Russian legislation provides for seven legal queues. A separate category is considered to be a group of disabled citizens who were dependent on the testator for at least one year during the life of the testator. The first priority heirs after the death of the husband are his wife, children and parents.
If the spouses did not enter into a marriage contract or the heirs of the first priority are not in conflict over the division of the inheritance, all existing property is divided in equal shares. If there are disagreements, the parties can agree among themselves and draw up an appropriate agreement with a notary about who will get what share of the property. If there is a will, the property after the death of the testator will be received only by those heirs indicated in this document. The exception will be disabled dependent citizens. In any case, they are entitled to a share equal to half of the property that they would have received by law if there had been no will.
Before considering your rights after the death of your husband, it is important to note that it matters greatly whether the marriage was official or civil.
Dear readers!
Our articles talk about typical ways to resolve legal issues, but each case is unique. If you want to find out how to solve your specific problem, please contact the online consultant form on the right →
It's fast and free!
Or call us by phone (24/7):
Marital share
All property acquired during an official marriage is considered jointly acquired. The exception is property that was gifted to one of the spouses, as well as the terms of the marriage contract, if one was drawn up. Property that is subject to division and is an inheritance means:
- All objects of real and movable property, including contributions and acquisitions from joint income;
- All income, cash, savings, benefits, etc., except material assistance;
- All other property that was acquired during the marriage. At the same time, for whose money and to whom it was issued does not matter.
Jointly acquired property is not considered property for personal use, except for jewelry, as well as property received by one of the spouses by inheritance or under a gift agreement. The heirs of the first stage, that is, the wife, children and parents, after the death of the testator, can claim his property with equal rights.
Spouse's share of inheritance after husband's death
The property subject to inheritance or hereditary estate does not include the marital share - property received during the time registered with the civil registry office or in other countries that have agreements with the Russian Federation on mutual assistance in family matters and marriage.
If there is no documentary evidence of marriage registration or if the marriage is registered in countries that do not have international treaties with the Russian Federation, it is considered that the spouses lived in a civil marriage. A wedding is not a legal basis for the recognition of marriage.
Jointly acquired property should be understood as any movable and immovable property acquired from the moment of marriage registration, regardless of whose income it was acquired with. The spouse's target income (bonuses, financial assistance), and property donated to the spouse are not joint property.
Important! If a spouse had any property before marriage, and during the marriage the spouse contributed to its improvement, for example, renovation of an apartment, renovation or completion of a private house, tuning a car - this property, according to a court decision, can be considered joint.
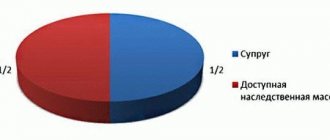
Half of the joint property is included in the estate. The other half is the marital share, which remains with the spouse and is not subject to inheritance either by will or by law. The personal property of the spouse, the property of the spouse acquired before marriage, is included in the inheritance estate.
Minor children of both or one of the spouses, persons dependent on the deceased for a year or more, disabled people, regardless of the disability group, if a will is not made in their favor, inherit half of the part that would be due to them in the event of inheritance by law.
Here are some examples:
- During marriage, the couple purchased an apartment.
The husband had a country house, which was purchased before marriage. After the death of the husband, the parents and adult daughter claim the inheritance. In this case, the wife will inherit half of the apartment plus a quarter from the other half and a quarter from the country house. Parents and daughter will inherit 1/8 of the apartment and 1/4 of the country house. - The property situation is the same.
The property is claimed by the wife, parents and minor son from his first marriage. The husband made a will for a third party. In this case, the wife receives only her marital share of 1/2 of the apartment. A minor son inherits 1/8 of the apartment and 1/4 of the country house. Everything else is inherited by a third party. - The husband did not draw up a will, but a marriage contract was drawn up, which states that all the husband’s property passes to his wife after his death. The property is the same. The husband's parents live in the apartment, and the wife has not made any contribution to improving the husband's real estate. Have no children. In this case, the parents have the right to challenge the contract, citing the wife’s selfish intentions.
Features of property division
The wife has the right to immediately claim half of her husband's property. Speaking of the common-law spouse, for this she will have to go through a complex legal process in order to confirm the fact of cohabitation with the deceased citizen. But even with a successful court decision, the common-law spouse will not be able to claim half of the property if she was not dependent on her husband.
Property that was acquired by the testator before entering into an official marriage is considered his personal property. This means that the widow will not be able to fully dispose of such an inheritance. She will not be able to sell it, give it away or pawn it. However, if the spouse invested her own funds in this property and there is confirmation of this, such property can be considered joint.
If after the death of the husband there are minor children, the inheritance will be divided equally among everyone. This is due to the fact that the rights of minors must be strictly protected by law. If the children have reached the age of eighteen, then one half of the inheritance is received by the spouse of the deceased citizen, and the second half is divided among the remaining heirs of the first priority.
The first heirs after the death of the mother
The first heirs entitled to accept property after the death of the mother are:
- father as husband of the deceased;
- children;
- maternal grandmother and grandfather (her parents).
When inheriting by law, an important aspect is documentary evidence of the relationship. It will be required regardless of the relationship between the testator and heirs. That is why the inheritance of spouses from each other is carried out exclusively in the presence of an officially registered marriage.
Similarly, in the event of the death of the mother, the father will be the heir only if he was officially married to the deceased.
Thus, when inheriting by law, relatives inherit depending on who they are related to each other. Their status is determined in accordance with generally accepted family ties, but in any case requires documentary confirmation.
A notary will not be able to formalize inheritance rights without presenting a document that reliably confirms the existence of a relationship. If such paper is lost or irretrievably lost for other reasons, it will have to be restored. If restoration is impossible, the successor will have to go to court to establish the relationship, and then register the inheritance.
Inheritance is the property remaining after the death of the owner, which is transferred to other owners according to the rules established by law. The inheritance procedure is regulated by Chapter 3 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation, which specifies the procedure and formal procedures required by the regulations for entering into rights. In order to protect your interests and not break the law, you should promptly familiarize yourself with the basic procedure for receiving an inheritance.
Rights of a common-law wife
Despite the fact that the wife is the heir of the first priority, this rule applies only to the spouse with whom the testator was officially married. A common-law wife is not considered a priority heir. This is due to the legal part of the registration, because the common-law spouse will not be able to provide documentary evidence of relations and kinship with the deceased citizen. Even if common-law spouses were registered in the same apartment, this does not confirm the marriage and does not give rise to a claim to inheritance.
An exception may be the incapacity of the common-law wife. That is, if she has a disability of the first or second group, or has reached retirement age and was fully dependent on her spouse for at least a year before his death. If this fact can be confirmed, the spouse has the right to claim a share of the property of her common-law husband.
Dependency means full financial support - the only source of income for a common-law wife. If the spouse, after his death, does not have any of the seven legal orders, then the common-law wife is recognized as the heir of the eighth order.
Dear readers!
It's fast and free!
Or call us by phone (24/7).
The practice of writing wills in Russia is not particularly widespread. More often, inheritance occurs on the basis of law.
Who is considered the first priority successor after the death of the testator in Russia in 2021? In Russia, wills are usually written in some special cases, when a person knows about his imminent death.
Often, testamentary dispositions are left by wealthy people who have many heirs.
Sometimes older people use this document to manipulate relatives. But in general, wills are rarely drawn up by ordinary ordinary citizens.
Inheritance after the death of the owner of the property occurs in accordance with the law. Who is ranked among the priority heirs in Russia in 2021?
Can a common-law wife claim inheritance?
According to the legislation of the Russian Federation, a common-law wife cannot claim an inheritance
, except by will or by the fact of the wife’s residence with her husband for 5 years or more, confirmed by witnesses. Then the common-law wife is included in the fourth line of inheritance.
If the common-law wife has been dependent on her husband for more than 1 year or is disabled, she is included in the eighth line of inheritance.
Whatever the true relationship between husband and wife may be behind the scenes of marriage, in the eyes of society it is considered the closest. And the law protects the rights of spouses, both during marriage and after the end of marriage - due to divorce or death.
We will not dwell on the issues of division of property during divorce - other articles on our blog are devoted to it. Today we will look at how property will be divided after the death of the husband. What is the wife's share and her right to inheritance after her husband's death?
Basic moments
The division of the property of a deceased person is legally carried out in cases where there is no will or it is declared invalid.
In this situation, the first priority successors will be able to distribute the property by mutual agreement.
The inheritance is divided similarly in a situation where the text of the will does not specify what exactly should go to whom.
But if candidates for inheritance cannot divide the property on their own, legal provisions come into force. On the basis of the law, property not reflected in the will is also divided.
The overall meaning of the law in this area boils down to the fact that inheritance according to the law is carried out when it is impossible to clearly establish the will of the testator and when the successors cannot come to a unanimous decision.
What it is
Inheritance is any property that remains after the death of the legal owner. An exception is compensation for damage caused.
As for the obligations of the deceased, they are also included in the inheritance and are distributed evenly among the heirs.
The right to inheritance cannot be transferred, donated or otherwise given to another person. Distribution of inheritance is carried out exclusively by approved methods.
The will is considered first. In the absence of this, legal norms apply.
Inheritance by law involves the transfer of property, taking into account the order of successors. In this case, the inheritance is divided in equal shares between the heirs of the same line.
According to the current law in the Russian Federation, there are seven lines of heirs. The order of assignment to one of the queues is determined by the degree of relationship with the testator.
Usually, when dividing property according to the law, the first three stages are involved, which includes the closest relatives.
The essence of the order is that the heirs of the next order receive the right to inheritance only in the absence of a previous order.
The so-called “mixed” inheritance also deserves attention. For example, the testator assigned part of the property to a specific person, but did not say anything about other valuables.
In such a situation, the will is reviewed first, and the named heir receives everything due to him.
The remaining share of the property is divided equally between the heirs of the corresponding order.
The legislative framework
Issues of inheritance on the territory of Russia are considered quite clearly in.
Anything that falls under the definition of “property” can become the subject of inheritance.
This is movable or immovable property, money, property and copyright rights, etc.
In fact, the concept of “inheritance” includes everything that can be transferred into the ownership of another person ().
Acceptance of an inheritance after the death of a person can be carried out by will or by law.
Inheritance by force of law is possible in the absence of a will or when the will of one of the heirs is contested with the subsequent recognition of the nullity or invalidity of the document.
To recognize the illegality of a testamentary disposition, compelling arguments must be presented in court, which may include the incapacity of the testator, a serious illness with clouding of reason, writing under duress, etc.
The main candidates for inheritance according to the law are the first-line successors. An exception is permissible if the fact of inadmissibility of inheritance is proven.
For example, parents were once deprived of parental rights. In this case, they do not have the right to inherit from the child.
Who is the first-priority heir by law after the death of the testator?
The first line of heirs includes the legal spouse, children and parents of the deceased.
Successors of the next orders can receive the inheritance or part of it only in the absence of primary heirs or when none of them has declared their rights.
That is, inheritance is not an obligation, but a right. Any heir has the right to waive his right in favor of the remaining heirs as a whole.
According to the law, the parts of the heirs of the same order are equivalent. But there is an exception related to inheritance by representation ( - , ).
Inheritance by right of representation occurs when the heir by law dies before the testator or at the same time as him.
In this case, the legal share of this heir passes to his descendants. In this case, the share of the deceased heir is divided equally between them.
Heirs by nomination may also be included in the first place as successors (Article 1142-), but only those who are direct descendants of the first-priority heirs.
husband
After the death of the husband, the legal spouse is the primary heir. The key point here is the presence of a registered marriage.
If the relationship has not been formalized, then the common-law spouse can inherit the husband’s property only according to the principle of a will or as a dependent of the testator.
The fact of cohabitation must be proven in court and the period must be at least a year.
In this case, a woman who is unable to work (over 55 years old) or has a confirmed illness that does not allow her to provide for herself independently can be recognized as a dependent.
But even the legality of marriage does not mean that the wife receives all the husband’s property. All property of spouses acquired during marriage is considered common.
Therefore, after the death of the husband, the existing property is divided in half. One part is the wife’s legal property; no one has the right to claim it.
The remaining half is the legal share of the testator and so it is subject to division.
Property belonging to the husband (spouse) is divided in equal shares between the wife and other heirs of the first priority. In the absence of the latter, the wife inherits everything.
But it is also necessary to take into account that some property may be acquired before marriage or gifted by someone personally to the testator.
Parents
After the death of parents, children become successors. The inheritance is distributed equally among all children, regardless of their number.
If the child heirs are minors, then the legal representative accepts the inheritance on their behalf.
This may be a court-appointed guardian or authorities.
In this case, the property is retained by the representative without the right of alienation until the child reaches the age of majority and receives the right of independent disposal.
Who is the first priority legal heir after the death of the father? This is his legal wife, children and parents.
At the same time, children from previous marriages are also considered heirs. have the same rights as their relatives.
When dividing the inheritance, their shares are equal. But the right of inheritance occurs only when the adoption is formalized.
When children are stepsons and stepdaughters, they receive the right to inheritance only in the seventh order.
After the death of the parents, heirs by nomination may also be included in the number of priority heirs. For example, grandchildren inherit from their grandparents due to the death of their parents.
If the children of elderly testator parents are alive, then the grandchildren can inherit only in order of priority.
Wives
The procedure for inheriting property after the death of a wife is similar to the same process after the death of a husband. That is, all common property is also divided in half.
Half goes to the husband by right of common ownership, and the remaining part is divided among the successors of the first priority.
For example, after the death of a wife, an apartment purchased during marriage and two cars purchased before marriage in the name of the wife remained.
The first-order heirs include the husband and the wife's father. By law, only an apartment is considered common property.
Therefore, the husband receives ½ of the apartment as the legal owner, another 25% of the apartment and one car he receives as an inheritance.
The remaining 25% of the apartment and the other car go to the father. The wife's property is also equally divided if there are children.
It does not matter whether the husband is the father of these children. All natural and adopted children of a spouse are considered her first-degree successors.
By right of representation, sisters and brothers of a wife (including half-siblings) can claim the inheritance if their common parents, recognized as the primary heirs, have died.
Sisters
After the death of a sister, the first priority heirs are her husband, children and parents. The legal part of her share in the common property and personal property are divided between the specified persons.
A claim to the inheritance left after the death of a sister is possible only in the absence of primary heirs or their refusal to accept the inheritance.
But you can get first priority for heirs if your parents have died. In this case, the right of inheritance by representation again applies.
But it must be taken into account that the heirs by designation are all the direct descendants of the deceased heir.
That is, if a sister dies, while her parents have already died, and there are several brothers and sisters left, then they all become heirs by nomination and have the right to declare their rights.
Video: inheritance by law. Inheritance of property by law
When it comes to a cousin's sister, there can be no priority inheritance. In this case, you can receive a share of the inheritance only in third order and only by right of representation.
That is, if the potential heir is among those who are the first-rank heir by law after the death of an aunt who is a relative of a cousin.
How to enter into an inheritance after the death of a husband?
According to the legislation of the Russian Federation, an inheritance can be obtained in two ways - by will and by law. For the wife, there is also a third one - a marriage contract. An inheritance based on a marriage contract can only be obtained if it states that the wife receives this or that property in the event of her husband’s death.
So, the inheritance can be received as follows:
- If the spouse has drawn up a will and a marriage contract
, the distribution of the inheritance is carried out on the basis of the will, since the contract is an agreement, and the will is an act provided for by law. According to the principle of the rule of law, the law has greater legal force than a contract. - If the deceased did not make a will
, and the marriage contract states that after death all the property of the spouse or some part of it goes to the wife, then inheritance occurs on the basis of the marriage contract.
However, in practice, if there is no joint property, such agreements are easy to challenge.
Again, if in the marriage contract the wife does not claim the property of her husband, then she has no right to inherit by law since, unlike a will, which is an act of unilateral expression of will, the contract is a bilateral marriage contract. The spouse’s signature under this agreement at the time of its conclusion means her agreement with the terms thereof.
However, neither a will nor a marriage contract can limit the right to receive a legal share in the inheritance of the minor children of the spouses, even if the children were born in a previous marriage and disabled persons who have been dependent on the deceased for a year or longer.
The procedure for entering into an inheritance without a will
The procedure for entering into inheritance according to the law is as follows:
The application must be submitted to the notary within six months from the date of death of the testator.
Otherwise, it is considered that the heir has renounced the inheritance and it is distributed among other heirs.
The deadline for applying can only be extended through the court by proving the justification for the untimely application.
Documents submitted to the notary include:
- passports or identity cards of all heirs;
- death certificate of the testator;
- or an extract from it confirming the place of last residence of the deceased;
- documents confirming the right of inheritance and family ties.
Property inherited by law is accepted only in full, without restrictions or reservations.
You cannot accept only part of the due share. The heir is considered the owner from the moment the inheritance is opened by a notary.
In conclusion, it should be said that the heirs of the first priority are, of course, the closest relatives of the deceased person.
But other persons predetermined by law can receive the right to inheritance on an equal basis with the primary heirs.
Direct heirs, primary heirs, first-priority heirs - those who are called upon to take ownership of property after the death of the testator have many names in the philistine environment. But if we speak strictly according to the law, then only one name will be correct: heirs of the first stage.
We are talking about those persons who, in accordance with the law, have the right to primarily count on receiving the property of the deceased in the absence of a will. Why are they usually called direct heirs? Probably because they include only the closest (direct) relatives and the spouse of the testator. What kind of people are these?
Contents of the article:
Who is the legal heir after the death of the husband?
The Civil Code of the Russian Federation provides for 8 lines of inheritance.
Property is inherited as follows:
- The spouse, as well as children and parents of the deceased belong to the first priority.
In this case, if the spouse does not refuse the inheritance or if it is not proven in court that the wife is the culprit in the death of her husband, or if the wife is declared incompetent, subsequent inheritance will not come into force. - Minor children, as well as persons dependent on the spouse,
have inviolable parts when dividing the inheritance, even if they were not indicated in the will. In this case, the will in this part is considered invalid. - If a spouse refuses an inheritance or is deprived of her right to inherit in court
, in case of refusal of an inheritance or the absence of heirs of the first priority, the right to inheritance is transferred to subsequent orders. - If no one wants to accept the inheritance or there are no subsequent heirs
, the spouse’s property is transferred to the ownership of municipal authorities. - If third parties who do not belong to any line of inheritance live in an apartment or private house, which at the time of death is the property of the spouse, they continue to live in this residential premises, but under a social tenancy agreement.
Parents
Direct heirs are persons who are directly related to the deceased, both in an ascending and descending line. In the ascending line, these are, of course, the parents. It is very sad when parents outlive their children, but life is life and everything happens in it, including this. Therefore, the legislator provided that in the absence of a will, the parents who survive their child are direct heirs.
It should be noted that in this case we are talking only about biological parents, and not about adoptive ones, and even more so they do not include guardians or trustees. The only exception to this rule is adoptive parents, because by virtue of the law they are equal in their formal status to biological parents, which means they have the right to claim the inheritance that opens up after the child they adopt.
Adoptive parents are deprived of this right if the adoption was canceled in court. By the way, about deprivation. Even biological parents can be disqualified from inheritance if their parental rights are terminated. The procedure and grounds for deprivation of parental rights are described in detail in the law. Let us only note that this decision is made only by the court.
About inheritance law
Legislation on inheritance of property
Inheritance law is a right given to all citizens of the Russian Federation without exception. If a person is represented by an heir, then he has the right to claim the acquired property of this or that person. In the case of the death of a mother, the division of things occurs in different ways:
- If there is a will, according to the provisions of this document. Thus, if the deceased mother drew up an inheritance document during her lifetime, then all her property goes to the person indicated in the document. At the same time, children or other persons who have claims to the property of the deceased who disagree with the provisions of the will have the right to appeal its legality through the court. However, it is important to understand that if a will is properly executed through a notary, it is almost impossible to refute its legality, so sometimes it is better not to resort to legal disputes of this kind. Otherwise, both money and time on legal proceedings will be wasted.
- In the absence of a will - according to the legally established procedure. If such a circumstance exists, that is, when the deceased mother did not draw up inheritance documentation during her lifetime, the division of the property remaining from her will occur in the order established by the relevant legislative acts. We will talk about this in more detail in the following paragraphs of our article.
It is important to understand that each type of inheritance has its own characteristics. The first type has the greatest number of subtleties, or rather, receiving an inheritance under a will.
First of all, we note that a will will be considered valid if:
- formalized in writing;
- contains the will of the citizen;
- compiled from the words of an adult and fully capable person;
- notarized.
Who is the direct heir after the death of the mother?
If at least one of the above aspects is not met, then the legality of the inheritance document can be challenged in court by persons who are interested in the distribution of wealth.
It is also worth noting such a concept as a mandatory inheritance share.
In general terms, this definition means that there are categories of legal heirs who, in any case, will receive a certain share of the property of the deceased.
In this case, it does not matter at all whether there is a will, whether they are indicated in it, and whether other subtleties of the inheritance procedure are observed.
The “mandatory” heirs include:
- minor children;
- dependents;
- incapacitated relatives;
- disabled parents.
The share that these persons will receive is determined in court. As a rule, all of them have the right to claim no less than half of the property left by the deceased mother, even if, by her will, they are not included in the will.
This legislative nuance is due to the fact that the citizens presented above are a vulnerable segment of the population, therefore, when dividing the inheritance, they should receive some privileges and protection from the state.
It is worth noting that this inheritance procedure only applies to the division of real estate; it is not used for other things.
Children
Children are direct heirs after the death of their parents. Moreover, they inherit even in the case when their parents were deprived of their parental rights. After all, the point of depriving such rights is to preserve all parental responsibilities in the absence of all parental privileges.
Whether a child has the right to inherit the property of a parent deprived of parental rights is described in the video below:
Just as in the situation described above, children are direct heirs only if they are biologically descended from the testator, or if they are adopted. Stepsons and stepdaughters are not considered children, and therefore they immediately move six lines back and stand in the seventh line of heirs.
The biological origin of children is confirmed by documents issued by the civil registry office - that is, a birth certificate in which the child’s parents are indicated. However, in practice there are also controversial situations when there is no direct evidence of the biological origin of a child from a specific person. In these cases, disputes are resolved in court by filing a claim to establish paternity (maternity).
Today there are reliable ways to prove relationship. The main ones are the so-called genetic fingerprinting, or simply genetic examination, which gives results with an accuracy of 99.99%.
Spouse
The spouse is a direct heir along with direct relatives: parents and children of the testator. Although the husband and wife are not relatives, the legislator designated them as heirs of the first priority after each other, which, of course, is quite fair. Because these are, whatever one may say, the closest people.
In this case, only the legal spouse has the right to inherit, that is, the one with whom the marriage was formalized according to all the rules in the registry office. So-called common-law spouses do not inherit from each other in the absence of a will.
In addition, all property acquired by spouses during marriage is their common joint property, which means that the husband or wife initially owns half of all property. Thus, when we determine the estate (that is, the property that will pass to the heirs), it is necessary to take into account the marital share. And this is at least half. In this case, from the second half, the spouse will inherit his share along with other heirs.
Who is the first heir after the death of his wife?
Following the example of inheritance after the death of a husband, it is possible to trace and designate the first-line heirs who receive the property left after the death of the wife. They will be:
- children;
- her parents (father-in-law and mother-in-law);
The rules for entering into inheritance rights, characteristic of all other cases, apply in full to inheritance after the death of the wife. The husband has the right to allocate a share of the common property with his wife acquired during the marriage through their joint efforts. The remaining property is divided in accordance with the principle of equality of heirs.
If the children died before the death of the wife or simultaneously with her, then their children (grandchildren of the testator) can act as heirs by right of representation.
However, do not forget that if a court decision has been made to deprive parental rights, parents cannot inherit from their children and vice versa.
Grandchildren
Grandchildren are not formally classified as direct heirs by law. But they inherit by the so-called right of representation. This means that if the testator’s child died before him or at the same time as him, then his share passes to his descendants - that is, the testator’s grandchildren.
This will be more clear with an example. Citizen Sergeev had two sons. The eldest son has two daughters, but the youngest son had no children. Citizen Sergeev and his eldest son get into a car accident and both die. After the death of citizen Sergeev, the house remains. This house will be divided as follows: 1/2 will go to the youngest son, and 1/4 will be inherited by the sons of the deceased eldest son of citizen Sergeev. This is inheritance by right of representation.
The following video explains whether it is possible to leave an inheritance to a great-granddaughter if there are first-degree heirs:
Unfortunately, each of us experiences unpleasant and painful situations when our loved ones die. Parents in the person of mother and father are no exception. In such a situation, it is necessary to deal with many issues, and one of them is receiving an inheritance. Without knowing your rights and the rules for receiving property by the first heirs in line, it will be very difficult to do this. Therefore, below we will learn about all this in more detail.
Dear readers!
Our articles talk about typical ways to resolve legal issues, but each case is unique. If you want to find out how to solve your specific problem, please contact the online consultant form on the right →
It's fast and free!
Or call us by phone (24/7):
Types of inheritance
There are two main types of inheritance: by law and by will. Each of them has its own pros and cons. Therefore, it is worth considering each of them in more detail.
Inheritance by will assumes that a citizen has the right to independently dispose of property after death and distribute shares among heirs at his own discretion. He may also not include some relatives or indicate that they have no right to property after his death. It is not necessary to describe the reasons for such a decision. This document is drawn up with the help of a notary and has been very popular lately.
If we talk about inheritance by law, then a person cannot decide who gets what. The law makes such decisions for him and distributes real estate according to the degree of relationship and only in turn. The wishes of the deceased do not matter. Despite the popularity of wills, this process remains just as common due to the ease of paperwork and receiving an inheritance.
Who is the first heir after the death of his father?
In the event of the death of the father and inheritance, the inheritance will be accepted by law:
- mother as his wife;
- children;
- grandmother, grandfather on the father's side (his parents).
After the death of the father, the heirs take over the rights to his property in accordance with the general rules. If none of the presented heirs is present, all are deprived of the right to inherit or have renounced their rights, the next steps proceed to inheritance.
If there is no heir, all the property of the deceased will be considered escheat. This automatically means its transfer to the benefit of the state.
What is a will?
There are several types of wills and everyone has the right to decide which one they like. The most common is an open will, which implies transparency of the process and a minimum of effort for its implementation. As for the closed type, everything is almost the same here. The main feature is that no one except the testator knows about the contents of the document, not even a notary. Although it is impossible to do without drawing up a document and having several witnesses.
There is also a will made in an emergency situation. It assumes that the document is drawn up at a time when a person’s life and health are in danger. Therefore, the procedure is simplified and does not require registration with a lawyer. But then it is necessary to prove in court that this was exactly the situation.
The main thing to remember is that a will must be drawn up in writing only by an adult and capable citizen. It is necessary not only to find witnesses, but also to have the document certified by a notary. It is impossible to do this by proxy or on behalf of several people.
Since the will describes the will of the citizen, and he has the right not to indicate any of the heirs, even his closest relatives, such as his mother and father, may not be included there. A parent may also omit children and spouses from the will. However, this does not mean that they will not be able to receive an inheritance, because there is a mandatory share by law.