Receipt of inheritance by full and half-blood relatives
Inheritance is a legal process that many citizens have to go through. One of the main issues in obtaining an inheritance is establishing the degree of relationship, since the possibility of receiving an inheritance depends on this.
Inheritance and inheritance law
Who has the right to inherit, in what order do full and half siblings receive inheritance? These and other current issues of inheritance will be described in detail in this article.
The Civil Code of the Russian Federation indicates that the right of inheritance is given to persons who are alive on the day of opening of the inheritance, citizens conceived during the life of the one who leaves the property, and those who were born alive after the process of opening it.
In addition to the above-mentioned citizens, legal entities that are valid on the day of its opening also have the rights to receive it.
To establish the circle of heirs, the notary must be based on family and kinship principles, since in order to include citizens in the list for receiving it by law, at least one of the following conditions must be proven:
- relationship with the testator. Kinship is a biological connection by origin between certain persons and a legal connection in cases where this is provided for by the norms of the Family Code of the Russian Federation;
- if the testator is adopted;
- if the testator's child is adopted;
- if a marriage was concluded with someone who leaves property;
- if there is a property between the recipient and the testator provided for by law;
- if the recipient is a dependent under certain conditions established by law.
Branches of one tree
When a man and a woman marry, a relationship arises between them that extends to their relatives. Such relationships are called properties and in the event of a marriage breakdown, they cease.
Remarriage gives rise to a new relationship, in which children from the first marriage become participants. Such children are called stepchildren or half-parents. The legislation will divide children living in the same family into several categories.
Which heir can be considered unworthy and what is needed for this, you will learn from this article.
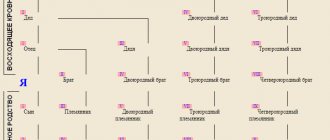
A sister is a female representative who has similar rights. Twins and twins are also considered full-born. Children who have only one parent in common are considered half-parents.
Who are half-siblings? Photo: ppt-online.org
In accordance with this, they are called half-uterine (if the children have a common mother) or half-blooded (if the children have a common father). When a joint child appears in a family where there are incomplete children, he will be classified as incomplete in relation to the others.
Right of inheritance
In the situation of receiving an inheritance, the relationship between the heirs and the degree of their relationship with the deceased family member play an important role, allowing them to lay claim to a certain part.
All relationships are necessarily supported by law and formalized through legal services, including legal marriage or adoption of children. And only after the inheritance situation occurs, the notary begins to understand the intricacies of family relationships and the right of each family member to act as an heir.
On the territory of the Russian Federation, the conditions for receiving an inheritance are regulated by the Civil Code, which describes the main legal subtleties of the inheritance procedure, as well as the conditions under which it occurs.
Who is a close relative according to law, details here.
Before determining the persons who have the right to receive the inheritance, the notary will have to understand the family and kinship principles. To have the right to inheritance, a citizen must provide evidence that meets one of the conditions:
- Presence of a biological relationship with the testator in accordance with the Family Code;
- The fact of adoption of the testator;
- Adoption of the testator's child;
- Registration of marriage with the person who left the property;
- The fact that the property exists in accordance with the law;
- The beneficiary's status as a dependent is subject to certain conditions.
How the order of inheritance works according to law, watch in this video:
The principle of priority
To make the procedure for transferring inheritance more orderly, the legislation establishes the order of inheritance; eight queues are distinguished, of which each subsequent one follows a decreasing degree of relationship.
- The first line includes the closest relatives: parents, children and spouses. At the same time, children born not in a registered marriage, but recognized later, also belong to this queue.
If we consider separately the category of sisters and brothers, full and half-blooded, then the former act as each other’s heirs, listed in the first line, while the latter inherit as participants in the second line.
Regarding half- and half-sisters and brothers, the legislation does not establish a difference.
Rules for transfer of priority
It is worth noting that the right of inheritance of each subsequent turn comes when the previous one is unable to exercise its right, this may be due to:
- Absence of relatives of the previous stage;
- Their lack of rights to inherit;
- Removing them from the inheritance procedure;
- Deprivation of inheritance or refusal of it.
What documents are needed to receive an inheritance, read here.
Any of the inheritors has the right to refuse their share, then it will be distributed among the remaining relatives or, if there are none, members of the next line.
USEFUL INFORMATION: How long does it take to inherit after death?
Kinship
The meaning of the word Kinship according to Ephraim: Kinship - 1. The relationship between people who have common ancestors. // Relationship created by marriage. 2. Family feeling. // transfer Closeness in spirit, habits, beliefs. 3. transfer Closeness in common origin.
The meaning of the word Kinship according to Ozhegov: Kinship - Closeness by common origin, by direct similarity
Kinship
Kin, relatives
Kinship
A connection between people based on the origin of one person from another (direct kinship), or different persons from a common ancestor, as well as on marital family relationships
Kinship in the Encyclopedic Dictionary: Kinship - in law - a blood connection between people, the presence of which is associated with certain rights and obligations by law.
The meaning of the word Kinship according to Ushakov’s dictionary: KINSHIP
kinship, plural
no, cf. 1. The relationship between people created by the presence of common immediate ancestors. Parents and children are related in the first degree. Close and distant kinship. kinship
(great-grandfather, grandfather, father, son, grandson, great-grandson, as well as great-grandmother, etc.). Lateral relationship (brothers, uncles, nephews; sisters, etc.). || The relationship created by marriage. They get married, and we are given kinship with the mistresses of fashion shops. Griboyedov. || collected Relatives, relatives (colloquial). He has a rich family background. 2. Family feeling. No kinship, no acquaintance, no friendship
The meaning of the word Kinship according to Dahl's dictionary: Kinship
etc. see give birth.
Kinship
cf. family, kinship, blood relations. Close relationship: they dried onuchi in the same sun! Kinship is a sacred thing; but money is a different matter. Rhoda Psk. hard relatives, relative, native, blood; | kinship, blood connection. He's been with me since birth.
Definition of the word "Kinship" according to TSB: Kinship
- in law, a blood connection between people, with the presence of which the law connects the emergence, change or termination of rights and obligations. In the USSR, legal significance has both direct relationship (for example, father-son, grandmother-granddaughter), and lateral, when family ties arise due to the presence of a common ancestor (for example, brother-sister, uncle-nephew). Direct R. can be ascending (from descendants to ancestors) and descending (from ancestors to descendants). Brothers and sisters can be full-blooded if they have a common mother and father, half-blooded if they have a common mother (half-born) or a common father (half-blooded). This division does not entail any legal differences in the relations of brothers and sisters (for example, a marriage between a brother and a sister is not subject to registration, regardless of whether they are full or half). There are also degrees of R., indicating the closeness of blood ties between relatives (parents and children are first-degree relatives, brothers and sisters are second-degree relatives, etc.). According to its legal meaning, the relationship between the adoptive parent and the adopted child is equivalent to R. The relationship between the spouses of R. is not. The legislation in each specific case determines the circle of persons between whom R. may have legal significance. The most widely used category of R. is in family law. In civil law, R. relations underlie the regulation of inheritance issues. In labor law, the assignment of pensions in the event of the loss of a breadwinner depends on the category of workers. In addition, the law prohibits the joint service in one organization of persons who are members of a close R., if this is due to the direct subordination or control of one of them to the other. In bourgeois legislation, R.'s relations are regulated mainly by inheritance legislation.
Related Kinship Kinship Languages
Half- and half-brothers and sisters
Who is legally the second-degree heir? Relatives of the second order are divided into relatives and half-relatives (that is, half-relatives). Children who have the same mother and father are considered siblings. Incomplete relatives have only a common father or a common mother. Inferior relatives, in turn, are divided into: How is the inheritance distributed among relatives? Subsequent heirs have the right to claim the inheritance only if the above categories of heirs have renounced their share of the inheritance, are absent or are recognized as unworthy by the terms of the will. Kinship and blood ties * Wedded sister (obsolete) - a sister born before the marriage of her parents and recognized by them. * Twins are identical children (in relation to each other), born at the same time to the same mother.
Who are close relatives according to the family code?
There is a family code in Russian legislation. If you look at article number 14, you can see a complete list of those people who can be called blood (direct) relatives.
All of them are divided into several levels, that is, lines: straight and lateral:
- Concept of a straight ascending line . What it is? These are the very ancestors from which man descended. First of all, these are his blood parents, mom and dad. Next, there are grandfathers, grandmothers, great-grandfathers, great-grandmothers and so on, this line can be continued endlessly. At the legal level there is no concept of blood relationship. That is, a relative is the person indicated in the document. For example, a couple who takes custody of a child is officially his parents.
- Concept of a straight downward line . This concept, on the contrary, means relatives who descended from a certain person, that is, his children, grandchildren, great-grandchildren, and so on.
- The concept of lateral lines. Lateral relatives are precisely those people who were born without his participation; we are talking about brothers and sisters.
There is another important indicator in describing a family relationship - its degree.
Who are half-siblings
Dear readers! Our articles talk about typical ways to resolve legal issues, but each case is unique.
If you want to know
It often happens that having spontaneously created a family without checking their feelings, people end up breaking up. Often such marriages already have children.
Starting a new family, of course, children are born again, from new unions. In such cases, an incomplete relationship is formed between brothers and sisters.
Half brother and sister - who are they?
Brothers and sister are people who have the same relatives.
In this case they can be:
- full-born
- half-bred
- consolidated.
The connection is determined based on two factors:
- Genetic.
- Social.
At the genetic level, relationships are divided into blood and non-blood. Half-siblings are people who have one common parent. Full siblings, or as they are commonly considered to be blood, are a brother and sister who have both a mother and a father in common.
Let's celebrate! Step-children are considered to be people who do not have common blood parents at all. They became brothers as a result of the fact that their parents got together having them from their first marriages.
Monouterine
Those people who have one common mother are considered to be uterine. That is, they were born from the same mother, while having different fathers.
Half-blooded
Between a half-brother and a half-sister, a connection is considered to be one that is cemented by the presence of the same father, while their mothers are different.
Examples of inheritance
The process of inheritance involves the transfer of property from one person to another. To transfer an inheritance, a notary must check all applicants for the inheritance in a blood connection with the deceased.
To do this, he needs to obtain the relevant documents, which the relatives must provide.
The very first people who should receive an inheritance out of turn are the parents, wife and children. Accordingly, it is necessary to have the following document:.
- Marriage certificate.
- birth certificate, which indicates that these heirs are the parents.
- passport.
- children's birth certificate.
Note! Second in line are non-full brothers and sisters.
For example:
- A mother who had two children suddenly dies. One is from one father, the second from another. Children are the only heirs. In this case, the property must be divided equally between the two children.
- A father dies, who had one son from his first marriage and a daughter from his second marriage. Since they are half-blooded, most of the inheritance will go to the eldest in the family.
- If a parent dies who had one adopted child from his wife, one from his first marriage and a joint child in his second marriage. The first heir is the child from the first marriage, followed by the child from the second marriage and then the adopted one.
- If, when inheriting property, there is a mother of the deceased and two half-children, then all property is divided by gender.
- If there are several claimants to the inheritance: a mother, two half-children and a wife. Most of the inheritance is divided between the wife and mother.
The principle of succession in inheritance
When transferring property by inheritance, there is a sequence:
- Husband or wife, children and parents of the deceased.
- Grandfathers, grandmothers, brothers and sister of the deceased.
- Aunts and uncles.
- Great-grandparents.
- Cousins and sister.
- Cousin grandchildren.
- Stepfather or stepmother
The degree of relationship is also determined by the number of births between the heirs and the testator. Children who have a step-by-step relationship are treated like relatives. Adopted children are also considered equal to natural children.
If the deceased did not have any natural children in marriage, then half-siblings followed by adoption are considered.
Note! You can often find families where there is one child in common and one from the first marriage of the husband or wife. Such children are no different in rights from those of full blood.
The only difference is the presence of one common parent. When inheriting, they look first at natural children, and then at half-blood children. From the point of view of the law this is true, although they have equal rights.
USEFUL INFORMATION: Is it possible to apply for alimony retroactively?
Half and full brothers and sisters
Brothers and sisters are considered representatives of the collateral line and in some cases have the right to inheritance.
And if a citizen who has made a will can transfer the inheritance to any person, then in the absence of such a document many questions often arise.
For example, what rights do full and half-siblings have to receive property? Is there a fundamental difference in the transfer of inheritance?
Full brothers and sisters
The term " full siblings " refers to relatives who have two common parents. The definition is largely genetic, meaning the descendants of two separate individuals, but is often used in legislation.
Both sisters and brothers who differ significantly in age but come from the same people, as well as twins born on the same day, will be considered full siblings.
However, in the latter case, everything is not so simple: in rare cases, children, even those born at the same time, come from different fathers. A similar case was recently reported in Vietnam.
Such twins will be considered half-bred.
There is also a category of persons who are called married. They refer to sons and daughters who were born before marriage and then recognized by both parents. Such children are also considered full-blooded, since they are descendants, and, accordingly, heirs of their father and mother.
What does inferiority mean?
If brothers or sisters have only one parent in common, they are classified as half-siblings.
There are several categories of such relatives:
- Those descended from one male representative are half-blooded;
- Those born by the same woman are consanguineous.
Even though children have only one parent in common, they are considered relatives. But half-brothers and sisters are not even considered half-brothers, since their fathers and mothers are completely different. Accordingly, they do not have the right to be included in the number of heirs of the second priority.
If in a marriage a man and a woman who have their own children from other persons have a common child, in relation to brothers and sisters who are step-brothers, he is considered incomplete and accordingly receives the right to inherit after them.
Inheritance by law, reflected in Article 1141 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation, is carried out exclusively after the death of the property holder. An important fact is the establishment of family ties between the testator and the successor. When submitting an application to a notary, only a citizen who has provided proof of family ties can claim to receive property belonging to the deceased.
The main documents confirming the existence of a connection between the testator and the legal successor are:
- Marriage certificate;
- A document where the citizen’s mother and father are registered – a birth certificate;
- If the child is not his own - a paper confirming the fact of adoption;
- If the person is a dependent - a special certificate.
Legal heirs include:
- Sons, daughters, mother and father, designated by Article 1142 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation as heirs of the first stage. This also includes grandchildren if the transfer of property is made by right of succession.
- If there are no relatives listed in Article 1142 of the normative act, Article 1143 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation comes into force, defining the second-priority heirs. These include, in addition to grandparents, brothers and sisters. It does not matter whether they are full-born, half-bred or half-blooded. Only stepchildren cannot lay claim to property.
- The third-priority heirs are the uncles and aunts specified in Article 1144 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation. The question of completeness in such a case is also not relevant.
- Next, inheritance is carried out in the manner established by Article 1145 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation. The determining factor is the number of births between the heir and the deceased, as indicated in the second paragraph of the regulation.
In the latter case, it is quite difficult to prove the existence of family ties. Often, such heirs have to resort to the help of a judicial authority in order to receive their share of the property remaining after the death of the testator.
Difficulties also arise when inheriting from parents. If a common child lays claim to the estate in any case, then his half-brother, as well as his sister, cannot claim a share of the property of the deceased spouse of their father or mother. The exception is adopted offspring.
If there are no living heirs of the first priority, persons included in the subsequent ones can apply for the property. However, one should remember the right of representation outlined in Article 1146 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation.
It comes into effect if the next heir died later than the testator, without having time to accept the inheritance. Then the share belonging to him is distributed among the persons inheriting after him.
Such a right is not realized if death occurs on the same day.
The order can be transferred even if the heirs of the previous order are alive.
This happens in the following cases:
- Relatives do not have the right to receive property;
- Refusal to accept inheritance;
- Removal from receiving inheritance;
- The presence of a will executed during the life of the owner of the property.
If a natural child of the deceased decides to share with a step-relative part of the property belonging to the deceased parent, he will be able to do this only after entering into an inheritance, that is, after 6 months, and in the case of real estate - after registering the property with the state accounting authorities. It is also impossible to refuse in favor of a half-sister or brother: in such a case, other persons from this line, or, in their absence, persons belonging to the next one, become heirs.
Source: https://lawinfo24.ru/heritage/heir/polnorodnye-i-nepolnorodnye-bratya-i-sestry
Full and half siblings
First, let's figure out who full and half-siblings are.
Full siblings are brothers and (or) sisters who have a common mother and father.
A brother is a child boy or an adult man, in relation to other children, he is the same heir by right as they are. A married brother is also included in this category; he is considered a child who was born out of wedlock, but was recognized as his own.
A sister is a child, girl or adult woman who has the same rights in relation to other children. This also includes twins and twins - children who were born from the same woman at the same time.
Brothers and sisters who have one parent, mother or father in common are considered half-siblings. They are all considered relatives.
Kinship is a biological and legal connection between persons.
In turn, half-parents are divided into 2 categories:
- Half-uterine, when they only have a mother in common (here, even according to the meaning of the word “half-uterine”, one can draw such a logical conclusion).
- Half-blooded, if the brothers and sisters have a common father.
All these facts must be documented, because when inheriting, the degree of relationship must be proven not in words. Step-siblings should not be confused here. They are not relatives, because they are children from previous marriages.
If a common child of father and mother is born in such a family, he will be considered incomplete relative to all the children of his parents. In legal terms, they do not have the right to inherit the property of a deceased half-brother or sister.
Definition of the word “Kinship” according to TSB:
Kinship - in law, a blood connection between people, with the presence of which the law connects the emergence, change or termination of rights and obligations. In the USSR, legal significance has both direct relationship (for example, father-son, grandmother-granddaughter), and lateral, when family ties arise due to the presence of a common ancestor (for example, brother-sister, uncle-nephew). Direct R. can be ascending (from descendants to ancestors) and descending (from ancestors to descendants). Brothers and sisters can be full-blooded if they have a common mother and father, half-blooded if they have a common mother (half-born) or a common father (half-blooded). This division does not entail any legal differences in the relations of brothers and sisters (for example, a marriage between a brother and a sister is not subject to registration, regardless of whether they are full or half). There are also degrees of R., indicating the closeness of blood ties between relatives (parents and children are first-degree relatives, brothers and sisters are second-degree relatives, etc.). According to its legal meaning, the relationship between the adoptive parent and the adopted child is equivalent to R. The relationship between the spouses of R. is not. The legislation in each specific case determines the circle of persons between whom R. may have legal significance. The most widely used category of R. is in family law. In civil law, R. relations underlie the regulation of inheritance issues. In labor law, the assignment of pensions in the event of the loss of a breadwinner depends on the category of workers. In addition, the law prohibits the joint service in one organization of persons who are members of a close R., if this is due to the direct subordination or control of one of them to the other. In bourgeois legislation, R.'s relations are regulated mainly by inheritance legislation.
So are they steps or relatives?
Nicholas. Sergei or Vera should have remained aloof from the inheritance, because in our country, as a general rule, inheritance requires a blood relationship with the testator; and therefore, if Zinaida had no paternal relatives at all, her property would have become escheat. But according to 1140 Art. in this case, a different order begins: if Zinaida does not have a sister, Elizabeth, then Sergei and Vera (half-born) have exactly the same right with Ivan and Marya (half-blooded). Therefore, together with Ivan, Sergei will also be called to inheritance; in the absence of Ivan, only his half-brother Sergei will be called to inherit, that is, a person of a completely foreign family; in the absence of Sergei, Marya and Vera will be called up with equal rights or, in the absence of Marya, one uterine Vera. Thus, the feature of 1140 Art.
Who are half-siblings
The institution of the modern family is far from perfect. According to moral standards, a family is considered ideal, where the father and mother have children of their own.
But sometimes we get caught up in such a carousel of life that, for example, one man having 3 children from different marriages does not cause negative emotions. If only this man was a father not only on paper. And some are in no hurry to become on paper.
And there are no matriarchal hints here; the same can be said about women. If we take family ties, they are divided into 3 groups: blood relatives (relatives by blood), relatives by marriage, and unrelated ties.
When dividing an inheritance, as a rule, many express a desire to feast on a piece, even if it does not belong according to the laws of the country and morality.
Have a question for a lawyer
If you mean do you have the right not to testify against each other, then yes, since you both have the same parent. There shouldn’t be any questions about this, even if you don’t live together and have never even seen each other.
Client clarification
No, I am interested in whether I can be recognized as a victim as a close relative, the circle of whom is defined by 5 of the Code of Criminal Procedure of the Russian Federation. The victim under Article 105 of the Criminal Code of the Russian Federation.
17 July 2015, 16:05
Article 42 of the Code of Criminal Procedure of the Russian Federation. Victim
8. In criminal cases of crimes, the consequence of which was the death of a person, the rights of the victim provided for in this article pass to one of his close relatives and (or) close persons, and in their absence or the impossibility of their participation in criminal proceedings - to one of relatives.
You can, the investigator decides who exactly to recognize.
Client clarification
From my brother’s circle, the closest relative after me is his cousin. And it is she who is recognized as the victim in the case. But they don’t want to recognize me, because... According to the investigator, the half-sister is not a full sister and therefore does not belong to the circle of close relatives.
17 July 2015, 16:14
Olya, I don’t know what was in the investigator’s head, how it was refused, to be honest, I don’t understand why you need to be recognized as a victim in a criminal case.
USEFUL INFORMATION: Court decision on deprivation of parental rights
If the issue is about money, you can go to court in civil proceedings for compensation for moral damage. Any relative can file such a claim.
If the issue is fundamental, you can appeal the investigator’s refusal, if it was official, in court, the prosecutor’s office, or the head of the Investigative Committee.
You can refer to:
Determination of the Constitutional Court of the Russian Federation dated January 18, 2005 N 131-O “At the request of the Volgograd Garrison Military Court to verify the constitutionality of part eight of Article 42 of the Criminal Procedure Code of the Russian Federation,” which determined that
1. The provision of part eight of Article 42 of the Code of Criminal Procedure of the Russian Federation cannot be considered as excluding the possibility of vesting procedural rights of a victim in more than one close relative of a person whose death occurred as a result of a crime.
Legal status of spouses
One of the most interesting questions is the status of spouses in relation to each other. It seems that two people live together under one roof, do various things, raise common children, it would seem that nothing else could be closer to their connection, but they cannot be called relatives, since between them there is no single person from whom they descended. light. What does the law “say” in such an unusual case?
Is the wife related to her husband?
Several codes provide different information regarding the relationship between spouses:
- In the criminal code, spouse and husband are not close relatives, they represent a separate type of relationship.
- In the tax code, they are closely related to each other.
- In the housing code they are completely one whole.
According to the law, if two people enter into an official relationship (marriage), then they become one unit of society bearing the same surname. Accordingly, they are new acquired relatives in relation to each other.
The degree of relationship between them is impossible to determine. If you pay attention to this fact from the inheritance side, then one of the spouses after the death of the second is its full owner. The exception is a civil relationship between two partners, which is not legally binding.
Good to know! A person cannot be alone. Everyone has a huge number of a wide variety of relatives: close and distant, living and deceased, blood and acquired. It doesn't matter what the law says about this. What matters much more is the sincere attitude of one person towards another, the manifestation of his care, attention and respect. Only in this case can people be called relatives.
Didn't find the answer to your question? Find out how to solve exactly your problem - call right now: +7 (Moscow) +7 (812) 309-53-42 (St. Petersburg) It's fast and free!
Inheritance and inheritance law
The Civil Code of the Russian Federation indicates that the right of inheritance is given to persons who are alive on the day of opening of the inheritance, citizens conceived during the life of the one who leaves the property, and those who were born alive after the process of opening it. In addition to the above-mentioned citizens, legal entities that are valid on the day of its opening also have the rights to receive it. To establish the circle of heirs, the notary must be based on family and kinship principles, since in order to include citizens in the list for receiving it by law, at least one of the following conditions must be proven:
- relationship with the testator. Kinship is a biological connection by origin between certain persons and a legal connection in cases where this is provided for by the norms of the Family Code of the Russian Federation;
- if the testator is adopted;
- if the testator's child is adopted;
- if a marriage was concluded with someone who leaves property;
- if there is a property between the recipient and the testator provided for by law;
- if the recipient is a dependent under certain conditions established by law.
The principle of priority
Taking into account the principle of kinship, the legislator sets priorities for receiving according to the principle of priority. The law establishes eight queues, each of which is divided into groups according to priority in descending order. According to the Civil Code of the Russian Federation, the priority group includes the spouse, children, and parents. According to Art. 1143, the second stage includes full and half-sisters and brothers, grandfathers and grandmothers on the mother’s and father’s side. According to the purpose of our research, we will dwell on full and half-kin relatives in more detail. Full brothers and sisters come from the same parents. A brother is a boy or a man in relation to other children, an older brother is a boy or a man in relation to younger ones, a younger brother is a boy or a man in relation to older ones. This also includes a married brother - a boy born before marriage and recognized by them. A sister is a girl in relation to other children, born from the same parents, an older sister is a girl in relation to younger children, a younger sister is a girl in relation to older ones. This also includes a married sister - a girl born before marriage and recognized by them. This group of children also includes twins. These are the children of one woman who developed and were born from one pregnancy. Half-parents are children who have only one common parent: mother or father. They are divided into: Monouterine (one-uterine) - originating from the same woman, but from different fathers. Consanguineous (homogeneous) - descended from the same man, but from different mothers. Such brothers and sisters are called half-blooded if they come from the same father. They are called half-bred if they have the same mother.
The above categories should not be confused with stepbrothers, which are not considered relatives because their relationship is not kinship, but is based on property relations. Therefore, step-relatives are not included in the second line of heirs. According to the Civil Code of the Russian Federation:
- If the deceased does not have heirs of the first stage, the heirs according to the law of the second stage are the half- and full-blooded brothers and sisters of the person leaving the inheritance.
- Modern legislation does not emphasize the differences between such relatives. Both (half-born and half-blooded) have the right to receive it.
As noted above, heirs of the second priority can receive it if there are no citizens of the first priority, and there are no persons who can inherit instead of them by right of representation, or all persons on any other grounds, which are provided for in the second paragraph of paragraph 1 of Article 1141 of the Civil Code, will not be called up or will not accept property. They note that their children, nieces and nephews, can receive it by right of representation.
Issues of inheritance are quite complex, therefore, on the advice of specialists, to resolve issues of obtaining it, it is best to contact certified specialists. Considering that there is a possibility of unforeseen situations when other applicants may appear, it is best to entrust this issue to professional lawyers.