Home / Labor Law / Employment / Employment contract
Back
Published: 07/15/2016
Reading time: 12 min
0
585
Article 15 of the Labor Code contains a ban on concluding civil contracts if there is an employment relationship.
When registering employees, concluding an employment contract is mandatory. The contract is drawn up in strict accordance with the requirements of the Labor Code.
- Legislation
- Secrets of proper design
- Signing procedure
- Design nuances
- Typical mistakes when concluding employment contracts Place of work
- Job title
- Terms of payment
- Start date
- Salary payment procedure
Legislation
The main law governing the relationship between a manager and a subordinate is the Labor Code.
Its 15th article explains the coincidence of which circumstances create an employment relationship:
- a specific job has been determined (permanent or temporary);
- one person (employee) agrees to such work;
- the second (employer) pays for it regularly;
- the work is performed in person at a specific location.
If all factors coincide, the signing of other contracts is illegal (with the exception of agency and contract agreements).
This addition was introduced into the Labor Code back in December 2013, so you should not trust those sources that recommend drawing up civil contracts instead of labor contracts. You can pay for this: the administrative fine for violating the Labor Code can reach one hundred thousand rubles (Part 3 of Article 5.27 of the Administrative Code).
Employment contracts are drawn up not only by a legal entity (organization, enterprise, company), but also on behalf of an entrepreneur and even an ordinary person. For example, an agreement is drawn up if one person hires another to work as a household assistant (in a poultry house, in a pigsty, for agricultural work). This is required by Article 20 of the Labor Code.
Secrets of proper design
There is no special form of employment contract (EA), it all depends on the rules of office work adopted by the company. Typically, the manager approves a draft agreement, according to the type of which individual agreements are drawn up.
According to the norm of Article 57 of the Labor Code, the preamble of the contract must include:
- who is the employer (name of company, full name of entrepreneur or individual);
- employer details (for a company: TIN, OGRN, address; for an entrepreneur: address and OGRNIP; for an individual: address and passport details);
- powers of the signatory (only for organizations: either a director under the charter, or another manager under a power of attorney, indicating its details);
- date of signing and place (city, town, village, etc.).
Mandatory inclusions in the TD are:
- place of work (address of production, company or its branch);
- position and profession (if the work is “harmful” or another that gives grounds for early retirement, the position and profession must comply with the directory of positions according to Resolution No. 787);
- date of the first working day;
- the end date of the fixed-term contract (or the onset of a certain moment: the end of the season, the departure of the replaced employee, etc.);
- salary amount (salary, bonuses, allowances in specific figures);
- work schedule (if it differs from that specified in the collective agreement or work schedule);
- compensation for harmfulness (milk supply rate or amount of monetary compensation);
- traveling or mobile nature of work (if any);
- workplace conditions (you can specify the type of equipment, machines, computerization, automation, etc.);
- social insurance (contributions to the Pension Fund, Social Insurance Fund).
Important: if any mandatory conditions from the list above are not specified, they need to be added:
- enter into the text of the contract;
- secured by an additional agreement.
In addition to the mandatory conditions, you can enter additional ones, for example:
- specify the location of the workplace (room, building no.);
- assign a probationary period;
- provide additional insurance.
Additional conditions should not contradict the Labor Code, for example, the full-time salary cannot be less than the minimum wage established in the region.
You can download a standard form of an employment contract in this article.
Contents of the employment contract (Article 57 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation)
The employment contract specifies a number of general information:
1) last name, first name, patronymic of the employee and employer who entered into an employment contract;
2) information about documents proving the identity of the employee and the employer - an individual;
3) taxpayer identification number;
4) information about the employer’s representative who signed the employment contract, and the basis on which he is vested with the appropriate powers;
5) place and date of conclusion of the employment contract.
Other information included in the employment contract is of a special nature. Among them are mandatory and additional conditions for inclusion in an employment contract.
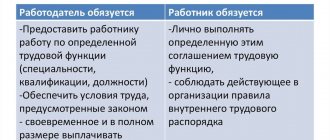
Mandatory terms of the employment contract are:
1) place of work;
2) labor function;
3) the start date of work, and in the case where a fixed-term employment contract is concluded, also its validity period;
4) terms of remuneration;
5) working hours and rest hours;
6) guarantees and compensation for work under harmful and (or) dangerous working conditions;
7) conditions determining, if necessary, the nature of the work (mobile, traveling, on the road, other nature of work);
 working conditions in the workplace;
working conditions in the workplace;
9) condition on compulsory social insurance of the employee.
Additional conditions when concluding an employment contract:
1) on clarification of the place of work and (or) workplace;
2) about the test;
3) on non-disclosure of secrets protected by law (state, official, commercial and other);
4) on the employee’s obligation to work after training for at least the period established by the contract, if the training was carried out at the expense of the employer;
5) on the types and conditions of additional insurance for the employee;
6) on improving the social and living conditions of the employee and his family members;
7) on additional non-state pension provision for the employee.
If any of the information or conditions were not included in the employment contract, this is not a reason for terminating the employment contract or canceling it. The missing information is simply entered, and the missing (among the mandatory) conditions are determined in the appendices to the employment contract.
There are two types of employment contracts:
1) open-ended employment contracts (concluded for an indefinite period)
2) fixed-term employment contracts (concluded for a certain period, but not more than five years)
The employment contract comes into force from the day it is signed by the employee and the employer. The employee is obliged to begin performing his job duties on the date specified in the employment contract.
If the employment contract does not specify the start date of work, the employee must begin work on the next working day after the contract enters into force.
Signing procedure
First, the employee must write an application for employment, after his approval by the director, an employment contract is drawn up. Before drawing up a contract, the personnel officer must request from the employee the documents listed in Article 65 of the Labor Code:
- passport (or temporary ID);
- work book (if there is no work experience, the book will be issued by a personnel officer);
- SNILS;
- military ID (in relation to those liable for military service);
- a certificate of criminal record (if a teacher or civil servant is employed);
- 2-NDFL certificate from previous place of work and children’s birth certificates (to the accounting department to calculate taxes and deductions);
- diplomas, certificates, certificates (to confirm rank, profession, qualifications).
Copies are made of documents and a personal file is created based on them..
Information in an employment contract is entered only on the basis of original documents; copies cannot be trusted!
Before signing the contract, the employee must be familiarized with local regulations (payment regulations, work rules, shift schedule, etc.).
In the contract (with details and signatures) you can provide a line of familiarization with the LNA and a receipt for receiving a copy with the example text: “I have read the rules of procedure, job description, regulations on bonuses and payment. A copy of the agreement has been received. Date, signature."
Agreement execution algorithm:
- print in duplicate;
- signed by an employee;
- endorsed by the director;
- give one original to the employee against signature;
- register the second in the journal and put it in the nomenclature folder.
The contract must be drawn up within three days from the date the employee returns to work!
In what cases can you work under a contract without a work book?
The Labor Code of the Russian Federation states that work under a contract without a work book is possible only in two cases:
- Chapter 24, section 14, part 4
: if the instructions of a person who is not an entrepreneur are carried out. Most often this is work as a nanny, housekeeper, or personal driver. When performing such types of work, the employer simply does not have the right to make an entry in the work book, since such activities do not bring him profit. - Chapter 44, section 12, part 4
: when several positions are combined.
There are usually three types of non-labor work contracts:
- Agency - work for a short period of time.
- Authorial - performing a specific task, for example, writing an article or song.
- Contract agreement - when workers are hired to perform a certain amount of work (repairs, cleaning of premises, etc.).
When formalizing such legal relations, it is worth paying special attention to the nuances: deadlines, conditions for fulfilling duties, fines for violating them, etc. It is necessary to familiarize yourself in advance with how the employment contract is drawn up, what rights and responsibilities are specified in it.
Design nuances
When registering a foreigner, a notification must be sent to the local
department of the Ministry of Internal Affairs on migration issues (former departments of the Federal Migration Service).
When hiring a former civil servant, you need to notify the body where he previously worked (according to data from the work book).
When registering a conscript undergoing alternative service with you, the military registration and enlistment office that sent him and the local regional administration are notified.
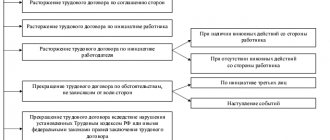
Every employee should know that if the employer forces him to resign of his own free will, then the employee has the right to file a lawsuit for illegal dismissal, even if this statement was written. If you want to resign due to the need to care for a child, this is your legal right. Read about the procedure for terminating the contract in this case here. Are you planning to fire your part-time worker? The detailed procedure for dismissing external and internal part-time workers is described in our article.