when it comes to the priority right to inherited property in relation to residential real estate. In this case, the property is not physically divided (belongs to the third category of successors).
These provisions have fairly strict conditions in relation to citizens who can exercise their pre-emptive rights in relation to inherited property. This advantage will be given to persons who, at the time of opening the inheritance case, directly disposed of the testator’s real estate and at the same time they do not have another place of residence.
Consider the situation: the mother owned an apartment in Moscow. Her daughter lived on the same territory as her, and her son had his own family and lived in another apartment. After the mother died, the daughter continued to manage her mother’s apartment, since she has no other housing. Therefore, the daughter retains an advantage over her brother when dividing the apartment.
What is “lack of other housing”? According to the law, it should be understood literally that the successor has no other property, not only in the sense of ownership, but also on the basis of an agreement on the social rental of residential premises, and the possibility of privatization in the future is excluded. That is, a person has no other housing except this.
What is meant by “residence”? From the point of view of the law, a person permanently or mainly lives in this apartment, which currently belongs to the inheritance. This does not mean staying there temporarily, for example, during the holidays or for some other reason.
The reason that contributes to the fact that the successor permanently lives in the living space, which belongs to indivisible property, for example, it is a relative, or an outsider who has entered into an agreement with the owner of the property, is of little interest to the law.
However, it should be noted that the second and third categories of successors do not include citizens who are owners of indivisible property.
The law applies as a general rule. This item can be transferred to one of the owners, and the owner of the item will be obliged to pay compensation in cash to the other heirs.
Distribution of order of heirs
Inheritance by law occurs on the basis of priority. Applicants for inheritance in the same line are entitled to property in equal shares. Let's look at who belongs to the first:
- children;
- spouse;
- parents.
In accordance with this procedure, the legislator establishes the circle of persons who can enter into the inheritance after the death of the testator in the first place, and who in the subsequent ones.
If the testator does not have relatives who would belong to the first line of heirs, the right to receive the remaining inheritance passes to the second. This includes brothers and sisters and grandparents on both sides.
It is worth noting that cousins of the deceased can receive the right of inheritance only by right of representation: if their parents were no longer alive at the time of opening the inheritance.
Read more about the procedure for receiving an inheritance by a succession of relatives in the article “The order of heirs.”
Rights of first-degree heirs
Heirs have the right to accept property rights (together with unfulfilled obligations), as well as to abandon them. It is not allowed to accept an inheritance in part if the heir is entitled to all the property of the deceased.
It is necessary to realize the rights to inheritance by taking actions to accept property.
If there are several heirs of the first stage, then the objects of property rights are transferred to them in equal shares. That is, each of the first-priority heirs who has the right to inheritance after the death of their father can claim an equal share with others in the total inheritance mass.
Detailed information about who the heirs of the first stage are and how they can enter into inheritance rights is set out in the article “Heirs of the first stage”.
Inheritance by will
The Civil Code in Articles 1118-1140 explains that the features and some situations in the case of inheritance based on a will are determined. In this case, a citizen who is recognized as fully capable at the time of drawing up the document can draw up a will. In addition, it is allowed to draw up a will directly by a citizen, and without the intervention of outsiders.
According to the law, the testator can exercise his absolute right and dispose of his property as he wishes. At the same time, he can divide the inheritance into parts, deprive the successor of the inheritance property by law, without even explaining his desire. In addition, the Civil Code gives the testator the right to make changes and other orders to his will.
In addition, restrictions may be imposed on the will of the testator related to the allocation of the obligatory part of the inheritance, which are defined in Art. 1149. In this case, the document can be drawn up for the entire property or for part of it. To do this, it is possible to draw up several papers.
The Civil Code of the Russian Federation contains a clarification, in accordance with which instructions are given regarding the determination of a reserve (nominated) successor who can claim the inheritance if the main person recognized for inheritance dies before the inheritance case is opened.
In the event that there are several heirs, and there is no information about the division into shares, then in this case the inherited property will be divided equally between the heirs. This rule can be found in Art. 1122 Civil Code.
It should be clarified that often the will indicates the shared division of property, which in principle is not divided, then in this case the law does not consider it possible to recognize the will as invalid, then the probability of distribution of property will depend on its parts, which are determined by its price.
It is worth noting that in practice such formulations often give rise to controversial issues that often require judicial intervention to determine their use.
At the same time, from the side of the law, the testator can take advantage of the right of secrecy when drawing up a document. The persons present during its preparation, as a rule, a lawyer and a translator, are obliged to keep secret the existence of this document, as well as any changes or its cancellation, until the opening of the inheritance case. Based on the provisions of the Civil Code, if the will is disclosed ahead of schedule, the testator may receive claims for compensation for moral damage.
Article 1124 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation establishes a certain procedure and form that a will must comply with.
The mandatory requirement is that a document drawn up in writing and necessarily certified by a notary can be recognized as a will.
At the same time, there are several exceptions to the rules provided for in Art. 1125, 1127 and 1128 of the specified Civil Code, which make it possible to certify the document by other persons. Otherwise, the will will be declared invalid, and therefore the entire procedure will take place exclusively according to the law.
The category of witnesses may include not only a lawyer, but also citizens who, according to the document, are recognized as heirs. These are children, spouses, parents, persons who cannot read, are not fully familiar with the language, or have been declared disabled.
In this case, the will must indicate information about where and when it was certified. In addition, it must be certified by the signature of the testator himself.
If the testator's condition does not allow him to physically perform this action, that is, he is not able to sign the will, then this action can be performed by another person. However, a notary must be present. The Civil Code requires a mandatory explanation of the reason and a full explanation (full name, place of permanent residence) of the person who signed the will.
Registration of inheritance rights
Receiving documentary evidence of inheritance makes it possible to register the property. Including registering real estate objects.
If the question arises of how to formalize an inheritance after the death of a mother without a will, you should collect documents and contact a notary to obtain a certificate of inheritance.
If a woman during her lifetime did not transfer real estate and assets to third parties by will, her children and spouse can take ownership rights first of all. If they renounce this right or do not use it, the property passes to other relatives.
To correctly write an application and collect the necessary list of documents for a notary, we recommend that you read the article “How to register an inheritance.”
Application of laws
If at the time of a person’s death there is no will drawn up or it does not reflect all the property that belonged to him, the legal provisions in the field of inheritance apply. Children and parents receive property in the order of priority.
In such a situation, the rules apply:
- the right to receive property on the basis of the law passes only to persons who are related to the deceased;
- the queue depends on the level of family ties.
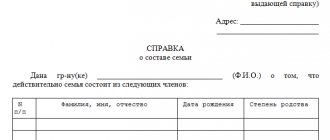
A priority has been established among relatives. Citizens included in the first group of legal successors have priority. This applies to husband/wife and children. When the division of property is based on laws, the rules regarding mandatory shares cannot be applied. The estate is divided among legal successors in equal parts. The opening of an inheritance case occurs at the time of death of a person. You will need to contact a notary and obtain the appropriate deed. The notary is given a paper received from the registry office and confirming the fact of the person’s death.
IMPORTANT !!! To obtain rights to the inheritance, you will need to write an application and send it to the notary. The law allows six months for this procedure. During the specified period, you need to contact the notary and submit an application. Each legal successor needs to draw up a deed. It expresses agreement regarding the receipt of property. To receive property from her ex-husband, a woman must be officially married to him.
It is necessary to submit to the notary a certificate confirming the fact of marriage. For children, it is necessary to present a document confirming their birth. This fact can be confirmed in court. All property of a person is divided among his legal successors in equal parts.
Which notary can register an inheritance?
You can accept property at the place where the inheritance was opened, by contacting a notary. In the absence of a notary in a particular village or locality, the question may arise of where to enter into inheritance after the death of a relative. In such cases, the legislation on notaries allows heads of local administrations or authorized persons of local government bodies to perform notarial acts.
These persons, in accordance with the Fundamentals of the legislation of the Russian Federation on notaries, have the right to accept the application and then register it in the register of notarial actions. Afterwards, submit the documents to the notary chamber in accordance with the approved procedure.
Find out details about where to go correctly to draw up documents in the material “Which notary can formalize an inheritance.”
How to open an inheritance case
The opening of an inheritance is preceded by the establishment of the fact of the death of the testator. This fact is confirmed by a death certificate or a court decision.
After the heirs contact the notary with statements based on the death certificate of the testator, an inheritance case is opened.
A single applicant can initiate the procedure for distributing a relative’s property after death. The remaining heirs will receive notification of the opening of the case.
The right decision when the question arises about what you need to enter into an inheritance after death is to familiarize yourself with the specific requirements of the notary office you plan to contact.
To determine what property is included in the estate, it is necessary to collect, if possible, all title documents.
How and when to inherit?
You should contact a notary with documents to open an inheritance case within six months after the death or recognition of the deceased of the testator. To know how to join correctly, it is recommended that you read the detailed instructions:
- Determine which notary should submit documents. Usually this is a notary office at the place of registration of the testator, and if there is no information about him, at the place of registration of the property.
- Prepare documents for inheritance.
- Evaluate the property you plan to receive. The result is the issuance of an appraisal report indicating the value of the property, which should be used as a guide when calculating the amount of state duty.
- Submit an application to the notary with attached documents confirming the right to the property. You must pay the state fee in advance.
- After six months, receive a certificate from a notary.
- Register real estate ownership through Rosreestr or MFC.
Expert commentary
Gorbunova Olga
Lawyer
The amount of the state fee for issuing a certificate depends on the degree of relationship of the heirs to the testator. For children, parents, siblings - 0.3% of the value of the inheritance, but not more than 100,000 rubles. For others - 0.6%, maximum - 1,000,000 rubles. If a notary takes measures to preserve real estate and other valuables, you will have to pay a fee of 600 rubles. (Article 333.24 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
Let's look at an example of duty calculation:
Anufriev R.P. left an inheritance to his daughter M.R. Skvortsova. apartment. After her father's death, she is the sole heir. The estimated value of the property is RUB 3,000,000. The state duty is calculated as follows: 3,000,000 x 0.3% = 9,000 rubles. – she needs to pay this amount as a state fee before contacting a notary.
Documentation
In addition to how the inheritance is formalized, you should know what documents will be needed when you first visit the notary.
The notary will need to provide:
- Statement. It can be filled out at a notary's office;
- Death certificate. Issued at the registry office;
- Certificate from the last place of residence of the testator. Issued at the passport office;
- Legal documents for inheritance. If this is real estate - a certificate or extract from the Unified State Register of Real Estate. For a car – PTS and STS. For bank deposits – passport and agreement;
- Passport;
- Marriage certificate, birth certificate and other certificates indicating relationship with the testator.
Expert commentary
Kireev Maxim
Lawyer
If the successor does not have the opportunity to enter into inheritance personally, he can do this through a legal representative by issuing an appropriate power of attorney for him. It is important to consider that the representative cannot be an interested person.
What is a compulsory inheritance share?
In accordance with the provisions of Section 3 of Chapter 62 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation, the owner of the property has the right to leave a will, thereby disposing of the property belonging to him in the event of death.
And although the owner can bequeath the property belonging to him to anyone, including those not related to blood relatives, there is a certain part of the property that, in accordance with the law, cannot be transferred to other persons other than those who are obligatory heirs. You can find out what share they are entitled to from the article “Obligatory share under a will.”
In the absence of a written disposition of assets, after the death of the owner, the rights to the property pass, in accordance with the law, to his relatives.
The rights to an obligatory share of persons are established by Art. 1149 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation. In addition to children and disabled parents, the testator's dependents are entitled to the obligatory portion.
You can find out who is entitled to the obligatory share of the inheritance from the materials in the article “Obligatory share by law.”
Unworthy heirs
Dignity as a moral category is associated with respect for a person. People who do not deserve respect are perceived by society as dishonest and immoral. The legislator proceeds from this, classifying among unworthy heirs those who:
- contributed to the speedy death of a relative;
- did not provide him with adequate assistance;
- sought to turn the last will of the deceased in his favor, ignoring the wishes of the latter.
If the heir was found unworthy by a court decision, he can appeal this decision and regain his good name and right to inheritance. The list of actions condemned by law and society, as well as possible solutions to the issue, can be found in the material “Who are the unworthy heirs.”
What documents are required
Having received news that an inheritance has been opened, if there is a will, the interested person submits an application and documents that confirm the identity of the heir. It doesn’t matter whether all the property or part of it is transferred, the registration procedure is the same for all co-heirs. Without confirming the identity of the heir, the notary will not determine that he is the one indicated in the text of the posthumous order.
The fact of opening an inheritance is recorded by a notary on the basis of information received from direct heirs about the death of a citizen. The procedure for registration consists of the following steps:
- Obtaining documents confirming the death of the testator.
- Collection of title documents and identification of property that remains after death.
- Submitting an application to a notary office for the issuance of a certificate.
- After receiving the certificate, registration of the new owner’s rights to the property.
The procedure for entering into corporate rights under the right of inheritance is longer. The procedure must be consistent with the constituent documents of the organization.
Who can be disinherited
In addition to unworthy heirs, absolutely law-abiding successors may also lose what they received under a will if the document is declared invalid. This may happen if a lawsuit is filed in court.
The basis for declaring a document invalid may be both errors and shortcomings in its execution, and the ill health of the testator.
Quite often, interested parties, usually relatives, who did not receive what they expected, raise the question of conducting a post-mortem forensic psychiatric examination in order to prove the incapacity of the testator at the time of drawing up the will.
You can also lose an inheritance at the will of the testator: if he leaves a will in which the potential heir is not indicated or in which his excommunication from the inheritance is indicated.
What are the deadlines for entering into inheritance?
In order to realize the opportunity provided by law to receive the inheritance that was left after the death of the mother or father, it is important to contact a notary in time and fill out the application properly.
Legislation sets the deadlines for entering into inheritance after the death of parents. Even if you register at the same address, lawyers recommend not to delay and to declare your rights within six calendar months.
Time limits begin to apply to the inheritance procedure from the moment of death of the testator. Find out more about the deadlines for entering into inheritance from the article “Term for entering into inheritance.”
Order of succession
To avoid confusion among those wishing to distribute material wealth that has suddenly fallen on their heads, the law has established a procedure according to which property is transferred to new owners.
In the case of inheritance by will, the document usually stipulates who will receive what and in what order, but this order is rather arbitrary.
The legislator clearly regulated:
- who belongs to the circle of inheritors;
- what is the order of the queue;
- how successors are replaced, and so on.
The topic of inheritance is far from new; it is constantly being adjusted and supplemented by judicial practice. For more detailed information, we recommend that you refer to the material “The order of heirs.”
What to do if deadlines are missed
Unfortunately, inheritance recipients do not always have time to complete everything in a timely manner. Then they have to face a situation where the notary refuses to issue a certificate due to missed deadlines.
Valid reasons for missing the deadline for entering into inheritance after the death of parents can become a valid reason for extending the deadline for entering into inheritance rights through the court. The notary is not independently authorized to extend the deadlines.
The basis for issuing a certificate taking into account the share of the heir who did not submit the application on time will be two documents:
- A statement that all relatives and co-heirs agree to the distribution of shares in his favor.
- A court decision to extend the deadline for entering into an inheritance, or recognizing the applicant as having actually entered into an inheritance.
What needs to be done if deadlines are missed, read the article “If deadlines are missed.”
How is property divided between heirs?
If inheritance is carried out by law, the property will be divided among all legal successors in equal shares. The same applies to inheritance under a will, if the shares are not indicated in it. If a testamentary document was drawn up with a precise definition of the shares, a certificate is issued to each legal successor indicating the part belonging to him.
Below we will consider a detailed example of separation according to the law:
Ignatiev O.P. left an apartment of 50 square meters as an inheritance to his two capable sons. m. After death, the brothers applied for inheritance. As a result of reviewing the documents, they were issued a general certificate, according to which the apartment is divided between them in equal shares. The kitchen, hallway and bathroom are considered shared.
An example of dividing shares according to a will looks like this:
Yunina O.V. made a will in which she indicated that 1/3 of her house after death should become the property of her son, and the remaining part should be inherited by her daughter. The notary issued two different certificates indicating the corresponding shares.
Expert commentary
Potapova Svetlana
Lawyer
It is worth considering that even if there is a will drawn up for other people, incapacitated children and parents must be allocated mandatory shares in the property. If this has not been done, they can challenge everything through the court, and then, by its decision, they will be allocated a part of the property by reducing the shares of other participants in the case.
Inheritance taxation procedure
In the process of accepting inherited property, the question arises of how and how much taxes need to be paid. Based on the norms of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation (Article 217, paragraph 18) dated August 5, 2000 No. 117-FZ, recipients of inheritance are exempt from paying tax.
The legislator has not clearly established that such a provision in the article applies exclusively to a specific queue. Therefore, we can conclude that all heirs are exempt from taxation when receiving inherited assets in cash or in kind.
How to recognize property rights by inheritance
Recognition of property rights, including the right to inheritance, is carried out exclusively in court. Disputes may arise after the opening of the inheritance, as well as due to the recognition of property as escheat.
In connection with the refusal of a notary to issue a certificate due to the presence of circumstances that do not allow this, if the inclusion or non-inclusion of property (or a certain part thereof) in the inheritance mass is unfounded, the dispute must be resolved in court.
The legislator has established a claim procedure for this type of disputes related to inheritance. Property rights can be recognized by inheritance, in particular, in the following cases:
- The testator began the privatization procedure and did not complete it until his death.
- The notary refused to include certain property in the estate.
- In the presence of unauthorized construction, the ownership of which was not formalized by the testator.
- The presence of obligations to the testator to transfer property or funds, if they were not fulfilled at the time of the testator’s death.
Since for such disputes, as mentioned above, a claim procedure is provided, the basis for going to court is the notary’s refusal to perform the above actions.
An important step in the procedure for recognizing ownership of an inheritance is the preparation and submission of documents to the court along with a statement of claim. The following facts are subject to mandatory proof:
- Presence of family ties with the deceased.
- Acceptance of an inheritance or taking legal actions to accept it.
- Ownership of rights to certain property not included in the inheritance mass.
- The fact that there is an unfulfilled obligation to the testator.
- Violation of rights.
For more information on how recognition of property rights occurs in matters of inheritance, read the article “Recognition of property rights in inheritance”.
Shares of heirs according to law
Heirs are entities who receive some material benefits after the death of a person. They mean both property (movable and immovable) and property rights.
The transfer of ownership of property is carried out in the manner prescribed by law: each subsequent stage is allowed to participate in the division only if there are no heirs of the previous one.
Moreover, within one queue, the shares of each participant are presumed to be equal. In some cases their size may be revised or changed.
How to accept an inheritance
To receive the property of deceased parents, it is necessary to accept an inheritance. After the reading of the will, including a closed one, the person indicated by the heir receives from a notary a certificate of right to the inherited property. Next, in accordance with the procedure established by law, it is necessary to register this property to the new owner.
In the absence of a will, the inheritance is received according to the law within the time frame when one can enter into an inheritance after the death of the mother or father. Find out more about the procedure for entering into inheritance rights in the article “Accepting an inheritance.”
Ways to receive an inheritance
At the legislative level, there are two ways to obtain inherited property:
| In law | By will |
| Relevant if there is no will. In this case, the certificate of inheritance is received by the legal successors of the first stage, and in the absence of such, by the second. If there are no heirs of the second stage, the legal successors of the third stage can claim the property. | The testator himself determines during his lifetime who will receive the property and in what shares. He can bequeath any thing even to a stranger. |
Expert commentary
Shadrin Alexey
Lawyer
In the latter case, do not forget about the right to an obligatory share established by Art. 1149 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation. The testator's minor or disabled children, as well as incompetent parents, must receive less than 50% of the share that could pass to them upon inheritance by law. That is why they can challenge the will, as well as the heirs of all three orders, if they manage to prove that their rights to property have been violated.
What norms of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation regulate inheritance issues:
| Article | Explanation |
| Art. 1113 Civil Code of the Russian Federation | The opening of the inheritance occurs on the day of the death of the testator or recognition of him as deceased |
| Art. 1122 Civil Code of the Russian Federation | If the will does not indicate shares for each legal successor, the property is distributed between them in equal parts |
| Art. 1125 Civil Code of the Russian Federation | The will must be drawn up in the presence of a notary, read and certified by him |
| Art. 1126 Civil Code of the Russian Federation | Citizens have the right to draw up closed wills, the contents of which become known only after death. Even a notary does not have information from it. It is packed in an envelope, sealed and certified by the signatures of two witnesses, as well as a notary |
| Art. 1142, 1143, 1144 Civil Code of the Russian Federation | First priority heirs include children, spouses, and parents. The second is grandparents, brothers and sisters, the third is aunts and uncles, nephews and nieces. |
| Art. 1154 Civil Code of the Russian Federation | The inheritance must be accepted within six months after the death of the testator. If the right to property arises only as a result of non-acceptance of the inheritance by other legal successors, the period is increased by three months |
| Art. 1155 Civil Code of the Russian Federation | If a citizen missed the deadline for entering into an inheritance, he can restore it through the court |
| Art. 1157 Civil Code of the Russian Federation | Successors have the right to abandon inherited property in favor of other persons or without specifying them |
| Art. 1162 Civil Code of the Russian Federation | After reviewing the documents from the heirs, the notary issues a certificate of the right to inheritance at the place of its opening. It can be either general or separate for each participant in the case. |
| Art. 1163 Civil Code of the Russian Federation | The certificate is issued six months from the date of opening the case, except in cases where it can be reliably established that there will be no other applicants for the property - then it is issued earlier |