Home / Government procurement / Federal Law 44
Back
Published: March 29, 2019
Reading time: 4 min
0
651
In the practice of public procurement, there was a precedent when a municipal customer signed an agreement with a supplier for an amount of up to 100 thousand rubles, and the Treasury recognized this name as unlawful, since, in its opinion, it was not an agreement, but a contract that should have been signed.
- Contract and agreement under 44-FZ
- General and differences between agreement and contract
- When do the parties sign an agreement and when do they sign a contract?
Contract or agreement?
In the broadest sense, the expressions contract, agreement and agreement are interchangeable. These are business customs and established practices. And in certain areas of law this is indeed the case. For example, in labor legislation the concepts of “employment contract” and “employment contract” are absolutely identical.
But in procurement there is a very specific division:
Registration in the ERUZ UIS
From January 1 2020 , in order to participate in bidding under 44-FZ, 223-FZ and 615-PP, registration in the ERUZ register (Unified Register of Procurement Participants) on the EIS (Unified Information System) portal in the field of procurement zakupki.gov is .ru.We provide a service for registration in the ERUZ in the EIS:
Order registration in the EIS
- a contract is concluded within the framework of law 44-FZ ;
- within the framework of law 223-FZ - agreement .
Document structure
In accordance with the civil legislation of the country, the agreement must contain the following information:
- Item. A document cannot be considered concluded if it does not contain a description of the goods or services that must be provided to the customer.
Essential conditions. For example, providing a collateral amount or property. The period of fulfillment of obligations secured by collateral.- Other conditions, the fulfillment of which is achieved through negotiations. For example, the type of transport by which the necessary goods are delivered.
- Responsibility measures for participants in case of non-fulfillment of conditions.
- Details and signatures.
The developed structure must guarantee the parties compliance with its terms and provide for liability measures for poor quality and untimely fulfillment of obligations.
What is a contract in procurement?
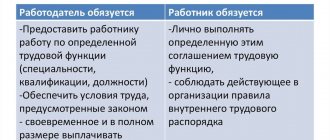
the state is one of the parties . It may operate through authorities or certain types of organizations. To meet the needs of the state, procurement is carried out in accordance with law 44-FZ. Within the framework of this norm, contracts are concluded between the customer and the contractor. In this case, the executor can be any person who meets certain requirements, both legal and physical. But the second party to contracts is always the state, that is:
- public authority;
- state corporation;
- state-financed organization;
- government agency;
- state or municipal unitary enterprise.
In other words, the contract is concluded with budget money . The customer declares his needs, the contractor satisfies them and receives payment for this from the budget of the appropriate level.
Contract - description and features
Today, a contract is a special form of employment contract, which is concluded between an employer, represented by an official authorized by a government agency, and a citizen. Considering that such relationships are regulated by special legislation, this type of document has some features.
Here we can highlight the following points:
- the employee cannot terminate the contract unilaterally;
- the employer has every right not to approve the dismissal of a citizen by agreement of the parties;
- a week before the end of the contract, the employer must notify the citizen of his reluctance to further cooperate (or in the reverse order);
- the document may provide for additional reasons for dismissal not provided for by the Labor Code of the Russian Federation;
- there is a possibility of punishment of one of the parties due to failure to fulfill the terms of the contract;
- always has a validity period. Cannot be indefinite;
- provides increased social guarantees for employees. Here the conditions for free provision of housing, compensation for travel, utility bills and other everyday issues may be indicated;
- Age and health restrictions may be imposed.
Remember, contract service differs from a regular employment contract in that it has a broader set of obligations and powers. Here the citizen is obliged to serve according to the regulations.
What is a procurement contract?
Unlike a contract, an agreement can be concluded between any persons. The party to the agreement can be an ordinary citizen, an individual entrepreneur or an organization of any type. Including a state corporation or monopoly, a company with state participation, as well as a budgetary institution or unitary enterprise (in terms of purchases using its own funds and not from budgetary funds). In this case, the mentioned persons make purchases within the framework of Law 223-FZ. When the winner is determined, a contract is concluded with him.
You can find out who can become the executor of the contract under 223-FZ from this material.
Differences from the point of view of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation
The Civil Code is a legal act that has the highest legal force. With its help, the procedure and conditions of transactions are regulated and established. In the Civil Code of the Russian Federation, the definition of “contract” is used in the case when one of the parties to the agreement is the state or its subordinate organizations. Similar wording is also applicable to fulfill similar obligations of the Budget Code of the Russian Federation.
Chapter 30 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation clearly distinguishes between the following concepts:
- State (municipal) contract.
- An agreement for the supply of goods or the provision of commercial services in order to meet the needs of budgetary organizations.
In the first case, a tender is held, where authorized persons acting on behalf of the state make a choice in favor of one of the bidders.
The second point involves agreeing on all conditions with the most suitable candidate, who subsequently fulfills all obligations assigned to him. All the nuances of working under a fixed-term employment contract are discussed in this article. What is an agreement for the provision of paid services with an individual - see here.
What is the difference
In procurement, contract and agreement differ quite significantly. And mainly due to the fact that the first of them is regulated by law 44-FZ, and the second by law 223-FZ. The second law gives the customer much more freedom. For example, they can independently choose the method of determining the supplier, while Law 44-FZ strictly regulates this issue.
The Public Procurement Law regulates almost all aspects - from procurement planning to acceptance of contract results. Any deviation from its norms is punishable by fines. In contrast, Law 223-FZ leaves almost all decisions to the parties to the contract.
From a legal point of view
There is no significant difference in concepts in the country's legislative acts. In the Federal Law of the Russian Federation on the contract system, these words are used interchangeably.
The Ministry of Economic Development regulates the contract system in the country. In accordance with the explanations of the Ministry, state bodies have the right to make conclusions. Other business entities draw up contracts.
What common
However, there are many similarities between an agreement and a contract under procurement law. By and large, any contract is an agreement. We can say it differently - a contract is a special case of an agreement in which the buyer/customer is the state.
Both the contract and the agreement must contain a number of parameters. Some of them are essential conditions, for example, the name of the parties, the subject of the contract, its cost. In their absence, the agreement will be considered invalid .
There are also provisions that are included at the request of the parties. For example, this is an agreement on prepayment or the involvement of subcontractors.
Features of the document
Federal Law No. 44 of the Russian Federation will help you understand the specifics of the contract. The law regulates the procedure for purchasing goods and providing services for the state. Based on the law, the contract is used as a guarantee that the customer and contractor will fulfill their obligations regarding the provision of goods (services) and subsequent payment for them.
The following features of contracts are highlighted:
the customer is state or municipal authorities- is concluded for a certain time
- only the customer (state, municipality) or the employer, if the contract is an employment contract, has the power to terminate
- Only written form is legal
- in case of termination, the injured party is compensated for the damage incurred
In accordance with the standards of current legislation, the contract regulates the relationship between the state and the economic entity (citizen).
What is an agreement
In Russian law, an agreement is any agreement between the parties. This concept is much broader than an agreement, and even more so a contract (as it is understood in the field of procurement). An agreement can be oral, but in most cases a contract means a paper document.
At the same time, the term in question appears in the expressions “additional agreement to the contract” and “agreement on termination of the agreement (contract)”. These are established expressions that correspond to business customs.
So, the rules of law generally identify the concepts of “agreement”, “contract” and “agreement”. However, when it comes to procurement, the last two terms have clear differences. It is important to remember that no matter what the type of agreement between the parties is called, it must comply with the norms of the Civil Code.
About the features of the contract under 44-FZ:
Definition of concepts
The exact definition of each expression is as follows.
A contract is an agreement between two or more parties, which clearly states or stipulates the responsibilities of each of them . It is concluded in writing or orally, where the conditions for fulfilling obligations are agreed upon in advance, and cases of possible termination are also established.
Examples of contracts:
- purchase and sale;
- rent;
- loan and lending;
- bank deposits, etc.
A contract is a written document confirming the existence of a bilateral or multilateral transaction for a certain period . In addition, it contains a number of additional clauses that determine the degree of punishment (fines, complete termination of cooperation) in the event of failure to comply with one or more terms of the agreement.
Types of contracts:
- leasing;
- mortgage;
- marriage;
- stock exchange;
- currency.
From the resulting definitions, some similarity between these terms can be seen. The most striking points are:
- multilateralism of the parties to the agreement;
- the presence of mutual responsibilities;
- free subject composition;
- possibility of regulating relations.
Having defined each of the concepts, it is clearly visible that despite their functional similarity, there are a number of significant differences between them, including:
- Etymological origin.
- After agreeing on all points verbally, the contract must, after some time, turn into a written agreement. Otherwise, it has no legal force, which makes it impossible to clarify the relationship in court if disagreements arise. The agreement may remain in the form of a verbal agreement (applicable only to individuals).
- In a contract, counterparties have a wider range of powers. In most cases, they can terminate the agreement without the consent of the other party.
- The contract has a set time frame. In turn, the contract is not always so categorical in terms of time commitments.
- The definition of these values in the regulatory documents of the Russian Federation deserves special mention.