Types of liability for violation of labor laws
The following types of liability for violation of labor laws apply in the Russian Federation:
- Disciplinary - occurs for employees for violating labor regulations, which is a disciplinary offense. Expressed in the form of disciplinary action.
- Material - occurs for employers and employees in the event of damage to the injured party and consists of the obligation to compensate for the damage. Unlike the situation with an employee, the employer may be required to compensate not only the actual damage caused, but also the amount of lost profits.
- Administrative - occurs for the manager and other officials who have committed administrative offenses. Administrative punishment in the form of a fine is applied to those found guilty.
- Criminal - applies to managers who commit the most serious violations of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation. Those found guilty may be temporarily banned from holding a number of positions or conducting certain activities.
It is worth noting: there is also civil liability for violations of labor laws. It is in many ways similar to financial liability, however, unlike the latter, it is regulated not by the Labor Code, but by federal laws and the Civil Code of the Russian Federation. Civil liability provides for the manager the need to compensate the organization or employees for losses caused by his guilty actions.
Material and disciplinary
The employer's financial liability is compensation to the employee for material damage that was caused as a result of the employee's illegal violation of his right to work.
Note 2
For example, the employer will have to compensate the employee for damages if he illegally removes him from work, dismisses him or transfers him to another job, refuses to execute the decision of the labor dispute resolution body, delays the issuance of a work book, or enters into the work book an incorrect or non-legislative wording of the reason for dismissal.
The employer is liable in the amount of no less than 1/300 of the current refinancing rate of the Central Bank of the Russian Federation for unpaid wages (for each day of delay).
Disciplinary liability can be imposed on officials of the organization for violating labor law norms containing labor law norms, and will be expressed in the application of disciplinary sanctions in the form of a reprimand, reprimand, dismissal.
Need advice on your academic work? Ask a question to the teacher and get an answer in 15 minutes! Ask a Question
Officials may be involved both on the own initiative of the organization’s senior management, and on the proposals of the prosecutor’s office and the federal labor inspectorate.
Examples of bringing to different types of liability
Let us consider in more detail for which violations certain types of liability are applied and what penalties are provided.
Disciplinary responsibility
Disciplinary liability for an employee occurs when a disciplinary offense is committed. This is failure to perform or improper performance of official duties due to the fault of the employee. According to para. 1 tbsp. 192 of Law No. 197-FZ, the following types of penalties are permissible:
- comment;
- rebuke;
- dismissal for appropriate reasons.
Some categories of employees may be subject to other types of disciplinary sanctions. For them, there are charters and regulations on discipline established by federal laws (Regulations on the discipline of railway transport workers of the Russian Federation, etc.).
Some enterprises introduce fines for late arrivals and non-compliance with the internal dress code. Such sanctions are illegal. In para. 4 tbsp. 192 of Law No. 197-FZ contains an instruction prohibiting the use of disciplinary sanctions that are not specified in the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, charters and regulations on discipline established by federal laws.
According to para. 5 tbsp. 193 of Law No. 197-FZ, it is allowed to apply only 1 disciplinary punishment for each violation. The type of punishment is chosen based on the severity of the offense and the circumstances of the incident.
Bringing disciplinary action against an employee for violating labor laws in 2021 is not a mandatory measure. The employer has the right not to apply penalties according to his decision (paragraph 1 of Article 192 of Law No. 197-FZ).
Before imposing disciplinary action, the employer must request a written explanation from the employee. If the employee refuses to give an explanation, this will not be an obstacle to applying a penalty. A disciplinary sanction can be applied no later than 1 month from the date of discovery of the offense and no later than 6 months from the date of the commission of the offense, and based on the results of an inspection or audit - no later than 2 years from the date of its commission.
Material liability
The financial manager's obligation to the company is to fully compensate for direct actual damage (Part 1, Article 277 of Law No. 197-FZ). The manager also compensates the legal entity for losses that arose through his fault.
The employer's financial liability for violation of labor laws in relation to an employee arises when:
- illegal deprivation of an employee of the opportunity to perform official duties (Article 234 of Law No. 197-FZ);
- causing property damage to an employee (Article 235 of Law No. 197-FZ);
- delay in the payment of wages or other due payments to the employee (Article 236 of Law No. 197-FZ). Read about employer liability for late payment of wages here;
- causing moral harm to an employee (Article 237 of Law No. 197-FZ).
The employee’s financial liability to the employer consists of the obligation to compensate for direct actual damage caused by his guilty actions (Part 1 of Article 238 of Law No. 197-FZ). The amount of compensation is limited to the amount of average monthly earnings, with the exception of employees who bear full financial responsibility. Find out about the procedure for bringing an employee to financial liability from the article https://otdelkadrov.online/6107-usloviya-poryadok-privlecheniya-rabotnika-k-materialnoi-otvetstvennosti-vzyskanie-ushherba.
Depending on the circumstances of the damage, the employer has the right to decide not to recover it on the basis of Art. 240 of Law No. 197-FZ.
Administrative responsibility
Additional fact
Each manager has information about the personal data of his employees. Disclosure of this information may also result in the official being punished. He may be brought to administrative, financial, and even criminal liability. Read more about responsibility for disclosure of personal data by an employer here.
The Code of Administrative Offenses provides for administrative liability for violation of labor laws. Administrative violations include the following:
- violation of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation and labor protection legislation (Article 5.27 of the Administrative Code);
- avoidance of participation in negotiations on the signing of a collective agreement or violation of the deadline for its conclusion (Article 5.28 of the Administrative Code);
- failure to provide information necessary for conducting collective negotiations and organizing control over compliance with the terms of the collective agreement (Article 5.29 of the Administrative Code);
- unmotivated refusal to conclude a collective agreement (Article 5.30 of the Administrative Code);
- violation or refusal to fulfill obligations under a collective agreement (Article 5.31 of the Administrative Code);
- avoidance of receiving employee demands and participation in reconciliation procedures (Article 5.32 of the Administrative Code);
- failure to fulfill the terms of the agreement (Article 5.33 of the Administrative Code);
- dismissal of employees as a result of a collective labor dispute and strike (Article 5.34 of the Administrative Code);
- coercion to participate or refuse to participate in a strike (Article 5.40 of the Administrative Code);
- violation of the rights of people with disabilities in terms of employment and employment (Article 5.42 of the Administrative Code);
- concealment of an insured event (Article 5.44 of the Administrative Code);
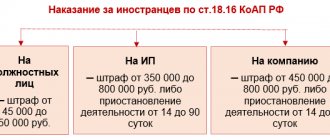
- non-compliance with the rules for attracting and using foreign labor in the Russian Federation (Article 18.10 of the Administrative Code).
The manager's administrative responsibility for violating labor laws (most often this is the employer's responsibility for non-payment of wages) is the imposition of a fine. Disqualification is also possible - depriving a person of the right to work as a manager, to join the board of directors, or to conduct entrepreneurial activities in managing a legal entity (Article 3.11 of the Administrative Code).
Disqualification applies to individuals who perform managerial functions in companies. Fines for administrative offenses provided for in Articles 5.28 - 5.33, 5.44 of the Code of Administrative Offenses can be applied to legal entities - employers, and to officials - their representatives. Fines for committing offenses provided for in articles of Art. 5.27, 5.40, 5.42 apply only to individuals.
This video will tell you about fines for violating labor laws.
Criminal liability
In some cases, criminal liability is introduced for violation of labor laws. Criminal offenses include:
- violations of labor safety rules committed through negligence and resulting in serious harm to health or death of an employee (Article 143 of the Criminal Code);
- unmotivated refusal of employment, unjustified dismissal of a pregnant woman or mother of children under 3 years of age (Article 145 of the Criminal Code);
- delay of salary for a period of more than 2 months, which arose due to selfish or other personal interest (Article 145.1 of the Criminal Code).
For committing these crimes, along with other types of punishment, the perpetrators may be deprived of the right to take certain positions or engage in certain types of activities for a period of up to 5 years.
To get an answer from a specialist, ask questions in the comments
Classification of legal liability
Note 1
Legal liability is understood as the application of various measures of state coercion to the offender.
As a general rule, the structure of legal liability can include the following three components:
- an authorized entity, which refers to government bodies that have the authority to bring a violator to justice of a certain type (criminal, administrative, etc.);
- the subject who committed the offense, and, as a result, is obliged to fulfill the requirements of the authorized subject and suffer adverse consequences in his address;
- legal rights and obligations of the authorized subject and the offender.
Finished works on a similar topic
- Course work Legal liability of the employer 490 rub.
- Abstract Legal liability of the employer 240 rub.
- Test work Legal liability of the employer 210 rub.
Receive completed work or specialist advice on your educational project Find out the cost
The main types of employer responsibilities are:
- material and disciplinary;
- criminal;
- administrative.