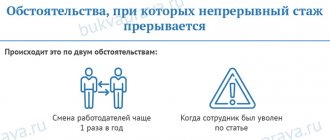
Does it affect your pension?
This indicator is determined in accordance with existing formulas by summing up the periods:
- when a person performed labor duties on the basis of relevant contracts;
- when municipal or civil service took place;
- the person must be insured for a situation related to temporary disability.
It turns out that the fact of continuous work does not have any impact on the size of pensions or even on the size of social benefits. This is due to the fact that in all practical circumstances the basis is the actual work activity, and these breaks sometimes have no actual significance.
How to calculate length of service using a work book?
The rules for calculating continuous work experience are quite simple. The basis for its calculation are the following documents:
- contract or work agreements;
- employment history;
- certificates from places of work;
- military ID.
When calculating, we first add up the time worked in each company, and then add up the periods if the breaks did not exceed the duration established by law (or occurred for a good reason).
Definition of the concept
Continuous work experience - the time interval during which the employee worked, and the “gaps” spent on transitions between jobs, for this reason do not exceed the duration limit established by law.
This parameter is calculated in 2021 by analogy with the previous period, and to preserve it it is necessary that no more than a month pass between the time of termination of the employment contract and employment in a new workplace.
Often in practice, circumstances develop such that after the moment of dismissal a person is registered with the employment service as an unemployed person. All this time he can be looking for a new job. If a sudden illness occurs during this period, it can provoke an increase in the gap between dismissal and the next employment.
In this situation, there is no interruption of work experience, since illness is a force majeure situation. To prove your “innocence” you only need to obtain a certain list of medical documents.
Continuous work experience upon dismissal at will
When is the length of service interrupted after voluntary dismissal? Continuous service after voluntary dismissal is 30 days. The length of service after dismissal by agreement of the parties. According to the legislation of the Russian Federation, the period is 3 weeks - in the case of mutual consent.
Upon completion of the specified time, it acquires intermittent status. What could be the consequences? If a worker is dismissed before amendments are made to the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, and the period is interrupted due to exceeding the unemployment limit, then his benefits will be canceled if:
Free legal consultation
We will answer your question in 5 minutes!
Free legal consultation We will answer your question in 5 minutes!
Ask a Question
Ask a Question
- he was entitled to length of service, and it was accrued;
- for the new workplace, payments are restored.
This is also important to know:
What is an advance and how to return it under the contract
If, before the introduction of the latest amendments, continuous experience was extremely important, then from now on most of the calculations are carried out on the basis of insurance. The pensioner should build on it.
When the length of service remains uninterrupted
Now let’s talk directly about the deadlines that are determined by the legislator for the possibility of changing jobs and are not considered an interruption of work experience.
All deadlines can be identified in the following sequence:
- Three weeks. The employee terminates the employment relationship on his own initiative, but does not have any valid circumstances or reasons.
- Month. Leaving work is carried out at your own request. There is a reason why you need to change the company either by agreement of the parties to the employment relationship.
- Two month. Designated for workers of the Far North or areas equivalent to it to find a new place of work.
- Three months. Here the employee is fired due to staffing or due to the liquidation of the company. The same amount is allocated for the spouse to find a job if the other spouse was transferred to work in another area and the whole family moved.
- Six months. Allocated to employees of the government or the State Duma of the Russian Federation to find a new job.
- One year. Contract uniformed military personnel after the end of their contract period.
- Without any time restrictions. This category included veterans (combatants) and military personnel with more than 25 years of military experience.
The serviceman's service is not interrupted for a year after the end of the contract
If it is necessary to increase the time interval for selecting a new job or to reduce the gap between dismissal and new employment, it is advisable to take a vacation, the last day of which will be dismissal. This allows you to have maximum freedom of action to choose a new job. You will still be listed as an employee of the old company, but you already have a properly executed work book.
The legislator has provided for cases when the accrual of seniority does not stop upon the actual termination of the employment relationship. These included:
- cancellation of an employment agreement with an employee who has a child not older than 14 years (if the child is disabled, then up to 16 years old) for the entire period until the children reach the agreed age;
- for the entire period of maternity leave;
- after the citizen has received a legal pension;
- if the dismissal occurred in regions with high unemployment rates;
- when a previously illegally dismissed employee was reinstated;
- if the worker was involved in performing public works with payment.
What is the length of service?
All concepts of length of service available in various laws and normative documents issued on their basis can be simply divided into 4 main categories.
| Category | Definition |
| Total work experience | The entire actual (including breaks) period when the citizen performed socially significant useful actions that are fixed at the legislative level. This is the performance of any paid or creative work, service in government agencies, individual entrepreneurial detail, and other periods determined by law that are considered part of the length of service. |
| Special experience | This includes periods of time (including breaks) when a citizen performed socially significant labor functions in certain positions, under special (different from normal) conditions of activity, or had a special status. Examples are service in the armed forces, work of disabled people of groups 1 and 2, work of prisoners beyond the period prescribed by the sentence. |
| Continuous experience | They include all periods of time when an employee, without breaks (or their duration should not exceed the period established by law in each specific case), performed labor functions in one company (in different positions) or in several enterprises. |
| Insurance experience | The time interval when insurance contributions are paid for an employee directly to the Pension Fund in order to create the proper level of pension coverage for him in the future. The concept was introduced in 2007 and is just beginning to take root. |
It is worthwhile to dwell on the procedure for calculating length of service for various periods of performance of work functions. For certain working conditions, work experience can be calculated using increasing factors. The increased coefficient will be used to calculate:
- one and a half times the rate if the citizen worked in the Far North or equivalent areas;
- double the amount when performing military service (conscription), labor activity in anti-plague institutions, leper colonies;
- in triple the amount when military service is carried out during hostilities, illegal stay in places of deprivation of liberty, illegally repressed citizens, and over time, rehabilitated.
Remember, the calculation of the general, special, continuous period of work is carried out by summing up the time of actual work in the company, taking into account the time intervals provided for by law for the period of job change.
How many days is the period of service interrupted after dismissal?
Sometimes practical cases arise in which, after dismissal, subject to rapid subsequent employment, an interruption of service does not occur, because the periods of involuntary unemployment are not taken into account. These are the practical cases:
- liquidation of the organization;
- staff reduction;
- transfer of deputies to another settlement;
- a significant increase in unemployment;
- erroneously drawn up medical report;
- involving an employee in public works.
The time during which you may not work after the termination procedure depends on who initiates the dismissal:
- the employee himself – 3 weeks;
- objective circumstances – 3 months;
- by agreement of the parties – 1 month.
It turns out that the indicator does not depend on breaks between jobs, but the personality of the initiator of operations affects this point. There are several more auxiliary factors prescribed and stipulated within the framework of current legislation (the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
Thus, continuous work and insurance experience after leaving work of one’s own free will is preserved, but only for a short time.
A description of continuous experience according to the Labor Code of the Russian Federation is presented below.
Is the length of service retained when applying to the labor exchange after dismissal?
Registration at the Employment Center means assigning a person the status of unemployed. This means that he will receive unemployment benefits.
Thus, there is no reason to maintain the working period. Therefore, the employee receives only the one or two months due to him after losing his job. The exception is cases of termination of the contract at the initiative of the employer.
- In this case, the period remains for one month. The calculation of the specified time begins with a mark in the work book.
- Reduction or complete liquidation of an enterprise makes it possible to maintain continuity for a period of three months from the date of termination of legal relations with the employer. This is the maximum time allowed by law.
How interruption of service depends on the reason for dismissal
The impact on the time period when a citizen actually remains unemployed, but the time is counted towards continuous work experience, is direct. In the classic case of leaving work (by agreement of the parties, at one’s own request, if there are reasons for dismissal), the law establishes a one-month period for finding a new job after dismissal. The same period is allotted to an employee who transfers, by agreement between employers, from one company to another.
A little more is allocated to former employees of enterprises located in the regions of the Far North (two months), as well as to those who lost their jobs not on their own initiative, in particular due to layoffs (three months).
In order to maintain continuity of work experience for an employee who decides to change jobs, it is advisable to take into account the following points:
- You should look for a new job in advance (while you are still on staff at the old company).
- To increase the search period, you can use vacation followed by dismissal.
- If an employee is on leave without pay, his length of service is also not interrupted, but the amount of time to find a new job increases.
- If you find a new job, it is advisable to resign by transfer (you are guaranteed to be accepted at the new place of work) or by agreement of the parties (this allows you to resign without working off).
- If you have been laid off but have already found a new job, you should not wait until the warning expires. Based on your application, the employer may dismiss you by reducing the previously agreed period.
- Women on maternity leave, even if the company is completely liquidated, retain their seniority until the baby turns three years old. But to do this, having received a document on the liquidation of the company and dismissal, they are required to register with the Employment Center.
Watch this video about continuous experience:
Interruption of service due to voluntary dismissal
Normative acts providing for the conditions for the continuity of labor activity of working people do not yet exist in the legislation of the Russian Federation.
This is also important to know:
Gray salary: judicial practice, is there any point in suing, employer’s responsibility
Not so long ago, this issue was spelled out in the Rules, according to which the continuous work experience of an employee resigning on his own initiative was interrupted in the following situations:
- the former employee did not find a new job within three weeks from the date of dismissal from the previous one;
- there is no compelling reason to miss work.
The following situations did not affect continuity in any way:
- the employee had to leave work due to the transfer of his spouse to a workplace in another city, town, etc.;
- The employee left due to retirement.
How to calculate continuous work experience using a work book?
You can calculate the continuous work experience from your work book using a calculator. This can be an online program or a simple regular calculator with which you can manually perform the calculation. It is quite obvious that it is much easier to calculate the duration of work using an online calculator. The numbers from the work book are simply entered into it, indicating the dates of hiring and dismissal. The calculation is performed automatically by clicking the “Calculate” button.
In this case, during the calculation it is necessary to take into account certain values based on clause 1 of Article 13 of the current Labor Code of the Russian Federation. To calculate length of service, you need to use the dates from the book. The number of days in a month is 30, and the number of months in a year is 12.
First you need to calculate how many years, months and days correspond to a certain place of work. Next, you need to pay attention to the period that was in between and take into account the reasons and conditions for dismissal. If the duration of the break is longer than the period established by the code, then the chain is interrupted and the further period of work is not added to the previous one.
Free legal consultation
We will answer your question in 5 minutes!
Free legal consultation We will answer your question in 5 minutes!
Call: 8 800 511-39-66
Ask a Question
Continuous work experience for calculating sick leave in 2019
The period of work for calculating sick leave affects the amount of benefits that are provided for temporary disability. At the same time, in 2021, the calculation is carried out according to the length of insurance; continuous coverage is not important when determining the amount of sick leave.
This is also important to know:
What is unemployment benefit and how to get it
The main point is that to calculate this amount, the employee’s periods of work are taken for which payments were made to insurance funds. In addition, this does not include contract service in the army and compulsory military service. Therefore, when calculating sick leave, it is important to take into account such nuances.
How many days does work experience end after dismissal?
State Duma, who are transferred, as well as members of their families who are forced to change jobs;
- leaving the enterprise of a pensioner upon returning to work in the future;
- loss of a job in a place where there is no possibility of finding another one - in closed administrative entities, remote duty stations;
- dismissal due to unfair accusations or suspension from work due to an erroneous medical report with subsequent reinstatement to the same place;
- period of participation in public works with monetary compensation;
- a person's stay in custody followed by acquittal and reinstatement to his previous position and some others.
Conscientious, properly registered workers and employees are officially given time to solve problems that arise as a result of these circumstances.
When is employment interrupted after dismissal?
But many are trying to either no longer strive for continuity, or to find a new place of work as soon as possible, within the first 30 days. This is an additional safety net that will help avoid surprises.
Maintaining a profession How to calculate continuous experience? It is already clear that we are talking about periods of continuous labor. In Russia, it is still possible to characterize the periods of transfer of funds to the Pension Fund for a future pension using the term being studied.
Attention There is one more small nuance that has not been taken into account. Continuity of work experience will not be affected if a citizen quits for good reasons, but at the same time he retains his profession
True, a new job will have to be found in one or another field of activity within the previously specified time frame. This feature is not entirely clear to many. Other Continuous length of service is considered as such, even if citizens resign.
Is it worth holding on to continuous service after voluntarily resigning?
- If the enterprise is liquidated, then while on maternity leave, the length of service will include a period of up to 3 years, provided that the employee was registered with the Employment Center, but could not get a suitable job.
- If an employee resigns due to transfer to another organization, the new employer is obliged to employ him within a month: this is the period of continuity.
Despite the fact that now the procedure for calculating seniority has been significantly simplified, there are still some areas in which it is carried out according to the old rules established by the regulations of organizations.
What benefits does continuous service provide to employees?
Crisis
Continuous work experience is the duration of a citizen’s work in one or more organizations, if the period of unemployment in the intervals between employment did not exceed the established period.
To maintain continuous service, you need to know the following nuances:
- if within one year the employee changes his place of work, then it is interrupted, even if all deadlines are met.
- if a citizen is fired “under an article”, the period will be interrupted, even if the deadlines for placement with another employer are met;
- if an employee was forced to interrupt her work activity due to maternity leave, this period is considered a valid reason for maintaining it.
Continuous service after voluntary dismissal allows employees to count on some benefits, unlike those for whom it was interrupted for a long time:
- the opportunity to receive regular salary increases for continuous work in state budgetary institutions;
- increasing the amount of social benefits;
- receiving benefits; receiving bonuses and additional leaves established by the employer for length of service.
Does continuous service affect the size of the pension?
The calculation procedure is regulated by Art. 16 of Law No. 255-FZ, by virtue of which, to determine the amount of benefits in connection with pregnancy, childbirth or unemployment, the insurance period includes all periods of work in the state, municipal or other service, during which the employee’s social insurance was carried out and payments were accrued.
Law No. 173-FZ “On Labor Pensions” dated December 17, 2001, when assigning pensions, the amount of insurance contributions and the total working period of work are taken into account. The same practice is followed by Law No. 400-FZ “On Insurance Pensions” dated December 28, 2013.
Consequently, for calculating the size of pensions, continuity of work does not matter. The insurance period is taken as a basis, which includes all periods of official work activity, regardless of the presence or absence of gaps between them.
What does continuity of experience affect?
Now that we have the concept of length of service, it is advisable to consider why it is necessary to maintain its continuity and why it is important to ensure that length of service is always taken into account continuously. Regarding continuity, it should be noted that there is a direct dependence during the calculation of the cash disability benefit due. Depending on the length of service, the employee will receive:
- 100% of average monthly earnings when continuous work is over 8 years;
- 80% is paid when the employee has accumulated from 5 to 8 years of continuous work experience;
- 60% will be paid to employees who have worked for over a year (up to 5 years inclusive).
Experience affects the amount of sick leave payments
The next point, which directly depends on the amount of labor baggage a citizen has, is the size of his future pension. You need to understand that a change in the concept of length of service in insurance took place in 2007. Therefore, citizens who began their working activity before this turning point and continue it now will benefit from both new legislation and old laws.
Commentary on Article 314 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation
Law of the Russian Federation of February 19, 1993 N 4520-1 “On state guarantees and compensation for persons working and living in the Far North and equivalent areas” did not have norms with such content. It, in Article 12, provided that the procedure for establishing and calculating the length of service for receiving a percentage increase in wages is determined by the Government of the Russian Federation.
Despite the fact that Article 314 of the Labor Code does not directly say this, it deals with the establishment and calculation of length of service for receiving guarantees and compensation by persons working in the named areas and localities.
At the federal level, only state guarantees and compensation can be established. Therefore, the procedure for calculating length of service adopted by the Government of the Russian Federation applies only to them. With regard to guarantees and compensation for employees of organizations financed from the budget of a constituent entity of the Federation or from the local budget, the rules for provision apply, respectively, established by the state authorities of the constituent entities of the Federation or local government bodies. These rules may apply to cases of provision of additional guarantees and compensation, rules established for the provision of state guarantees and compensation, including the rules for calculating length of service established by the Government of the Russian Federation.
Based on the provisions of Article 314 of the Labor Code, federal law and the Government of the Russian Federation must regulate the procedure for establishing and calculating length of service to receive all guarantees and compensation provided in connection with work in the Far North and equivalent areas.
Currently, only the right to:
— percentage bonuses to wages;
- payment once every two years of the cost of travel to the place of use of the vacation and back, as well as the cost of baggage transportation, in accordance with Article 325 of the Labor Code;
- purchasing an apartment or joining a housing construction cooperative or allocating a land plot for individual housing construction at a newly chosen place of residence, on the basis of Article 327 of the Labor Code;
— labor pensions on preferential terms (Article 327 of the Labor Code);
— Article 327 of the Labor Code provides for the summation of length of service for work with various special working conditions;
— maintaining the size of the pension when leaving the northern regions, in accordance with Article 327 of the Labor Code;
— compensation for travel expenses to a place of rest and back for old-age pensioners (Article 327 of the Labor Code).
All other guarantees and compensations are not conditional on the presence of a certain length of service, and the right to them arises immediately after the conclusion of an employment contract for work in the Far North and equivalent areas.
These guarantees and indemnities include:
— payment of the regional coefficient;
— additional leave for work in the North;
— maintaining the average salary for the period of employment;
— additional day off;
— payment of travel costs for medical consultations or treatment;
— compensation for expenses associated with relocation.
To receive the above-mentioned guarantees and compensations, the length of service includes all working time and rest time, as well as periods stipulated by a concluded labor or collective agreement, as well as legislation, during which the employee was on the payroll of the employer and was subject to state social insurance .
Such periods may include: time of actual work activity, annual leave, parental leave until they reach the age of three, time off, rest between shifts, business trips, temporary disability, performance of state and public duties, advanced training without interruption or with interruption. from production, forced absenteeism due to illegal dismissal.
It is important to remember that it does not matter where the employee was at one time or another - in the regions of the Far North or in equivalent areas or beyond.
The length of service that gives the right to the specified guarantees and compensations includes certain periods during which the citizen was not on the staff (payroll) of the employer, that is, he was not an employee, but was in the regions of the Far North, or in equivalent areas:
- military service, service in internal affairs bodies and tax police;
— full-time studies in educational institutions of primary vocational, secondary vocational, higher vocational, postgraduate vocational education and other educational institutions, with the exception of general education;
- higher professional, postgraduate professional education and other educational institutions, regardless of the duration of breaks in work related to training;
- work or practical training (regardless of their payment) during the period of study in educational institutions of primary vocational and secondary vocational education;
- unemployment, when a citizen received unemployment benefits or a scholarship in accordance with employment legislation, as well as time spent traveling in the direction of the employment service to another area for employment.
The main issues of calculating length of service for receiving percentage bonuses to wages for work in the regions of the Far North and equivalent areas, which arise regarding the summation of this length of service and the recalculation of earned bonuses when moving to work from one northern region to another, are explained in the Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation dated October 7, 1993 No. 1012 and clarification of the Ministry of Labor of Russia dated May 16, 1994 No. 7. They provide that:
— length of service, which gives the right to a percentage increase in wages, is calculated for persons who have entered into an employment contract from the date of work for employers located in the regions of the Far North and equivalent areas, as well as in the southern regions of the Far East, Krasnoyarsk Territory, Irkutsk and Chita regions, in the Republic of Tyva, the Republic of Khakassia;
— length of service is summed up regardless of the duration of the break in work and the motives for terminating the employment relationship, with the exception of dismissal for guilty actions, which was made on the following grounds:
convicting the employee to a punishment that precludes the possibility of continuing his previous work, in accordance with a court verdict that has entered into legal force;
repeated failure by an employee to perform labor duties without good reason, if he has a disciplinary sanction;
absenteeism;
showing up at work in a state of alcohol, drugs, toxic or other intoxication;
disclosure of secrets protected by law;
theft by an employee at the place of work of someone else's property (including small property), embezzlement, intentional destruction or damage, established by a court verdict that has entered into legal force or a resolution of an authority authorized to apply administrative penalties;
violation by an employee of labor protection requirements, if these violations entailed serious consequences (industrial accident, accident, catastrophe) or knowingly created a real threat of such consequences;
the commission of guilty actions by an employee directly servicing monetary or commodity assets, if these actions give rise to a loss of confidence in him on the part of the employer;
the commission by an employee performing educational functions of an immoral act that is incompatible with the continuation of this work;
adoption of an unjustified decision by the head of the organization (branch, representative office), his deputies and the chief accountant, which entailed a violation of the safety of property, its unlawful use or other damage to the property of the organization;
a single gross violation by the head of the organization (branch, representative office), or his deputies of their labor duties;
submission by an employee to the employer of forged documents or knowingly false information when concluding an employment contract.
In accordance with Part 2 of Article 77 and Paragraph 14 of Article 81 of the Labor Code, federal laws may provide for other grounds on which an employee may be dismissed for committing other guilty actions.
When an employee is dismissed, committing guilty actions, or when starting a job with another employer, previous work experience for receiving a percentage increase in wages (even if it allowed him to receive an increase in the maximum amount) is not counted (not summed up). Thus, the employee needs to complete his seniority again to receive bonuses, including the first one.
Recalculation of the bonus, in the event of a transfer of an employee who has the work experience necessary to receive a percentage bonus, to work for an employer located in another region or another locality, is carried out in proportion to the time worked in the relevant regions of the Far North, equivalent areas, in the manner established at the new place of work, in compliance with the following rules:
— when an employee moves from an employer located in the Far North region to an employer located in an area equated to the Far North regions, the amount of percentage bonuses is established at the rate of one ten percent increment for every 12 months worked in the Far North regions. The next regular percentage increase must be accrued in the general manner one year from the moment the employee transfers to an employer located in an area equated to the regions of the Far North, in the amount established for these areas;
— in the event of a transfer of an employee from an employer located in an area equated to the regions of the Far North to an employer located in the Far North, the amount of bonuses (as a percentage) accrued for full years of work remains in the same amount, and for those worked in excess During these months, an additional premium is calculated in proportion to the number of months. The next regular percentage increase must be accrued in the general manner six months from the moment the employee transfers to an employer located in the Far North region established for this region;
- when an employee transfers from an employer located in an area equated to the regions of the Far North to an employer located in the Far North region, who previously transferred to work in this area from the regions of the Far North, the total amount of percentage bonuses to be paid to wages (in percentage terms) calculus) should be determined by summing the percentage allowances earned by him from each of these employers. In this case, the total amount of percentage increases in wages should not exceed the established limit.
The same procedure is used to determine the size of the percentage bonus for an employee transferring from an employer located in the Chukotka Autonomous Okrug, in the North Evensky District of the Magadan Region, the Koryak Autonomous Okrug, the Aleutian District of the Kamchatka Region, as well as on the islands of the Arctic Ocean and its seas (beyond with the exception of the White Sea islands), to work for an employer located in other regions of the Far North or in equivalent areas, and back;
- in the event of a transfer of an employee who has the work experience necessary to receive a percentage increase from employers located in the southern regions of the Far East, Krasnoyarsk Territory, Irkutsk and Chita regions, the Republic of Buryatia, the Republic of Tyva, the Republic of Khakassia, to an employer located in the region of the Extreme North or areas equated to the regions of the Far North, he retains the earned percentage premium. The next regular allowance for this employee is accrued in the general manner six months from the date of transfer to an employer located in the Far North region, and one year from the date of transfer to an employer located in an area equated to the Far North region.
If at the time of the employee’s transfer to an employer located in the Far North or an equivalent area, he has not fully earned the percentage bonus and its amount is less than 30%, then the time of work after the first or second bonus is recalculated based on the year of work in the southern regions. regions of the Far East, Krasnoyarsk Territory, Irkutsk and Chita regions, the Republic of Buryatia, the Republic of Tyva, the Republic of Khakassia, for three months of work in the regions of the Far North and for six months of work in areas equated to regions of the Far North.
If an employee who has the work experience necessary to receive the bonus moves from an employer located in the Far North region or an area equivalent to the Far North regions, to an employer located in the southern regions of the Far East, Krasnoyarsk Territory, Irkutsk or Chita regions, the Republic of Buryatia, in the Republic Tyva, the Republic of Khakassia, and then back to the regions of the Far North or areas equated to the regions of the Far North, he is paid an allowance for service in the regions of the Far North or areas equated to the regions of the Far North;
- when individual territories are classified in the established manner as regions of the Far North or localities equivalent to them, the calculation of the length of service for receiving the next earned percentage bonus for those working and living in these territories is carried out from the day the specified territories are classified as regions of the Far North or localities equivalent to them.
This rule does not apply to employees employed by employers located in these areas and who have previously earned bonuses for years of work in the Far North or equivalent areas. In this case, from the moment the area is classified as a region of the Far North or areas equivalent to them, these workers are restored to previously earned allowances.
Motherhood
Continuous work experience is maintained if a woman goes on maternity leave. But is continuity maintained if the expectant mother goes on maternity leave? There are two completely opposite opinions on this matter.
Russian labor legislation does not contain information regarding maternity leave and continuous service. In essence, the length of service is maintained, since the woman remains employed, the nature of the work performed changes. On maternity leave, a woman deals only with family matters, but not with work duties. However, lawyers tend to believe that the length of service in this situation is not interrupted.