Disputes under the agency agreement
Most often, disputes under an agency agreement arise in connection with a violation of the agent’s right to remuneration. The subject of such disputes is the grounds and amount of remuneration. The agency agreement is paid, that is, the principal is obliged to pay remuneration to the agent even if the contract itself does not indicate either the amount of payments due to the contractor for the service provided, or the condition itself on the obligation to make payment. The obligation to pay remains with the principal also when the customer himself has performed the actions that the agent should have done in fulfillment of the contract. This is due to the existence of a valid agreement between the parties, as well as the fact that the agent did not declare his intention to refuse to perform the contract.
In judicial practice, there are often disagreements between the agent and the principal regarding the issue of the performer’s actions outside the scope of the agreement. For example, the agent performed additional work that was not provided for in the contract. In this situation, disputes arise about the need to pay for additional work, the validity of its completion in order to fulfill a previously concluded contract.
It is, of course, not possible to completely exclude the possibility of an alleged dispute under an agency agreement, but the more detailed approach is taken when drawing up an agreement between the parties, the less likely there will be disagreements in the future.
VIDEO : it is also possible to challenge transactions under an agency agreement
Amount of agency fee
The amount of remuneration is set in different ways. Let's look at the main ones.
Payment in a fixed amount
An option that does not increase, but rather reduces, the economic efficiency of the contract. It is risky from the point of view of the possible assessment by the tax authority of the principal's expenses for remuneration of the agent as economically unjustified expenses (in the event that the agent does not submit a report for the paid period or a zero report).
Amount of agency fee as a percentage of the result (achieved indicator)
As a rule, as a percentage of the amounts of transactions made by the agent in the interests of the principal. This is 1 of the most transparent options. If the value is taken into account as a percentage of the profit on transactions, the situation becomes much more complicated. The fact is that the concept of “profit” is ambiguous and is not normatively established for civil law. The concept contained in the Tax Code of the Russian Federation is not applicable in this case. It belongs to a different branch of law (tax law, not civil law). In addition, in entrepreneurial practice, profit is understood somewhat differently. If the parties do not regulate in detail the method of determining profit in the contract, then ultimately the court will be forced to find the answer to this complex question. A reasonable option would be to turn to the concept of lost profits as interpreted by the Supreme Arbitration Court of the Russian Federation (see Resolution of the Federal Antimonopoly Service of the Volga Region dated March 31, 2008 No. A65-8205/07SG3-25). In practice, there are options for determining the agent’s remuneration as a percentage of his costs (for example, if the agent purchases raw materials for the principal plant).
Combining a fixed amount and a percentage of the result
This option of agency remuneration requires detailed regulation. Typically, a fixed amount is paid for the time period of the agent’s activity, and a percentage is paid for specific achievements (for example, a percentage of the transaction amount with buyers who came from the agent).
Procedure for collecting agency fees
Payment of agency fees is the responsibility of the principal. In the absence of payments, the procedure for collecting agency fees is recommended to be structured as follows:
- Establish the reason for non-payment of remuneration . There are a great many reasons why a party to a contract does not want to make payment and, first of all, it is necessary to establish a specific one.
- Notify the principal about the debt . The agent should name the exact amount he is claiming and justify its amount.
- Sending an official request for payment of remuneration . In a written claim, you should state a demand not only for payment of the amount owed, but also for the penalty incurred in connection with the delay in fulfilling the obligation.
- Going to court . If the counterparty does not cooperate, then it is necessary to seek legal protection. In the statement of claim, in addition to the amount of the principal debt and the penalty, we add court costs and the amount of the state duty paid.
- Enforcement of a judicial act . After a court decision has entered into legal force, which has not been executed by the losing party, it is necessary to obtain a writ of execution for its subsequent presentation to the debtor’s bank or bailiff service to initiate enforcement proceedings.
Claim under agency agreement
The claim is intended to resolve the conflict before going to court, so it must be drawn up correctly, stating the facts and clearly stating the requirements. The claim under the agency agreement includes:
- name of the parties . Already from the “header” of the claim it should be clear to whom and from whom the claim is directed;
- description of the event . The main part of the request indicates the number and date of conclusion of the agency agreement, the rights and obligations of the parties under it, the deadline for execution and the amount to be paid. Most often, this amount is the subject of dispute. In the descriptive part of the requirement, you should state your position in detail and convincingly, and document each argument;
- formulation of requirements . After stating the essence of the violated right, the claim specifies certain requirements for the counterparty. They must logically follow from the previous text of the claim, be specific and not allow for double interpretation;
- signature and attachments . The claim is signed by a competent person, that is, the party to the agency agreement or its representative. The application consists of documents confirming the validity of the requirements.
The claim is sent by mail or courier delivery to the address specified in the contract or to the legal address. Sending by email is allowed if the parties actively used it during cooperation.
USEFUL : follow the link for our proposal for filing a claim, as well as a video with additional advice from a lawyer
○ Advice from a lawyer:
✔ What to do if no deductions have been made under the agency agreement? Reports were submitted on time, but there was no reward.
The agent's services are always paid, so he can file a claim against the principal in court. But before starting a dispute, it is advisable to write a claim to the counterparty, demanding payment of the amount due.
✔ Can such an agreement be concluded remotely?
Yes. Nowadays, many contracts are concluded in this way. To do this, it is necessary to reflect in the agreement the provision that it comes into force after affixing seals by both parties. First, one party must put its stamp and signature of the manager, then the documents are scanned and sent to the counterparty, who in turn puts a seal and sends the finished documents to the first party. As a result, both the agent and the principal must have agreements with seals and signatures of both parties.
Video
Specialist Yuri Baykov will tell you in detail what an agency agreement is and how to draw it up correctly.
Published by: Vadim Kalyuzhny , specialist of the TopYurist.RU portal
Claim for debt collection under an agency agreement
If the parties to the agency agreement are entrepreneurs, then the statement of claim is filed with the arbitration court, but if one of the parties is an individual, then the statement is sent to a court of general jurisdiction. The claim is sent to the court at the location of the defendant, unless other rules of jurisdiction are established by the contract. Before filing an application with the arbitration court, you must send a copy of the claim to the defendant and pay a state fee.
The statement of claim is drawn up in a derivative form, but conditionally it can be divided into 4 components:
- Introductory . The name of the court and the parties with identification characteristics is indicated - the number of the certificate of delivery for tax registration, place of registration, location, etc.
- Motivational . The terms of the agency agreement and the essence of the applicant’s violated rights are described. The plaintiff, with references to the rules of law, substantiates his claims against the defendant.
- Petitionary . The applicant formulates demands on the defendant and asks the court to satisfy them.
- Applications . A copy of the agency agreement, calculations of debt and penalties, documents confirming payment of the state duty and sending a copy of the claim to the defendant, as well as any other documents proving the plaintiff’s case are attached to the statement of claim.
USEFUL : follow the link for our proposal for filing a claim in court, as well as a video with additional advice from a lawyer
How to properly terminate an agency agreement?
The easiest way to terminate a contract is by agreement of the parties. Mutual consent of the parties to the agency agreement to terminate the relationship will allow all controversial issues to be resolved through negotiations. If there is no agreement, a termination process will need to be initiated.
A party may request termination of an agreement when concluding an agreement for an indefinite period. In this case, the initiator of termination sends a corresponding notification to the counterparty. The notice must indicate the date of termination of the relationship. The amount of the unused advance is subject to return as unjust enrichment.
When concluding a contract for a certain period, there is no clear position on the possibility of initiating the termination process. In practice, there are examples of both the fact that a party can demand termination of a contract if the agreement itself provides for such a possibility, and that unilateral termination is impossible when the term is specified in the contract. In any case, the party wishing to terminate the contract has the right to demand its termination in court.
Consequences of termination of an agency agreement
Upon termination of the agency agreement, all obligations between the parties cease.
As a general rule, the parties do not have the right to claim what they have completed before the moment of termination. Meanwhile, situations are possible when, for example, the obligation has been fulfilled, but payment has not been made in full, or the customer has provided an advance that has not been fully worked out. In such circumstances, the parties should, before terminating the contract, agree on the conditions, procedure and timing of the return of the unearned advance or payment of the remuneration intended for the agent.
If the parties terminated the agency agreement in court, the procedure for returning funds may be prescribed in the court decision.
Commission and agency agreements. Application of CCP
About the use of CCP
Letter of the Federal Tax Service of the Russian Federation dated June 20, 2005 No. 22-3-11/1115
In accordance with paragraph 1 of Art. 2 of the Federal Law of the Russian Federation of May 22, 2003 No. 54-FZ “On the use of cash register equipment when making cash payments and (or) payments using payment cards”
Cash register equipment is mandatory for all organizations and individual entrepreneurs when making cash payments and (or) payments using payment cards in cases of selling goods, performing work or providing services.
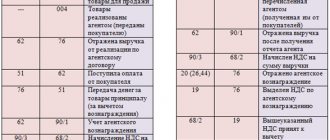
Commission agreements
According to Art.
990 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation , under a commission agreement,
one party (the commission agent) undertakes, on behalf of the other party (the principal), for a fee, to carry out one or more transactions
on its own behalf
, but at the expense of the principal.
When selling goods under a commission agreement, the commission agent who sells goods belonging to the principal for cash is at the same time the seller under the purchase and sale agreement,
concluded with the buyer
on its own behalf
(including under a retail purchase and sale agreement).
When making sales for cash, he is required to use cash register equipment
.
On what exactly the commission agent is
, and not the principal is obliged to use cash register equipment in the case of the sale of goods under a commission agreement, is also oriented by
judicial and arbitration practice
.
A different situation arises when transferring cash to the principal or principal
: since in this case there are no transactions for the sale of goods, performance of work or provision of services, the principal can accept money
by issuing a cash receipt order
.
Meanwhile, if a commission agent or attorney (organization, individual entrepreneur) receives cash from organizations (committent, principal) to pay for the intermediary services they provide
(in the case when the intermediary does not take part in the settlements), then the commission agent or attorney is obliged, at the time of accepting the money, to issue to the principal or principal a cash
receipt printed by cash
.
Agency contract
In accordance with Art.
1005 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation , under an agency agreement,
one party (agent) undertakes, for a fee, to perform legal and other actions
on behalf of the other party (principal) on its own behalf
, but at the expense of the principal, or
on behalf and at the expense of the principal
.
The emergence of rights and obligations for one or another party to an agency agreement depends, first of all, on the conditions under which the agreement was concluded
and, first of all, on the condition defining the party to the transaction (agent or principal) on whose behalf legal and other actions will be performed.
If these transactions will be carried out by an agent in accordance with the terms of the agreement on his own behalf
(using cash register equipment registered by the agent) and at the expense of the principal through a stationary trade facility owned by the agent (used by the agent), then such activity of the agent should be qualified as retail trade and the
agent is obliged to use cash register systems when selling goods.
If these transactions are carried out by an agent on behalf of the principal
(using a cash register registered by the principal) and at his expense through a specified stationary trade organization facility or through a stationary trade organization facility owned by the principal (used by the principal), then the activities of the principal should be classified as retail trade and
the principal is obliged to use cash register equipment
when selling goods.