Good day to all!
Dismissal due to failure to fulfill job duties is a fairly common occurrence. But, as wise practice consistently shows, just as often the employer does not think about the meaning of this reason.
Can't do the job? Well, that means you can fire him! Some employees think in the same direction (and this is worse, you should never blame yourself).
Dismissal due to unsuitability: procedure
In some cases, a situation may arise when the employer will need to dismiss one or more employees for unsuitability. In this case, the established standards of labor legislation should be followed as strictly as possible, since illegal termination of an employment contract may entail large costs for the organization to pay fines and compensation to the employee. At the same time, the Labor Code of the Russian Federation contains precise information on how to properly dismiss someone for reasons of unsuitability in various cases, including health reasons.
LOOK CAREFULLY WITH THE EVIDENCE
Based on materials from the Review of Judicial Practice in Labor and Social Cases of the Judicial Collegium for Civil Cases of the Supreme Court of the Russian Federation for 2005
Sh., lawyer of the Moscow representative office, was fired on May 14, 1999 under clause 2 of part 1 of Art. 33 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation (inconsistency between the position held and the work performed due to insufficient qualifications identified on the basis of certification). The defendant presented to the court the results of the certification conducted by the legal personnel committee: two letters from the firm's partners D. and A. regarding the assessment of the work of lawyers, including Sh., as well as the minutes of the committee meeting. From the latter it followed that Sh. was recognized as an insufficiently professional employee on the basis of the mentioned letters. However, from the same letters it was clear that the experience of D. and A. working together with Sh. is limited, his professional experience should correspond to a higher level of independence in work, as well as the fact that for objective reasons it was difficult for him to cover the entire issue and present recommendations of practical significance.
The case reached the Judicial Collegium for Civil Cases of the Supreme Court of the Russian Federation, which confirmed the correctness of the conclusions of the lower courts regarding the reinstatement of Sh. in his position and compensation for moral damage. In its Definition No. 5-B05-64 we read the following:
“The defendant did not present evidence at the court hearing that the procedure for certifying lawyers was in any way formalized and regulated in the local regulatory act of the company... The court came to the correct conclusion that there was no reliable evidence of Sh.’s insufficient qualifications, which would indicate his inadequacy position occupied..." (https://www.supcourt.ru).
Dismissal due to unsuitability - what is it, legal framework
First of all, when considering the issues of dismissal due to professional incompetence, it should be noted that such a concept as “unsuitability” in Russian legislation is found only in a few departmental documents. At the same time, labor legislation as a whole does not contain such a term and its explanation. However, in practice, the concept of professional unsuitability is used quite often, and it is professional unsuitability that can be the reason for dismissal. In this case, the types of professional incompetence should be distinguished:
- Due to lack of qualifications, knowledge, skills. In this case, professional incompetence is ensured either by the personal qualities of the employee, or simply by the discrepancy between his existing qualifications and skills required to perform the work of his position. From the point of view of labor legislation, in the event of such professional unsuitability, dismissal is carried out at the initiative of the employer.
- For medical reasons and health. Dismissal due to unsuitability due to health conditions presupposes that the employee has been issued a medical certificate, according to which he is prohibited from engaging in activities in his previously held position. At the same time, labor legislation directly allows for the possibility of terminating an employment contract in this situation, subject to compliance with a certain established procedure.
In this case, both employers and employees should pay special attention to the provisions of the following articles of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, which consider dismissal due to unsuitability:
- Article 73 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation. The provisions of this article regulate not the issues of dismissal due to professional incompetence due to health, but the transfer of employees. However, it is also precisely in this article of the Labor Code that the possibility of dismissing an employee for medical reasons is considered if it was not possible to transfer him to another job.
- Article 77 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation. The provisions of this article regulate the procedure for dismissal based on professional incompetence, as well as other possible grounds for dismissal of employees. It is the said article of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, indicating the points and sub-points, that must be referred to as the basis for dismissal when recording an entry in the work book.
- Article 81 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation. The standards of this article govern all cases of dismissal, which is carried out at the request of the employer. And the professional incompetence of an employee, not related to his health, but related to insufficient qualifications or failure to fulfill established labor requirements, applies precisely to such cases.
How to fire for incompetence
How to fire for unsuitability
Dismissal of an employee due to professional unsuitability will be legal if all the rules stated in the regulations are followed. Clause 3 of Art. 81 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation states that it is possible to terminate an employment contract on the basis of unsuitability when it is revealed that the employee’s qualifications do not correspond to the position he occupies. In this case, this fact must be confirmed by the results of the audit.
Back in 2008, Rostrud letter No. 1028-s was published, which clarifies the issue of the procedure for dismissing workers under the article of the Labor Code related to unsuitability. The labor legislation of our country states that the head of a company can initiate the removal of a person from his position if his professional qualities do not correspond to it. In this case, the decision must be supported by the results of the certification. An important feature of this article is that if there are vacancies in the organization that are suitable for the dismissed employee in terms of his physical condition and skill level, the employer must offer him a transfer. Dismissal is possible only when there are no such positions in the company or the employee officially refuses to take another position.
Moreover, if the head of the enterprise has another position suitable for the employee in the same area, he is also obliged to offer him to transfer to it. The need to transfer a specialist to another locality is determined by the conditions specified in the labor or collective agreement under which the citizen worked. As for the certification procedure, the rules for its implementation are enshrined in labor legislation. The internal documents of the organization, in the adoption of which representatives of trade unions participated, can also be taken into account. There is no possibility of releasing a person from his position without special procedures.
Two more important conditions must be met:
- In Part 3 of Art. 82 of the Labor Code states that the results of certification, during which the employee’s professional incompetence was confirmed, are considered a reason for dismissal only if a member of the elected trade union body was present on the certification commission.
- In Art. 373 of the Labor Code specifies the terms for terminating an employment contract with an employee due to professional unsuitability. To do this, the employer has a month from the day he received the opinion of the elected trade union body.
There are some nuances associated with ensuring that the termination of an employment contract with the consent of the elected body of the trade union is legal. The head of the organization must prove the fact that representatives of the trade union did not object to the grounds for dismissal that he outlined when requesting the opinion of the trade union. It is this reason that must be indicated in the order to dismiss the employee from office.
Also, when considering cases of this nature, judges pay attention to compliance with the deadlines specified in Art. 373. It is necessary that the contract with the employee be terminated within a month after the opinion of the elected body of the trade union has been received. This period does not include periods when for any reason a person was absent from work, but at the same time continued to be officially registered in his position (was sick, was on vacation, etc.).
The Labor Code does not contain specific instructions on what period is given to the head of the company to dismiss an employee whose unsuitability has been resolved by contacting a trade union. Therefore, when considering such cases, judges take as the maximum period a month from the day the employer received the consent of the trade union representatives with the reason for termination of the contract, as specified in Art. 373.
If an employer has issued an order to dismiss an employee, but has not previously contacted the trade union to obtain consent to such a step, or has not secured the support of representatives of the elected body of the trade union confirming the specialist’s professional incompetence, this is considered a violation of the law. In this case, the dismissal order is invalidated and the employee is reinstated to his previous place of work.
- Compensation and payments.
As for specialists who are disabled (clause 5 of Article 83 of the Code) and refuse to be transferred to another place of work (clause 8 of Part 1 of Article 77 of the Code), they are entitled to a benefit in the amount of the average salary for two weeks.
- What entries are made in the work book upon dismissal?
The note in the work book is dated the day the employee was dismissed.
The entry is assigned a serial number, it indicates the number of the dismissal order and provides a link to the rule of law that served as the basis for termination of the employment contract.
- Dismissal while on sick leave.
The Labor Code of the Russian Federation establishes that an employer cannot legally dismiss a person who is on sick leave.
Dismissal can be initiated by the employee himself. To do this, he must notify his supervisor two weeks in advance. And if you have to take sick leave during this period, this will not affect the further process in any way.
On the day indicated in the application, the employee may be dismissed. In this case, no detentions are assigned.
- Sick leave after dismissal.
The possibility of paying sick leave after dismissal is fixed in the law on compulsory social insurance in case of temporary loss of ability to work and in connection with maternity. The conditions for receiving the money are as follows: the employee fell ill less than a month after dismissal and did not have time to find another job during this time.
Regardless of the length of stay on sick leave, the payment should be 60% of earnings.
- Payment of sick leave.
The employer is obliged to pay for sick leave if it was opened before the termination of the employment relationship or closed after termination of the contract. Presentation of this document for payment is possible within six months.
- Dismissal on the last day of sick leave.
Termination of a contract initiated by an ill employee is subject to the same rules that apply in other cases. That is, an employee can be fired on the last day of his sick leave if he warned the manager about this two weeks in advance.
At the same time, the employer does not have the legal right to pay the employee in this way on his own initiative, which is confirmed by Art. 81 of the Code.
How to reduce costs when dismissing an employee for incompetence
When an employee is fired, the company incurs certain costs.
Read in the electronic magazine “General Director” how to calculate the amount of these costs and reduce them as much as possible.
Calculate and reduce costs
How to dismiss an employee for unsuitability at the initiative of the employer
If an employee does not fulfill his job duties, or if he does not have sufficient qualifications or education for the job, the employer has the right to dismiss him for unsuitability. In this case, first of all, the employer is obliged to prove the fact that the employee lacks professional suitability. This fact can be expressed both in matters of compliance with formal requirements - for example, if the legislation provides for the mandatory presence of a certain education for workers in specific positions, and in the actual non-fulfillment or incomplete fulfillment of the duties assigned to the worker.
The procedure for dismissal due to unsuitability, in accordance with Article 81 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, should generally be as follows:
- The employer receives grounds to initiate the dismissal procedure. This may be a report that reflects the employee’s failure to comply with standards, a complaint from clients, other employees or third parties, an entry in the complaint book, an order from the labor inspectorate, or other documentary evidence of the fact of existing professional incompetence.
- Based on evidence of unsuitability, the employer issues an order to dismiss the employee. This employee must be familiarized with the order, and a separate act on familiarization must be drawn up - it will be required if the employee wants to challenge the entire dismissal procedure. The act is drawn up in the presence of two witnesses, who must also sign it, and if the employee refuses to familiarize himself with the order, then they must sign an act of refusal to familiarize himself. If necessary, the employee has the right to demand that the employer give him a copy of the order.
- Based on the order, on the day of dismissal, the employee is given his work book with a record of dismissal due to inadequacy of the position held, or failure to fulfill job duties. The employee is also issued a certificate of income.
- After issuing the work book, it is also necessary to ensure final settlement with the employee - to issue him the salary due to him and compensation for unused vacation days.
It should be noted that the specific conduct of the dismissal procedure for unsuitability may differ, since unsuitability may imply different grounds for dismissal:
- Inconsistency with the position held. In this case, the employer is obliged to ensure that the employee’s qualifications are checked, and the employee himself has the right to undergo such verification independently in a certification center accredited for this procedure.
- Gross violation of labor discipline. These may include absenteeism, being drunk at work and other serious offenses.
- Repeated violation of labor discipline. If disciplinary sanctions have been taken against the employee previously, then a second disciplinary sanction in the form of a reprimand or reprimand within one year is a legal reason for dismissal.
Some categories of workers cannot be dismissed due to unsuitability. In particular, these include pregnant women. Women raising children under 3 years of age also have certain restrictions on dismissal, as well as minor employees - their employer can dismiss them only if these actions are agreed upon by the commission on minors' affairs.
Step-by-step dismissal procedure if the employee is declared completely disabled
If the medical board assigned the first disability group to an employee, this means that he has completely lost the ability to work. He has no possibility of transfer to another position.
Step-by-step instructions for dismissing such an employee are given below:
- obtain a certificate of disability from the employee;
- issue an order to terminate the employment contract based on the provided medical report;
- register the order in the internal correspondence journal;
- familiarize the subordinate with the order against signature;
- on the day of the actual termination of the employment relationship, make a full financial settlement with the employee and give him a completed book.
In case of complete loss of ability to work, the subordinate is dismissed under the fifth paragraph of Article No. 83 of the Labor Code. In this case, working off for two weeks is not established.
Dismissal due to unsuitability for health reasons
If the work is harmful or dangerous, and also contains other certain factors that impose health restrictions on the employees performing it, a deterioration in the employee’s health may be grounds for dismissal. So, if an employee receives a medical certificate confirming his unfitness for work, the employer’s procedure in this case will be as follows:
- The employer is obliged to offer the employee to transfer to another position in the enterprise.
- If the period during which the employee has medical contraindications to work is less than four months, if the transfer is refused, or if there are no positions at the enterprise, the employee should be suspended from work without pay. Dismissal in this case is prohibited by labor legislation.
- If the employee must be transferred for a period of more than 4 months, or permanently - due to a long-term change in health status or the impossibility of treatment, then in case of refusal to transfer to another position or in the absence of positions suitable for him in terms of health and qualifications at the enterprise , he may be fired by the employer.
- It should be noted that professional incompetence for health reasons must be confirmed by a medical report. Moreover, such a conclusion can either be voluntarily provided by the employee to the employer, or be requested by the employer if local regulations or legislation require the employee to undergo a periodic medical examination or an extraordinary medical examination.
Various categories of employees may be dismissed due to incompetence for health reasons. This dismissal is not considered to be carried out at the initiative of the employer, therefore the restrictions in force by law on the dismissal of certain categories of workers in this case do not apply. However, it will still not be possible to get rid of a pregnant employee in this way - the employer does not have the right to fire her, even if her situation does not allow her to carry out work activities.
The employer should confirm the fact that the employee is familiar with the positions available at the enterprise and record his refusal to be hired for these positions if a dismissal procedure is being carried out due to unsuitability due to health conditions. Otherwise, the employer will not have factual evidence in the event of a possible challenge to the dismissal procedure by the employee.
How to conduct certification according to the law
The rules for this procedure describe:
- Labor Code of the Russian Federation: Art. 81;
- letter from Rostrud dated 1028-c “On the dismissal of an employee due to insufficient qualifications.”
If a manager wants to prove an employee’s professional incompetence, HR employees need to conduct certification using the following recommendations:
- Make sure that the company has local regulations, such as “Regulations on Certification”, “Regulations of the Certification Commission”, etc., which describe the rules for carrying out this procedure. Employees must be familiarized with these documents upon signature.
- Check whether there are job descriptions for each of the positions for which certification will be carried out. The fact that employees are familiar with them is also confirmed by their signatures.
- Record the decision to conduct certification for the selected positions by order of the director. Familiarize employees with this document.
- Consider the possibility of participation of trade union representatives in the work of the certification commission and how their opinion will be taken into account when summing up the results.
- Organize the work of the commission, in particular, determine the list of skills that a person in a certain position should have.
- Certification must be carried out within the time period specified in the regulations of the organization. After this, a decision must be made regarding those employees whose incompetence was confirmed during the audit.
- It is worth preparing documents related to the transfer of dismissed employees to other positions. If they refuse to change jobs, this also needs to be recorded in writing.
The practitioner tells
Professional incompetence is one of the main reasons for the dismissal of employees in Russian companies
Evgenia Sarycheva , deputy editor-in-chief of the magazine “Commercial Director”
About half of domestic companies practice dismissing managers due to the fact that they cannot cope with their responsibilities and show insufficient results.
The main reasons for professional incompetence are considered to be a low level of motivation, as well as laziness and irresponsibility. Hiring people who are unable to cope with the position becomes possible due to the mistakes of personnel officers who, during the interview, do not notice the shortcomings of applicants. In most companies, candidate assessment methods are used incorrectly, which results in errors in the selection of employees.
Possible consequences of dismissal due to unsuitability for an employee
Dismissal due to professional incompetence is an extremely unpleasant occurrence for an employee, at least if the professional incompetence is not due to medical reasons. Due to the fact that a notice of dismissal is entered in the work book with a description of the full wording, the fact of failure to fulfill job duties or violation of discipline can become an extremely negative aspect in matters of subsequent employment, significantly spoiling the labor and career path of the employee himself.
However, in practice, you can get rid of this wording in the work book in several ways:
- Resign of your own free will. Many employers themselves offer their employees, if disagreements arise, to write a letter of resignation of their own free will. However, in this case, the employee almost completely loses the opportunity to subsequently challenge the dismissal and protect his rights in court.
- Dismissal by agreement of the parties. In this case, the employer can enter into an agreement with the employee. This entry in the work book, on the contrary, indicates the employee’s contact and is not negative. Moreover, the agreement itself can establish almost any possible conditions for termination of the employment contract.
- Opening a new work book. Despite the fact that maintaining two work books is not a good practice, the law also does not prohibit employees from having several such documents.
- Challenging dismissal in court. The court may declare the dismissal illegal - however, in this case, the burden of proof falls directly on the parties to the labor relationship. By a court decision, an employee can achieve either reinstatement at work with payment of compensation, or simply change the wording of the entry in the work book.
Kunitsky Igor Sergeevich
What should a certificate of unsuitability contain?
There is no certificate of professional incompetence. There is a certificate of professional suitability Based on the results of passing a mandatory medical examination by a medical commission for professional suitability for professions, a conclusion is drawn up (clauses 12, 31 of the Order of the Ministry of Health and Social Development dated April 12, 2011 No. 302 n). The conclusion indicates (clause 13 of the Order of the Ministry of Health and Social Development dated April 12, 2011 No. 302 n): the date of its issue; last name, first name, patronymic, date of birth, gender of the person applying for work (employee); employer's name; name of the employer's structural unit (if any), position (profession) or type of work; name of the harmful production factor (HF) and (or) type of work; the result of the medical examination (medical contraindications were identified or not identified). The conclusion is signed by the chairman of the medical commission indicating the surname and initials and certified by the seal of the medical organization that conducted the medical examination. The conclusion is drawn up in 2 copies (for the employee and for inclusion in the outpatient medical record).
You should not seek a reduction. And how do you imagine this? You simply do not write a letter of resignation of your own free will. And then look at the grounds on which you are being fired, and if you are not satisfied with it, go to court. Of course, this is the case if the employer does not listen to the voice of reason.
You need to complain to the prosecutor's office. According to Federal Law of the Russian Federation No. 59-FZ, the complaint is written in any form (in your own words), or you can order it in a personal message to a lawyer, submitted by mail or delivered in person.
How does dismissal for health reasons occur under the Labor Code of the Russian Federation?
Last modified: March 2019
Can they be fired due to unnecessary reasons? – the question that arises among working citizens has a positive answer only with official medical confirmation and compliance with certain regulations, since the employer’s view of dismissal for health reasons can differ significantly from the view of labor law.
The resulting diseases, leading to consequences in the form of long-term, turning into permanent inability to perform work duties, are a sentence that turns a previously in-demand employee into a “waste material” that has become a burden.
Legal aspects
Termination of an individual contract due to health reasons that does not allow the performance of official functions, based on a verdict rendered by the employer, is categorically prohibited by the adoption of Law No. 90-FZ of June 30, 2006, which excluded the allowing subclause from Article 81 of the Labor Code.
However, the law provides for dismissal for health reasons if it is impossible to continue fulfilling the assigned obligations. Disability and termination clause depend on the circumstances:
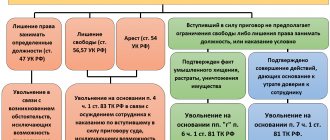
- Statement of complete loss of ability to work, accompanied by disability. There are no alternative options for dismissal; according to a medical report, it is done in accordance with paragraph 5 of Art. 83 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, an entry in the work book with the issuance of a preliminary order.
- Statement of partial loss of labor functions and the need to provide work that simplifies labor functions due to deteriorating health. Rejection of a transfer proposal by an employee or the absence of a sought-after suitable vacancy based on a medical certificate is grounds for termination of the contract under clause 8 of Art. 77 Labor Code of the Russian Federation.
Both articles stating the illness of an employee are united by the Labor Code by the main legal fact - the presence of a medical report. Neither the employer, observing the poor health and decline in the employee’s performance, nor the employee due to deteriorating health, nor the mutual consent of the parties, allows dismissing a citizen from work with reference to professional incompetence due to illness.
The procedure for issuing relevant conclusions was approved by Order of the Ministry of Health of the Russian Federation No. 441n dated May 2, 2012 and includes an examination and substantiation of conclusions for the implementation or imposition of a ban on certain types of work activities.
An employer who does not have the appropriate education and is obliged to make a decision on transfer or dismissal specifically for medical reasons in the absence of specifics or the presence of controversial issues is allowed to contact the institution that issued the conclusion for written explanations. Incorrect registration or refusal to specify, for which the doctor can be fired, is fraught with liability for the organization. Additional consultation in each specific case is the responsibility of doctors, since the standard list of diseases that serve as reasons for dismissal is approved only for military units.
If an employee “falls short” of the clauses of termination of the contract based on medical criteria, and cannot continue to carry out production activities due to illness at the proper level, then the law allows for voluntary dismissal for health reasons. The presence of diseases is an additional factor in “beautiful care” even in the case of obsolete industrial relations.
Medical indications for dismissal
All diseases reduce a person’s ability to work.
But not every pathology deprives a citizen of the ability to work. There are three disability groups. The first one is considered non-working. The second and third categories indicate that the employee has partially lost the ability to work and requires organization of work in accordance with certain conditions.
The first group of disability indicates that serious disorders have occurred in the human body, causing difficulties with movement, communication, self-care, etc.
As a rule, conditions for which group 1 is given can be caused by the following pathologies:
- hematological diseases;
- cancer;
- deafness;
- limb amputation;
- complete loss of vision;
- paralysis;
- muteness.
The second group of disabilities is characterized by quite noticeable health problems, examples of which include dysfunctions:
- CNS;
- Gastrointestinal tract;
- cardiac systems;
- urinary system;
- visual or auditory analyzers.
An indication for dismissal is the inability of a subordinate due to health reasons to perform the same work or lighter work due to the risk of deterioration of health or injury.
The basis for dismissal is the conclusion of the medical commission.
Algorithm for dismissal due to health reasons
The procedure for terminating an individual contract in the event of a general illness is clearly regulated and is based solely on an analysis of the health status and physical capabilities of the employee, and not on mutual claims of the parties.
To terminate a relationship, a step-by-step procedure is provided for refusal to transfer to a position that has no contraindications in accordance with Article 73 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, including:
- The employee undergoes a medical examination and provides the results of the conclusion of the MSEC or a specialized commission. The establishment of disability or an indication of professional incompetence must be recorded.
- Removal from position followed by:
- dismissal if it is impossible to continue any activity based on a medical opinion;
- offering a list of vacancies that meet health conditions.
- Refusal of alternative. It is important to have written confirmation of the vacancy and the applicant’s non-acceptance, after which:
- The employee retains his job for 4 months without accrual of salary;
- the pregnant woman retains not only her job, but also payment of average earnings for the entire period;
- A managerial specialist, including directors, first deputies and chief accountants, does not retain a position and is dismissed immediately.
- Time to recover. If, according to medical forecasts, the rehabilitation period is envisaged for a period exceeding 4 months, then the employee is dismissed immediately. This is true both in the absence of alternative vacancies, and in case of refusal of the proposed options, including demotion and reduction in cash payments.
- Application for dismissal due to health reasons. The document is accompanied by medical reports confirming the impossibility of continuing the relationship. Who should I write a statement to? Even in case of refusal of the provided vacancies, a sickness statement with reference to a medical examination is written in the name of the first person of the employer.
- Issuance of an order. Regardless of the preamble, the sample order must contain a reference to the relevant “medical” articles of the Labor Code, since the absence exempts the enterprise from additional compensation payments.
Failure to comply with the algorithm and unauthorized performance of the functions of a medical institution by the employer personally in terms of recognizing the employee’s professional incompetence for health reasons leads to losses in lawsuits. Download
Sample order of dismissal for health reasons (31.0 KiB, 131 hits)
Judicial practice knows cases where failure to fulfill official duties was punishable by dismissal for medical reasons without providing the employee with the right to an explanatory note. The courts recognized such measures as illegal, and the actions of employers as exceeding their official authority.
When can you fire an employee due to unsuitability?
Inconsistency with a position is understood as an employee’s inability to perform job duties correctly for objective reasons.
The main reason is inappropriate qualifications and professional incompetence .
The Labor Code allows the dismissal of an employee at the initiative of the employer under the mandatory and simultaneous presence of two conditions:
- insufficient qualifications of the employee, confirmed by an unsatisfactory certification result;
- lack of possibility of transfer to another position.
Dismissal is considered legal if the following conditions are met:
- The company conducted personnel certification, which confirmed the lack of qualifications.
Important! Dismissal of an employee without certification results is not permitted.
The procedure for testing employees is determined by the internal regulatory documentation of the enterprise. A special commission is created for certification.
The conclusions of the certification commission are assessed in conjunction with other evidence in the case. For example, failure to meet production standards.
Despite the fact that the employee’s inadequacy is determined by the commission, the decision to dismiss can only be made by the employer himself.
Important! The employer has the right to decide not to dismiss an employee, even if the commission finds him unsuitable for the position.
- It is not possible to transfer the employee to another place, or he himself refused the transfer. The employer is obligated to offer all possible positions that meet the qualifications.
- The employee does not belong to the preferential category: pregnant woman; single parent, guardian, trustee raising a child under 14 years of age (disabled person under 18 years of age).
If all of the above conditions are met, the employer has the right to carry out the procedure for terminating the employment contract at the initiative of the employer.
Which article of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation applies to an employee?
When dismissing an employee for non-compliance with his qualifications and position, the employer relies on clause 3 of part 1 of Article 81 of the Labor Code.
How to apply - step-by-step instructions
The employee has the right to challenge the employer’s actions in court and be reinstated at his place of work. However, this will be almost impossible to do if the employer carries out the dismissal procedure correctly.
To do this you need to adhere to the basic rules:
- When hiring personnel, they must be familiarized with the job description and signed.
- The enterprise must have an approved order for certification.
- The employee must be notified in advance and against signature of the certification.
If a worker, for objective reasons, cannot attend a meeting of the commission and confirms this in writing, the certification is postponed for a period no later than two weeks from the previously appointed date.
- The employee is familiarized with the decision of the commission against his signature.
- The result of the certification must be documented in the form of a protocol.
- Based on the decision of the enterprise commission, an order is issued to improve the quality of work. Advanced training courses are conducted for employees. On the recommendation of the commission, he may be transferred to another position where the level of his knowledge will be sufficient.
- If the transfer is refused, the employee is allowed to be dismissed. Therefore, it is recommended to formalize both the transfer offer and the employee’s refusal in writing.
- After receiving the refusal, the employer issues a dismissal order using the unified T-8 form.
It is allowed to use another form of order , but with the designation of mandatory details:
- Company name;
- date and order number;
- dismissal order and date of dismissal;
- document's name;
- who needs to be fired: name, position and structural unit;
- on what basis is the dismissal carried out;
- executive visa;
- the employee’s signature and date indicating familiarization with the order.
It is mandatory to familiarize the employee with the order
If the employee refuses to sign the order,
a statement of refusal is created. At least two witnesses are invited to sign it.
Next you need to do the following:
- The HR officer closes the employee’s personal card. The dismissed person must also put his signatures on it (in specially designated sheets). The specialist also makes an entry in the work book.
- The payroll accountant makes the calculation and prints the calculation note.
- On the day of dismissal, the employee must receive a full payment and work book.
The calculation consists of wages for hours worked, as well as compensation for unused vacation.
Additionally, the employment contract may provide for other payments. Also, before paying the required amounts, the accountant makes all required deductions: personal income tax, alimony and others.
Important! Withholdings by order of the enterprise are made at a maximum of 20%. If the employee remains in debt and has no intention of repaying it, the employer has the right to file a lawsuit in court demanding collection of the debt.
If the employee does not appear on the day of dismissal for documents, the employer sends a notice to him with a requirement to pick up the work book or send written permission to send the document by mail (by registered mail with acknowledgment of delivery and an inventory of the attachment).
If the employer fails to notify the employee in writing, he may be subject to liability.
Then he will have to pay a fine and compensation to the worker.
Additionally, on the day of dismissal, the employer issues certificates: 182-N, SZV-M and SZV-STAZH.
If an employee needs other certificates, he has the right to make a written request, and the employer will issue them within 3 days.
Useful video
The procedure for dismissing an employee who has not passed workplace certification is described in detail in this video:
Categories of citizens
The dismissal of citizens, depending on their status due to deteriorating physical health, has features determined by labor legislation, federal laws and clarifications, and internal local documentation providing for the establishment of guarantees and compensation.
Pregnant woman
Termination of an individual contract with pregnant women is prohibited at the initiative of management, and in case of expiration, it is subject to extension until the end of pregnancy in accordance with Article 261 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation. The basis is to write a statement of intent to continue labor cooperation and provide a certificate from the antenatal clinic confirming pregnancy every three months.
An exception is a complete reduction in staff due to the liquidation of an organization or structural unit. A woman can quit if she has her own desire, while the employer has no right to initiate termination of the contract.
If a woman became aware of her pregnancy after writing her resignation letter, then the two-week rule allows her to withdraw it. If you refuse the proposed options, the pregnant woman will retain her average earnings.
Single mother and mother of many children
Even professional incompetence caused by illness does not allow dismissing a woman of this category on the basis of Article 261 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation.
This can be done if one of the following conditions exists:
- the level of professionalism as concluded by certified commissions does not correspond to the position held;
- structural changes carried out at the enterprise include a change of owner and reduction of staff positions;
- complete disability confirmed by a medical examination.
Pensioner
Legislation equalizes the category's rights with others. Question: can a pensioner be laid off using this wording? It amounts to discrimination.
You can dismiss a pensioner in the same way as other categories of citizens:
- when establishing absolute professional incompetence by a medical institution;
- after refusing the provided vacancies due to partial loss of ability to work.
Release from a position based on the results of a medical examination gives the right to receive severance pay and parting with the employer without working out. However, in the case of an employee acting on an “expressed desire” under pressure from the employer, these guarantees do not apply.
Serviceman
Termination of a contract with a military personnel occurs on the basis of a decision of a medical military commission, with the establishment of a category of suitability for military service of a certain type in accordance with the list of diseases.
The officer writes a corresponding report on transfer to another position corresponding to the rank and not contraindicated by a medical opinion, or dismissal addressed to the immediate head of the military unit.
Compensation payments
On the final day of the production relationship, a full settlement is made with the employee, and the following payments are made upon dismissal for health reasons:
- basic and additional salary for the current month;
- monetary compensation for earned and unused vacation rights;
- severance pay in the amount of two weeks' average earnings on the basis of Article 178 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation.
For military personnel, the amount of severance pay is:
- for a service period of up to 20 years – two official salaries;
- with a service life exceeding the 20-year mark - seven official salaries.
If internal local documents provide for additional payments, including compensation for treatment, financial assistance for recovery and rehabilitation, then they have legal force and oblige the employer to carry out measures.
Forced termination of labor relations due to the inability to continue production activities under the influence of disease factors is an unpleasant and painful procedure for the parties. Therefore, carrying out the meeting taking into account compliance with the regulations will allow us to “smooth out the rough edges” and part on the highest possible “major note” in the material and moral aspects.
Video consultation from Elena Anatolyevna Ponomareva - teacher at the Educational Center Alternative:
Professional unsuitability for a specific profession
⇐ PreviousPage 2 of 5
They talk about professional incompetence in cases where there are deviations in the state of health that, from the point of view of doctors, are incompatible with work in a particular field of activity. However, contraindications may not only be medical. There is a whole group of professions that require special abilities. For example, if a person does not have the ability for fine arts, he is unlikely to become a good artist, architect, or sculptor.
Direct professional incompetence is visible to the naked eye - unfortunately, we come across such examples all the time.
Hidden professional incompetence is not so obvious - a specialist can remain at the required professional level at the cost of great neuropsychic stress, compensating for the lack of some necessary qualities with others. The degree of tension depends on the nature of professional functions, the individual characteristics of a person, the motives of his behavior, experience, knowledge, skills and abilities.
9Specifics of educational and professional training of psychologists.
Today, in the context of constant reform of the higher education system, the issues of training qualified psychologists are becoming extremely important. It is worth noting that currently the number of universities offering training in psychology is in the hundreds, and the number of graduates is in the thousands. But, oddly enough, there are not enough people capable of providing qualified psychological services in various fields. Thus, today in Russia there is an acute shortage of qualified psychologists. It follows that we need to understand what are the features of the professional training of psychologists in universities and identify the difficulties that arise during its implementation.
We believe that an important limitation that arises on the path to training a professional psychologist is that, when entering a university to study psychology, yesterday’s student is guided to a greater extent by the results of final exams, the prestige of the profession, the recommendations of others, and to a lesser extent by his own personal characteristics, which act as the basis for the formation of professionally important qualities.
Undoubtedly, one cannot but agree with the position of S.L. Rubinstein, who believed that “by actually being carried out in various types of specific activities, mental processes are formed in them.” At the same time, there is reason to believe that having some basis for the development of certain qualities, it will be easier for a person to form them, and the quality of these new formations, their strength will be higher than if the person did not have the initial prerequisites for the development of certain traits.
An important feature of today's system of higher education, in general, and the professional training of psychologists, in particular, is its focus primarily on practice. The emphasis is on teaching the student specific techniques used in the work of a psychologist. Today, psychology has become a predominantly practical field. There is no doubt that without knowledge of individual ways of working, a psychologist will not be able to solve the professional task facing him. Practice is not only necessary, it is necessary. But this approach has a number of limitations and even dangers, both for the psychologist himself and for customers of psychological services.
First of all, it is necessary to remember the inextricable unity of theory and practice. Before solving an existing professional problem, it is necessary to understand its essence, evaluate the available resources, determine solutions, and only then select an adequate method of action and get to work. In order to successfully cope with the first three stages, a psychologist needs to learn to think psychologically: to competently operate with concepts, build various models of mental reality, in a word, to form a specifically psychological way of perceiving reality. And this is only possible in case. If the student, from the very beginning of his studies, receives a variety of knowledge in the field of theory and methodology of psychology, as well as related sciences.
In addition, theoretical training allows the future psychologist to develop professional preferences and interests, which determines his cognitive needs.
As already mentioned, under the influence of mastering various theories, the thinking of the future professional is formed: he learns to analyze, compare, classify, compare, separate the main from the secondary, etc. These skills are designed to help him solve a wide range of problems.
It is also important to note that practical mastery of the methods of practical activity of a psychologist allows one to assimilate already existing methods of action, while knowledge of theoretical and methodological foundations allows the psychologist to construct new ways of solving assigned problems. This is especially important due to the fact that in the real work of a psychologist, typical tasks for which certain solutions have been prepared practically do not exist. Each situation is unique and original, therefore the psychologist is required to be constantly creative in choosing methods of work.
The most important ethical principle of psychology is the principle of non-harm. Therefore, the psychologist is required to be able to select methods of action that are adequate to the task at hand. And for this you need to know what theoretical principles and methodological principles this or that method is based on. Otherwise, there is every chance of causing harm to the customer.
Thus, we note the need to train student psychologists not only in practical skills, but also in the theoretical and methodological foundations of psychology.
It can be noted that at the beginning of training, as a rule, predominantly theoretical disciplines are taught, and at later stages of professional training, the emphasis is on practice-oriented courses. Perhaps this is due to the fact that initially there is a need to develop in students a psychological way of thinking and perceiving reality. And on this basis, to form a specialist who is not only knowledgeable, but also able. It is also important to note that at the beginning of training, the student adapts to a new social position, accepts the norms accepted in the professional environment, on the basis of which the formation of professionally important qualities and the development of the personality as a whole occurs in the future.
A professional is an active, responsible and free subject in choosing the means of his activity. Consequently, a qualified psychologist must be able to express himself creatively and realize his competencies in a non-stereotypical form. Therefore, as part of various courses, psychology students are offered a variety of creative tasks that allow them to “revive” theory and learn to think outside the box.
In the process of professional training, personal development of students inevitably occurs, the source of which is educational and professional activity as the leading one.
V.Ya. Lyaudis gives a central place to joint productive activity that arises when jointly solving creative problems, and considers it as “a unit of analysis of the formation of personality in the process of learning.” A system of joint activities can be considered normal when all its components are interconnected: the attitude of students to the goals and content of learning, the attitude of students among themselves and towards teachers; conditions in which educational activities take place.
V.A. Ivannikov established the phase nature of educational activity.
In the first phase, the current situation is comprehended, the overall readiness to perform long-term mental work increases, and organization increases. This phase marks the development of such qualities as hard work, perseverance in achieving goals, attentiveness, self-organization, curiosity, etc. There is an interest in studying certain sciences.
The next phase is a period of sustainable adaptation, when the goal is fully realized and the prerequisites for its implementation appear, the entire system of activity levels comes into line with the main goal of learning. In this phase, qualities are formed that characterize the development in students of general professional skills necessary for a future specialist, a sense of self-esteem and a sense of social duty develop.
Based on various studies by O.K. Sokolovskaya highlights the main psychological features of the formation of the professional position of psychology students:
professional position develops as a result of educational and professional activities, contributes to the active acquisition of knowledge, skills and abilities for further professional activities;
uneven nature of development in the development of the professional position of psychology students; latent and crisis periods are observed;
under equal conditions created by the university, students develop different types of professional positions; some students, after graduating from a higher educational institution, plan to work in their specialty, others prefer other professions not related to the specialty obtained at the university
It is important to note here that only external conditions can be called equal, while the future professional position of a psychologist is largely determined by intrapersonal factors: characteristics of the motivational-need sphere, orientation, value orientations, personal meanings, etc.
It should be especially noted that the profession of a psychologist involves constant replenishment of knowledge and mastery of new competencies, since the psychologist works with people, and they respond to socio-economic transformations with personal changes. Therefore, the task of a psychologist is to be sensitive to innovations in science and practice. Therefore, an extremely important skill that is acquired in the learning process is the ability and desire to engage in self-education.
So, today, the professional training of psychologists in universities should include a harmonious combination of a knowledge component, represented by the theoretical and methodological foundations of psychology, and a practical one, which consists of introducing students to specific methods of practical activity of psychologists and acquiring primary experience of their application in educational situations.
In addition, such training, which involves a creative approach to solving problematic problems, occupies a special place in the training of future psychologists. During this process, the formation and development of professionally important qualities of a psychologist occurs, as well as the personality of the future professional, his interests and professional position.
Related topics:
- Dismissal during liquidation How dismissal during liquidation of an organization is regulated - article of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, lawsLegal regulation of issues related to...
- Liability for illegal dismissal Legal consequences for the employer If the court satisfied the plaintiff’s demands, then the defendant is obliged to: reinstate the employee to his previous position...
- Dismissal without service for a pensioner When you can resign without service at your own request in 2019An important guarantee for the employer of his rights...
What is professional suitability?
People differ from each other in their personal qualities.
And among these qualities there are those that are professionally valuable. For example, attentiveness and composure, quick reaction and the ability to act clearly in extreme situations are important for the driver; the teacher must have a penchant for working with children and developed communication skills; the surgeon must be decisive, careful and precise. Thus, for each profession, you can make a list where professionally valuable qualities will be indicated. Any professional activity puts forward certain conditions and requirements in terms of the required level of suitability for it, which imposes a number of restrictions on the choice of a particular profession. If the requirements imposed by a profession on a person coincide with his personal qualities and capabilities, then they speak of professional suitability.
Professional suitability is a set of psychological and psychophysical properties, as well as special knowledge, skills and abilities necessary to achieve acceptable labor efficiency. The concept of professional suitability also includes the satisfaction experienced by a person in the process of work itself and when evaluating its results.
Experts define professional suitability as the mutual suitability of a person and his profession. This is the degree of compliance of a person’s professional capabilities with the requirements of the profession, the ratio of the level of development of a professionally important quality to the level of the requirements of the profession.
Professional suitability is manifested in the fact that a specialist is able to successfully master a complex of knowledge, skills and abilities, creatively perform job functions, while showing independence, courage and initiative, experiencing a sense of moral satisfaction not only from the results, but also from the process of activity itself.
The essence of the category of a person’s professional suitability is that it reflects:
- choosing the type of activity (profession) that most fully corresponds to the inclinations and abilities of a particular person;
- satisfaction of interest in the chosen profession and satisfaction with the process and results of specific work;
- a measure of assessing the ability and readiness to work, efficiency, reliability, safety of performing labor functions, an individual measure of labor productivity;
- one of the manifestations of social (professional) self-determination of an individual, his self-affirmation, self-realization, self-improvement in work;
- development of the “I-concept”, the emergence and formation of the image “I am a professional” and the desire of the subject of activity to achieve the standard model of a professional.
The modern view of professional suitability is that it is formed in work activity, in the course of mastering a profession, and is not given to a person initially, as some kind of innate quality. To master professional skills, appropriate abilities are required, on the basis of which knowledge and skills are formed, as well as a propensity to work, that is, positive professional motivation. At each stage, the profession makes certain demands on thinking, memory, attention, motor skills, and other mental functions and personality qualities. Under the influence of these requirements, in the course of mastering a profession, professionally important qualities and human abilities are formed, which ensure the development of the necessary skills, knowledge, and abilities that determine qualifications and mastery.
Different professions make different demands on a person: some - on his typological and psychophysiological characteristics, others - on mental processes, and others - on personality traits. Thus, each profession “addresses” demands to different structures of a person’s personality.
Thus, professionally important qualities of a doctor are high responsibility, absence of conflict behavior, tolerance, empathy, ability to establish contact with patients, low level of anxiety, composure, ability to concentrate and make decisions, quickly and adequately navigate difficult situations.
Any person is suitable for any profession if he has professionally important qualities that are the key to success in a particular chosen profession or type of profession. But certain restrictions still exist when choosing professions, and they must be taken into account. A special role here is played by such natural prerequisites as the health and properties of the human nervous system. It is not for nothing that a person, before getting a specific job, must undergo a medical examination to find out whether he has any medical contraindications that will prevent him from effectively working in his chosen profession.
A person’s professional suitability must be understood as the mutual suitability of a specific person in a specific area, the use of his forces at a specific time. Questions of professional suitability should always be considered individually.
Degrees of professional aptitude
Unsuitability. This characteristic is spoken of when there are deviations in health that are incompatible with work. This means that activities in this area can worsen a person's health. However, contraindications can be not only medical, but also psychological (certain persistent personal qualities that may interfere with obtaining a certain profession).
In addition, there is a whole group of professions that require special abilities. For example, if a person does not have the ability for fine arts, he is unlikely to become a good artist, architect, or sculptor.
Direct professional incompetence is visible to the naked eye - unfortunately, we come across such examples all the time.
Hidden professional incompetence is not so obvious - a specialist can remain at the required professional level at the cost of great neuropsychic stress, compensating for the lack of some necessary qualities with others. The degree of tension depends on the nature of professional functions, the individual characteristics of a person, the motives of his behavior, experience, knowledge, skills and abilities.
Suitability. Suitability is characterized by the absence of contraindications to work in a particular area, but it does not mean clearly expressed inclinations. In other words, there are no contraindications, but there are no obvious indications either. “You can choose this profession, it is possible that you will become a good specialist” - this is approximately how one can characterize this degree of professional suitability.
Correspondence. This concept means that there are no contraindications, and there are some personal qualities that meet the requirements of the profession. For example, there is a expressed interest in certain objects of labor (technology, nature, people, art) or successful experience in this field. At the same time, compliance with other professions is not excluded.
Vocation. This is the highest level of professional fitness. It is characterized by the presence of clear signs of a person’s compliance with the requirements of the chosen profession. We are talking about the characteristics by which a person stands out among his peers and colleagues who are in equal conditions of learning and development. This degree is most often revealed in the process of work.
A professional calling is not only an absolute coincidence of the requirements of the profession and the personal, physiological, and intellectual characteristics of a person, but also a pronounced interest in this type of activity, bordering on love.
Not everyone is given the opportunity to find their calling. And not at all because some people know how to search, while others do not. At all times there were only a few creators and professionals in their field, and they were valued like gold. If someone seems that this level is inaccessible to him, do not give up: firstly, you are only at the very beginning of your professional path, secondly, you still do not know what you are capable of, and thirdly, outstanding success these people achieved thanks to work motivation, that is, an incentive to action.
It should be noted that the determination of the degree of suitability is based on taking into account a number of individual characteristics of a person (psychological, educational, professional, medical, etc.), the unsatisfactory state of each of which may be the cause of insufficient suitability and a contraindication for certain professional activities.
Types of vocational suitability
Professional suitability determines the level of profession requirements for performers. These requirements can be absolute or relative. There are two types of professional suitability:
- absolute (for professions of this type that require special abilities and impeccable health: healthy nervous and mental systems, good vision and hearing, good function of the musculoskeletal, vestibular apparatus, etc.);
- relative (to professions, mastery of which is accessible to almost any healthy person).
Absolute professional suitability is characterized by certain natural characteristics that are difficult to develop. These features depend, first of all, on the characteristics of the nervous system (the basic properties of the nervous system, such as the strength and mobility of the processes of excitation and inhibition, their balance).
Relative professional suitability includes qualities that can be formed under appropriate conditions and desire (motivation) of a person.
There are professions where relative professional suitability is acceptable, although undesirable, but in some types of activities it is unacceptable - where absolute professional suitability is required. With absolute professional suitability, a person must meet the strict requirements of the profession, while relative professional suitability is typical for most professions.
Sometimes professional suitability is defined as the absence of contraindications (somatic or psychological to a given profession).
Thus, in some professions, the requirements for professional suitability are high if there are some absolute contraindications to the profession. For example, the profession of a pilot is absolutely contraindicated for people with increased fatigue in monotonous conditions. Professions that require self-control are contraindicated for people who are unbalanced and forgetful.
For such persons, the professions of driver, rescuer, policeman, etc. are not recommended. Absolute contraindications are more often present in those professions where unexpected situations may arise that require urgent decisions related to responsibility for the life and safety of people, for large material values. Professional selection is used to determine whether people meet the requirements of such occupational groups. Most types of professional work can be carried out with relative professional suitability, that is, with a less stringent list of necessary psychological qualities and properties.
Five structural components of human fitness for work
- Civic qualities (attitudes towards society, ideological, moral character of a person). In some professions, the lack of expression of precisely these qualities makes a person professionally unsuitable (teacher, educator, doctor, judge, investigator, etc.).
- Attitude to work, to profession, interests, inclinations towards a given area of work (professional and labor orientation of the individual). For example, the profession is such that it requires constant work alone, without external control over performance. In this case, such a character trait as conscientiousness acts as an important link in professional suitability. Unfair - unsuitable.
- General capacity (physical and mental). Includes intellectual abilities, mental flexibility, self-control, initiative. As well as physical characteristics: health, strength, endurance, etc.
- Single, private, special abilities, that is, qualities necessary in any specific type of activity. These are personality traits that help achieve high results in any particular area of activity. For example, a cutter needs an eye, and a perfumer needs high olfactory sensitivity. A well-developed speech ability is necessary for the teacher, and the ability to communicate is necessary for the educator. If a person distinguishes odors well and remembers them, these are the abilities necessary for a chemist, taster, or cook. If a person is able to retain many numbers, letters, words or external signs in memory, he can combine them in his mind - these are the abilities necessary for a mathematician, programmer, designer.
However, individual abilities of a person do not guarantee the successful performance of complex activities. The subtle perception of form and color developed in a person does not yet make him an artist. An excellent ear for music in itself does not create a musician. To successfully master any activity, a certain combination of individual, private, special abilities that form a unity is necessary.
- Knowledge, abilities, skills, experience. A person cannot have fully developed professional suitability before he has engaged in vocational training and related work activities. Skills and knowledge are formed in the process of professional activity based on acquired experience.
Professional suitability largely depends on a person’s attitude towards work in general and, in particular, towards a particular profession. Ideal professional suitability is achieved when three components coincide:
- “need”, that is, awareness of social necessity;
- “I want”, that is, the desire and interests of a person;
- “I can”, that is, having the necessary abilities to work.
Professional suitability is not an innate quality of a person. It is formed during long-term professional work taking place in certain socio-economic conditions.
Formation of professional suitability is always an individual process. The formation of suitability for a profession is influenced by a large number of factors, and a certain level of development of abilities is not always the main one among them. Professional development depends on such features as professional motivation, interest in the profession, passion for it, relationships in the team, first achievements and their evaluation.