When planning the renovation and arrangement of a future office, few thoroughly study all the regulations containing requirements for office workspaces. One day, inspectors will appear on the doorstep, and the matter may not be limited to a fine - violations will have to be corrected and work will have to be suspended for the duration of repairs, which will entail costs.
Troubles happen not only to small businesses; even giants with huge resources and a staff of lawyers behind them make mistakes. Thus, in 2021, Russian Post was fined for violating fire safety. An inspection by the State Fire Supervision Service found in a number of departments the absence of automatic fire alarms, warning systems and management of evacuation of people in case of fire. Since the shortcomings were not eliminated within the allotted time, the company had to pay a fine of 75,000 rubles.
To prevent this from happening to you, we have prepared an article in which we talk in detail about what norms and requirements must be followed when organizing office workspaces and arranging other public spaces. We take them into account in our projects, so we know them by heart!
If you're planning a move to a new office, check out our step-by-step guide to help you save time and money!
The legislative framework
- The issue of square footage per person in office premises is regulated by sanitary and epidemiological rules and regulations (SanPiN), which were developed in accordance with the Federal Law “On the sanitary and epidemiological welfare of the population” dated March 30, 1999. No. 52 and the Regulations on state sanitary and epidemiological regulation, approved by Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation of July 24, 2000 No. 554.
- As for the hygienic requirements for personal electronic computers (computers), they are specified in the document SanPin 2.2.2/2.4.1340-03.
- Also, there are regulatory requirements for square footage in offices in the code of rules SP 118.13330.2012 “Public buildings and structures.”
Legal workplace area
Requirements for office premises are based on two main laws: SanPiN 2.2.2.1340-03 and SNiP 2.09.04-87.
By default, the required minimum workplace area per employee is 4 square meters . Depending on the specifics of the job, position and responsibilities, these standards may change.
For those who work at the computer
A workplace equipped with a personal computer with a modern liquid crystal (or plasma) monitor must be located on an area of at least 4.5 m² in the absence of other devices that consume electricity and are a source of additional electromagnetic radiation.
A second monitor, printer, fax, scanner, copier require additional space. However, if an employee spends no more than half of the working day at the computer (less than 4 hours), then the area of his workplace can be the same 4.5 m².
Office space without computers
In the case where the office space does not involve working at a computer, this norm is reduced to 4 square meters. This is the required minimum, regardless of any other conditions.
For employees with disabilities
For employees from low-mobility groups (disabled people) the employer is obliged to provide a workplace with an area of at least 5.65 m² per person, and for wheelchair users - at least 7.65 m².
Standards for non-working areas
To understand whether there is enough space for workers in an office space, we present the amount of minimum required area per person :
- The rest room should have 0.9 m² per person.
- The area of the dining room is determined at the rate of 1 m² per visitor and at least 1.65 m² per person using a wheelchair, but not less than 12 m².
- In the case of work with a high level of stress and emotional tension, each workplace must be fenced off with special partitions, and the distance between employees must be at least 2 meters.
- According to SanPin standards, the aisle distance between tables is from 50 to 100 cm, depending on the number of employees at a given enterprise.
Standard office space per employee
In accordance with Part 1 of Art. 211 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, state regulatory requirements for labor protection, contained in federal laws and other regulatory legal acts of the Russian Federation and laws and other regulatory legal acts of the constituent entities of the Russian Federation, establish rules, procedures, criteria and standards aimed at preserving the life and health of workers in the labor process activities.
In accordance with paragraph 3.4 of SanPiN 2.2.2/2.4.1340-03 “2.2.2. Occupational hygiene, technological processes, raw materials, materials, equipment, working tools. 2.4. Hygiene of children and adolescents.
Hygienic requirements for personal electronic computers and work organization.
Sanitary and epidemiological rules and standards”, approved by the Chief State Sanitary Doctor of the Russian Federation on May 30, 2003
Determination of hygienic standards for working conditions
Sanitary and hygienic working conditions (SHUT) are characteristics of the environment in which the work process takes place, strict requirements for the organization of the workplace. The maximum permissible standards are described in the Labor Code of the Russian Federation and Guideline R 2.2.2006-05 “Occupational Hygiene”. They are assessed using sanitary and hygienic research methods, by measuring indoor microclimate parameters.
Acceptable factors are those that do not cause deviations in the employee’s health and do not lead to occupational diseases. As a rule, standards are calculated for a forty-hour work week, eight hours a day.
Classification of working conditions according to hygienic criteria:
- Optimal elements. Do not cause health problems, favorable for professional activities.
- Valid elements. Those environmental conditions in which performance of official duties is acceptable.
- Harmful elements. They cause a gradual decrease in performance, lower immunity, lead to chronic diseases, and affect the nervous and cardiovascular systems.
- Dangerous elements. They cause a sharp deterioration in health, acute illness or death. With prolonged exposure, the harmful element can become dangerous.
The third and fourth groups are undoubtedly harmful to humans, therefore work in their conditions is carried out using personal protective equipment. PPE must be certified, and when used, the level of environmental hazards can be reduced.
IMPORTANT! Even minimal levels of harmfulness will gradually lead to health problems.
According to the norms of the relevant area of legislation, employees of any enterprise have the right to labor protection. This right is enshrined in law, the state has developed an entire labor protection system, and established special inspectorates to monitor compliance with the law. They are the ones who organize inspections at enterprises and assess the level of environmental safety for workers.
You may be interested in: Classification of working conditions according to working environment factors
If the rights of citizens to labor protection are violated, then the management compensates for the amount of damage caused and pays the employee all expenses associated with treatment and elimination of harm, as well as subsequent prevention. Thus, it is more profitable for management to provide optimal working conditions than to pay compensation.
There are separate hygienic requirements for working conditions for disabled people:
- the activity must correspond to the specifics of the disease;
- the schedule is correlated with the treatment schedule;
- working hours are reduced;
- provide medical supervision;
- the presence of special equipment for labor, as automated as possible;
- absence of harmful and dangerous factors.
If production conditions do not meet the necessary requirements, then a candidate with a disability is denied employment.
Requirements for the minimum level of comfort in the office
The minimum requirements for office staff workplaces are their compliance with a number of basic standards:
- Each employee is allocated a minimum of 4 square meters of space, excluding the equipment used, additional furniture, and passages between workstations.
- Workplaces of employees whose work involves increased concentration and high stress on the nervous system are separated by partitions 1.5-2 m high.
- Maintaining temperature conditions for a standard 8-hour working day in the range from 20 to 28°C , depending on the season and intensity of work.
- Ensuring a comfortable level of illumination of the workplace, including both natural lighting (a mandatory requirement when working with computer equipment) and artificial lighting.
What is the standard area per person in an office?
When using a PVEM with a CRT-based VDT (without auxiliary devices - printer, scanner, etc.
), meeting the requirements of international computer safety standards, with a duration of less than 4 hours per day, a minimum area of 4.5 m2 per user workstation (adult and student of higher professional education) is allowed. 3.5.
For interior decoration of rooms where PCs are located, diffusely reflective materials with a reflectance coefficient for the ceiling of 0.7 - 0.8 should be used; for walls - 0.5 - 0.6; for the floor - 0.3 - 0.5. 3.6.
Polymer materials are used for interior decoration of premises with PCs in the presence of a sanitary and epidemiological conclusion. 3.7. Premises where workstations with PCs are located must be equipped with protective grounding (grounding) in accordance with the technical requirements for operation. 3.8.
General requirements for workplace organization
When organizing a workplace, the main goal for the employer is to ensure high-quality and efficient performance of work by the employee while making full use of the equipment assigned to him in compliance with the established deadlines. In this regard, the workplace is subject to organizational, technical, ergonomic, sanitary, hygienic and economic requirements.
One of the most important requirements when organizing a workplace is to ensure safe, comfortable working conditions, and to prevent the occurrence of occupational diseases and accidents. It should be noted that the employer needs to organize workplaces, taking into account not only the specific type of activity, qualifications, but also the individual physical and psychological characteristics of each employee.
General requirements for the organization of workplaces are regulated by the Labor Code, sanitary and epidemiological rules and regulations (SanPiN), as well as other legal documents.
Currently, SanPiN 2.2.4.335916 “Sanitary and epidemiological requirements for physical factors in the workplace” is in force, approved by Resolution of the Chief State Sanitary Doctor of the Russian Federation dated June 21, 2016 No. 81 (intended for citizens in labor relations, individual entrepreneurs and legal entities) .
This document establishes sanitary and epidemiological requirements for physical factors of a non-ionizing nature in the workplace and the sources of these physical factors, as well as requirements for the organization of control, methods for measuring physical factors in the workplace and measures to prevent the harmful effects of physical factors on the health of workers.
In Letter dated February 10, 2017 No. 0924381716, Rospotrebnadzor indicated that from January 1, 2021, the previously valid SanPiN 2.2.4.54896 “2.2.4. Physical factors of the production environment. Hygienic requirements for the microclimate of industrial premises" (approved by Resolution of the State Committee for Sanitary and Epidemiological Supervision of the Russian Federation dated October 1, 1996 No. 21) are applied to the extent that does not contradict SanPiN 2.2.4.335916.
The following sanitary standards and rules also apply to office workers:
- SanPiN 2.2.0.55596 “Occupational hygiene. Hygienic requirements for working conditions for women" (approved by Resolution of the State Committee for Sanitary and Epidemiological Supervision of the Russian Federation dated October 28, 1996 No. 32);
- SNiP 2.09.0487 “Administrative and domestic buildings” (approved by Decree of the USSR State Construction Committee dated December 30, 1987 No. 313);
- SanPiN 2.2.4.129403 “2.2.4. Physical factors of the production environment. Hygienic requirements for the aeroionic composition of air in industrial and public premises" (approved by the Chief State Sanitary Doctor of the Russian Federation on April 18, 2003).
When working with a PC, you must additionally be guided by the following documents[1].
| Title of the document | Brief description of the circle of persons and (or) the list of objects in respect of which mandatory requirements are established |
| SanPiN 2.2.2/2.4.134003 “Hygienic requirements for personal electronic computers and organization of work” (approved by Resolution of the Chief State Sanitary Doctor of the Russian Federation dated 06/03/2003 No. 118) | Establish sanitary and epidemiological requirements for personal electronic computers (PCs) and working conditions |
| SanPiN 2.2.2/2.4.219807 “Hygienic requirements for personal electronic computers and work organization. Amendment No. 1 to SanPiN 2.2.2/2.4.134003" (approved by Resolution of the Chief State Sanitary Doctor of the Russian Federation dated April 25, 2007 No. 22) | Amends SanPiN 2.2.2/2.4.134003 regarding the operation of PCs in rooms without natural light |
| SanPiN 2.2.2/2.4.262010 “Hygienic requirements for personal electronic computers and work organization. Amendments No. 2 to SanPiN 2.2.2/2.4.134003" (approved by Resolution of the Chief State Sanitary Inspector of the Russian Federation dated April 30, 2010 No. 48) | Amends SanPiN 2.2.2/2.4.134003 regarding instrumental monitoring and assessment of the levels of electromagnetic fields (EMF) from PCs |
| SanPiN 2.2.2/2.4.273210 “Hygienic requirements for personal electronic computers and work organization. Amendments No. 3 to SanPiN 2.2.2/2.4.134003" (approved by Resolution of the Chief State Sanitary Doctor of the Russian Federation dated 09/03/2010 No. 116) | Amendments are being made to SanPiN 2.2.2/2.4.134003 regarding the approval of the use of multi-lamp luminaires with electromagnetic ballasts |
| SanPiN 2.2.2.133203 “Hygienic requirements for organizing work on copying and duplicating equipment” (approved by Resolution of the Chief State Sanitary Doctor of the Russian Federation dated May 30, 2003 No. 107) | Establish requirements for designed, built, reconstructed and existing production facilities, workshops, areas, individual premises with permanent and non-permanent workplaces, including a single set of copying and duplicating equipment. Designed for organizations that have the above-mentioned production facilities, as well as for design, construction and other organizations involved in the design, construction, reconstruction and operation of institutions where copying equipment is used |
If situations arise that are not regulated by SanPiN (the toilet is faulty, the roof is leaking, etc.), the employee has the right to refuse work. In this case, the employer is obliged to offer him other employment until the problem is resolved. Otherwise, according to Art. 157 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, the employer is obliged to declare downtime with the payment of a penalty in the amount of at least 2/3 of the employee’s average salary.
Providing conditions for eating. The procedure for eating in the workplace is regulated by Art. 108 Labor Code of the Russian Federation, SNiP 2.09.0487:
- if the number of employees is less than 10 people, a space of at least 6 square meters is required. m, equipped with a dining table;
- with up to 29 employees, the required area is twice as large;
- if the enterprise employs up to 200 employees, it is obligatory to have a canteen-serving area;
- if the number of employees exceeds 200 people, the canteen must be provided with raw materials or semi-finished products.
Employer's liability. If the employer violates the established norms, the employee has the right to appeal to the trade union (Article 370 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation), the labor dispute commission (Article 385 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation), the State Labor Inspectorate in the subject of the Russian Federation (Articles 356-357, 360 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation), the court (Article 391 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation) or the prosecutor’s office in a subject of the Russian Federation (Articles 10, 21 of the Federal Law of January 17, 1992 No. 2202I “On the Prosecutor’s Office of the Russian Federation”).
Administrative liability of the employer for violation of legally established standards and labor protection requirements is in the form of a fine in the amount of 2,000 to 200,000 rubles. (depending on the type of violation) or suspension of activities for a legal entity for a period of up to 90 days (part 1, 5 of article 5.27.1 of the Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation).
Responsibility for non-compliance with SanPin
If during the inspection violations of sanitary standards are revealed, the employer will face administrative punishment in the form of a fine, disqualification and (or) suspension of activities.
For the first violation:
- officials and entrepreneurs will receive a warning and pay a small fine of 2-5 thousand rubles;
- organizations will get off with a warning and a fine in the amount of 50-80 thousand rubles.
In case of repeated violation:
- officials will face a fine of 30-40 thousand rubles and disqualification for 1-3 years;
- Individual entrepreneurs will receive a fine in the amount of 30-40 thousand rubles, and business activities will be stopped for 3 months;
- organizations will pay a fine of 100-200 thousand rubles, and their activities will be stopped for 3 months.
Organization of work and rest regime when working with a PC.
To maintain health and ensure optimal performance of PC users, regulated breaks should be established throughout the work shift.
Current regulations provide for a certain mode of computer work with breaks, the frequency and duration of which depends on the type of work performed, its category, as well as the duration of the shift. In an eight-hour workweek, breaks are 15 minutes two hours after the start of work and two hours after the lunch break for employees whose work involves reading information from a screen.
To prevent premature fatigue in those working with a PC, visual discomfort and other unfavorable subjective sensations, despite compliance with sanitary, hygienic, ergonomic requirements, work and rest schedules, an individual approach should be taken in limiting the time spent working with a PC, correction of the duration of rest breaks or change of activity to another, not related to the use of a personal computer.
In cases where the nature of the work requires constant interaction with a PC (typing text, data entry, etc.) and is associated with strained attention and concentration, with the exception of the possibility of periodically switching to other types of work activities not related to the PC, it is recommended to organize breaks for 10 - 15 minutes every 45 - 60 minutes of operation.
During regulated breaks, in order to reduce neuro-emotional stress, fatigue of the visual analyzer, eliminate the influence of physical inactivity and hypokinesia, and prevent the development of postural fatigue, it is advisable to perform sets of exercises. In addition, those working with a high level of tension during regulated breaks and at the end of the working day are given psychological relief in specially equipped rooms (psychological relief room).
From the time pregnancy is established, women should be transferred to work that does not involve the use of a PC, or their time working on a computer should be limited (no more than three hours per work shift), subject to the hygiene requirements established by SanPiN 2.2.2/2.4-1340- 03.
Should office workers undergo medical examinations? According to SanPiN 2.2.2/2.4.1340-03 and clause 3.2.2.4 of the List of harmful and dangerous factors[2], radiation from a computer, if an employee spends more than 50% of his working time on it, is a harmful factor in working conditions. Thus, since office workplaces contain factors that are classified as harmful based on their level of impact, office workers who spend more than half of their working time at the computer must undergo mandatory medical examinations.
At the same time, the obligation to undergo medical examinations for workers who are exposed to a harmful factor (in the form of radiation from a computer more than 50% of the working time) is not made dependent on the results of a special assessment of working conditions. Even if working conditions are considered acceptable based on the results of a special assessment, such workers still need to be sent for mandatory medical examinations, since they are exposed to harmful factors.
Office workers must undergo both a mandatory medical examination when applying for a job and periodic medical examinations (Letter of the Ministry of Labor of the Russian Federation dated March 21, 2014 No. 15-2/OOG-242).
In accordance with the Procedure for conducting medical examinations[3], periodic examinations are carried out at least within the periods specified in the List of harmful and dangerous factors and the List of hazardous work[4]. For office workers, periodic medical examinations are carried out at least once every two years (clause 3.2.2.4 of the List of harmful and dangerous factors). At the same time, employees under the age of 21 undergo periodic medical examinations annually.
An employer can avoid mandatory medical examinations of office workers whose workplaces are equipped with computers if they can prove that employees use computers less than half the working day. To do this, you need to establish the rules and working hours of the employee at the computer in an order or job description. They should also indicate what the employee does during the rest of his working time (for example, working with papers, clients, correspondence, etc.).
[1] A detailed list of SanPiN, SN and GN is given in section. VII List of acts containing mandatory requirements, compliance with which is assessed during control measures during the implementation of federal state sanitary and epidemiological supervision in organizations of certain industries with particularly hazardous working conditions (including during the preparation and execution of space flights, diving and caisson work ) and in certain territories of the Russian Federation, including on objects and territories of closed administrative-territorial entities, according to the list approved by the Government of the Russian Federation, approved. FMBA of the Russian Federation 08/30/2018.
[2] List of harmful and (or) dangerous production factors, in the presence of which mandatory preliminary and periodic medical examinations (examinations) are carried out, approved. By Order of the Ministry of Health and Social Development of the Russian Federation dated April 12, 2011 No. 302n.
[3] The procedure for conducting mandatory preliminary (upon entry to work) and periodic medical examinations (examinations) of workers engaged in heavy work and work with harmful and (or) dangerous working conditions, approved. By Order of the Ministry of Health and Social Development of the Russian Federation No. 302n.
[4] List of works during the performance of which mandatory preliminary and periodic medical examinations (examinations) of workers are carried out, approved. By Order of the Ministry of Health and Social Development of the Russian Federation No. 302n.
About the operating mode
It is not surprising that everyone who works at a computer has a regulated work schedule. The fact is that monotonous workload is harmful to the human body; if you don’t get up all day and continue to do work, then it is possible:
- development of osteochondrosis for both the cervical spine and the back;
- pathological abnormalities of the gastrointestinal tract;
- changes in blood composition;
- sleep is disturbed;
- vascular diseases and pathological abnormalities of the heart muscle appear;
- a person may experience depression and stress;
- motor activity decreases.
All of the above ultimately leads to deterioration in performance.
For information about safety when working on a computer, watch this video:
To work with a PC, the following conditions must be met:
- Set breaks, the duration of which should be at least 10 minutes.
- After every hour of work you need to rest.
- Breaks should be taken into account in the employee’s overall activities, that is, this time does not need to be minus from the working time as a whole, since they are paid for by the employer.
- If for some reason you have to work at night, then rest breaks should be increased by about 30%.
- In total, the length of time allotted for breaks should be from 50 minutes to one and a half hours, if you are supposed to be at the workplace for 8 hours.
- If the working time is 12 hours, then the total time spent on breaks should be between 80 minutes and 2 hours 20 minutes.
Office workplace standards: what ideal conditions should be
In order for company employees to feel comfortable, it is necessary to take into account several parameters of the selected premises. Here's what the SanPin standards say about the office workplace:
- Square
The area of one workplace in the office for an employee working on a computer with a plasma or LCD monitor must be at least 4.5 square meters. m.If the monitor is outdated (based on a cathode ray tube), then the standard workplace area in the office is at least 6 square meters. m. per person. For CRT screens, 4.5 square meters is lowered. m/person, but only if the working day lasts less than 4 hours, and during the work no additional devices are used (scanner, copier, printer, etc.)
The width of the side passage between employees’ desks (more precisely, between the sides of their computers) is at least 1.2 m. The minimum distance between the backs of colleagues’ monitors should be 2 m or more.
The copier and other office equipment should be placed at a distance of 0.6 m from the nearest wall or table, and at least a square meter of free space should be left in front of it.
- Temperature
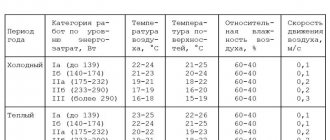
SanPin classifies office managers and other knowledge workers as Category Ia. The temperature in the office workplace for them should be no less than 20 and no more than 28 degrees above zero for a normal eight-hour working day.In summer, the most optimal temperature is considered to be 23-25 degrees Celsius. If the thermometer rises to 29 degrees, the working day cannot exceed 6 hours; up to 32.5 degrees – 1 hour.
In winter, the normal temperature in the office is set within 22-24 degrees. A decrease in temperature to 19 degrees entails a reduction in the working day by 1 hour. And if it drops to 13 degrees, office workers have the right to leave work an hour after they start.
- Illumination of the office workplace
In areas where managers work with personal computers, both artificial and natural lighting should be provided. The use of computers in rooms without natural light requires a permitting sanitary and epidemiological conclusion.Windows in offices should mostly face northeast and north. For artificial lighting, LED lamps should be used. All lighting sources in the office workplace should be placed parallel to the windows - this way natural and artificial light will fall in the same direction.
These are the sanitary standards for office premises, compliance with which will allow employees to maintain their health and work productively.
Sanpin standards for area per person for working without a computer
— Business law — Sanpin standards for area per person for working without a computer
For rooms where PCs are used, luminaires with mirror parabolic grilles, which are equipped with electronic ballasts (EPG), can also be used. But the use of lamps without diffusers and shielding grilles is not allowed.
To maintain normal lighting parameters in rooms where computers are used, glass window frames and lamps are cleaned and washed at least twice a year. And, of course, burnt out lamps are replaced in a timely manner.
General requirements for the organization of workstations for PC users When placing workstations where computers are located, the distance between desktops with monitors (towards the rear surface of one monitor and the screen of another monitor) must be at least 2.0 m, and the distance between the side surfaces of the monitors - 1.2 m.
Sanpin for office workers
Workplace standards in office premises According to statistics, less than 42% of bosses are concerned about the compliance of workplaces in the company's office with sanitary standards.
Requirements for the workplace It is very important for knowledge workers to have favorable conditions - this directly affects their well-being, and therefore productivity. Therefore, management needs to take a responsible approach to choosing office space for rent.
Standards for an office workplace: what ideal conditions should be In order for company employees to feel comfortable, it is necessary to take into account several parameters of the selected premises. Here's what the SanPin standards say about the office workplace:
- Area The area of one workplace in the office for an employee working on a computer with a plasma or LCD monitor must be at least 4.5 square meters. m.
Basic provisions of Sanpin on area per person for office work
Attention Do not place workstations with a PC near power cables and inputs, high-voltage transformers, or technological equipment that interferes with the operation of the PC.
In the event of a violation in the field of ensuring the sanitary and epidemiological well-being of the population, the administrative code (CAO) applies: Article 6.3.
Violation of legislation in the field of ensuring the sanitary and epidemiological welfare of the population and legislation on technical regulation (as amended by the Federal Law of December 28.
2009 N 380-FZ) Violation of legislation in the field of ensuring the sanitary and epidemiological well-being of the population, expressed in violation of current sanitary rules and hygienic standards, requirements of technical regulations, failure to comply with sanitary, hygienic and anti-epidemic measures - (as amended.
Standards and calculation of the number of square meters of area per workplace
There are no universal standards for all workers. Depending on the specific conditions in which a particular person is located, the requirements for his workplace in the office, as well as footage standards, will vary.
The main situations will be discussed below:
- For those whose work requires the presence of a modern computer model, at least 4.5 sq.m. should be allocated. If additional equipment is required for the device (scanner, printer, fax, second monitor), then the area must be increased.
- For those who work with old computers, a footage of 6 sq.m. is provided. But there is one caveat here: if an employee spends no more than 4 hours at this computer, then the workplace area can be reduced to 4.5 sq.m. Additionally, as with the above, additional equipment will require additional space.
- For employees who do not need to use a computer, up to 4 sq.m. should be allocated according to standard standards. In this case, the employee’s desk must have legroom of at least 60 cm, a width of 50 cm, and a depth at knee level of 45 cm or more. At the level of outstretched legs, the distance should be at least 65 cm.
- For an employee with a disability, it is necessary to allocate from 5.65 sq.m. under a workplace. If an employee with a disability uses a wheelchair, then this value increases to 7.65 sq.m.
- For employees of the design bureau, the employer must provide a workplace with an area of more than 6 sq.m.
- Also, the footage varies depending on the type of activity of the employee. Thus, employees whose duty is to individually receive visitors (for example, lawyers or administrators) are allocated from 9 sq.m. up to 12 sq.m. But accountants and engineers are entitled to 6.5 sq.m. For heads of departments - 9 sq.m.
In addition to the size of the workplace itself, there is a list of requirements for the distances between furniture and other objects in the room, as well as requirements for their location:
- There must be at least 2 meters between the desks of two employees.
- Between monitors – at least 1.2 meters.
- Monitors must be positioned at a certain angle to the window openings.
- Office windows should face north or northeast.
Following the standards described above will not only improve the performance of office employees, but will also bring financial benefits to the employer.
Norm m2 per person in the office – Lawyer
When using a PVEM with a CRT-based VDT (without auxiliary devices - printer, scanner, etc.
), meeting the requirements of international computer safety standards, with a duration of less than 4 hours per day, a minimum area of 4.5 m2 per user workstation (adult and student of higher professional education) is allowed. 3.5.
For interior decoration of rooms where PCs are located, diffusely reflective materials with a reflectance coefficient for the ceiling of 0.7 - 0.8 should be used; for walls - 0.5 - 0.6; for the floor - 0.3 - 0.5. 3.6.
Polymer materials are used for interior decoration of premises with PCs in the presence of a sanitary and epidemiological conclusion. 3.7. Premises where workstations with PCs are located must be equipped with protective grounding (grounding) in accordance with the technical requirements for operation. 3.8.
In our country, almost a third of the population is engaged in office work.
Attention
At the same time, not all Russian citizens know that the employer is obliged to provide a minimum level of mandatory requirements for the employee’s workplace.
There is even a special standard for the area per person in an office, prescribed in the current legislation. According to the portal https://aero-city.com/rent/, based on the established rules for the design of premises and sanitary standards, a workplace in any office must meet the following parameters:
- An office employee whose work involves the use of a personal computer with a modern monitor is provided with a workplace area of at least 4.5 m*2. At the same time, the presence of additional equipment that consumes electricity and emits electromagnetic waves requires the mandatory provision of a separate area.
How many square meters per person in an office?
We are talking about a printer, a second monitor and other office equipment.
- A workplace where a computer with an outdated monitor is used must be allocated at least 6 m*2. When working on it for less than 4 hours, the specified area can be reduced to 4.5 m*2.
- For each employee in an office building, not counting a workstation equipped with a computer, an area of 4 m*2 should be allocated.
- For design bureau employees, the employer is required to allocate more than 6 m*2 of office space.
- If an employee has a disability, he is entitled to 5.65 m*2.
If the employee uses a stroller, then this figure increases to 7.65 m*2.
- The current standard of area per person in an office, stated above, applies exclusively to the workplace.
- the distance between the desks of two employees is 2 meters;
- distance between monitors – 1.2 meters;
- placement of monitors - at an angle to the window openings;
- office windows - facing north or northeast;
- the presence of high loads on the nervous system - it is necessary to have partitions between workplaces of 1.5-2 meters.
For this reason, it does not include passages between arranged tables or areas of the room occupied by furniture or equipment. In addition to the minimum recommended area standard for each employee, other nuances of creating office workspaces should be taken into account:
Compliance with the described recommendations will significantly increase the efficiency of hired personnel, which will bring financial benefits to the employer himself, despite the costs incurred to create comfortable jobs.
www.tehdoc.ru
I. General provisions and scope 1.2. Sanitary rules apply throughout the Russian Federation and establish sanitary and epidemiological requirements for personal electronic computers (PCs) and working conditions.
1.4. These Sanitary Rules define the sanitary and epidemiological requirements for: - design, construction and reconstruction of premises intended for the operation of all types of PCs, - organization of workplaces with PCs. 1.5.
The requirements of the Sanitary Rules apply to: - the conditions and organization of work with a PC; 1.7.
Responsibility for the implementation of these Sanitary Rules rests with legal entities and individual entrepreneurs carrying out: - operation of PCs, - design, construction and reconstruction of premises intended for the operation of PCs in industrial and administrative public buildings 1.9.
How many sqm do you need? m per employee?
And after every hour of work, the room should be ventilated (Sanitary and epidemiological rules and regulations SanPiN 2.2.2/2.4.1340-03 “Hygienic requirements for personal electronic computers and organization of work”; approved.
Chief State Sanitary Doctor of the Russian Federation on May 30, 2003). Some situations are not directly regulated by sanitary standards, but in practice they occur regularly.
These include, for example, malfunctioning toilets in the building.
In this case, according to Rostrud, the employee has the right to refuse work, and the employer must provide him with another job that does not threaten his health until the problem is resolved. If this is not possible, downtime is declared, and the employee can count on wages during downtime in the amount of at least 2/3 of his average salary (Article 157 of the Labor Code).
4.5 square meters. what an ideal office workspace should be like
- Labor law
- Protection of workers' rights
- Good afternoon, dear Formus residents. We decided to rent an office for 20 people with a friend. Please tell me what is the minimum number of meters needed per employee in Russia? Thanks in advance for your answers. The question is that, in my opinion, 3 square meters per workplace is enough for each employee, but I heard somewhere that there are certain standards for workplaces. So far I have found these posts on the Internet. – An important aspect is the number of square meters per employee. In accordance with sanitary labor standards and state standards, an ordinary employee needs 5-6 square meters of working space, a manager - 34 meters, a secretary - 15 square meters.
Footage standards for non-working areas in office premises
The regulations also stipulate requirements for other premises in the office.
Below is the minimum area per person:
- A room intended for relaxation must have at least 0.9 sq.m. per person.
- The area of the dining room or dining area is from 1.65 sq.m. per employee.
- The aisle distance between tables should be from 0.5 to 1 m.
- The presence of high loads on the nervous system, emotional tension or a high level of stress during work requires the mandatory presence of partitions between workplaces, the distance between which must be at least 2 meters.
What to do and where to contact employees: step-by-step instructions
If an employee notices that the permissible noise levels in the office are exceeded and this interferes with his effective work, as well as his colleagues, he has the right to file a complaint with Rospotrebnadzor.
You can submit a complaint in several ways:
- In writing through the postal operator.
- During a personal visit/reception.
- On the official website, having previously logged in through the State Services website.
In your application you will need to provide the following information:
- Your personal data (full name, etc.).
- Contact details (phone, email).
- A detailed description of the reason for your application (in free form).
- Details of the organization against which you are filing a complaint (TIN, full name, legal address).
- Description of your requirements for this organization.
- Date and signature.
If necessary, you must attach documents to your application/complaint that can directly or indirectly confirm the fact of a violation.
The response from Rospotrebnadzor must arrive within 30 days from the date of delivery of the complaint to the institution. If the proposed methods for solving the problem do not suit you or cannot lead to the desired result, you should go to court.
The report drawn up by Rospotrebnadzor specialists will be indisputable proof that you are right.
However, remember that in order to file an application in court and bring the violator to justice, very significant evidence is required, which can be:
- Copies of written complaints.
- Video or audio recordings confirming the presence of harmful noise.
In accordance with the decision, the court may impose administrative or disciplinary punishment on the employer who violated the requirements for the permissible noise level in the office, as stated earlier.
Now, knowing all the nuances regarding square footage standards and the permissible noise level in office premises, you can be calm about your health and performance, because sanitary and epidemiological standards were created precisely for this.
When can the area be smaller?
The area can be reduced only in one case – when the employee’s working day lasts less than four hours. It is also possible to set up a hot desk: these are desks that are not assigned to a specific subordinate.
What happens if an entrepreneur does not comply with the rules?
If a manager tries to save at the expense of employees when renting or purchasing an office, then he will face:
- Negative attitude of employees;
- Conflicts;
- Low motivation of subordinates;
- Decline in team performance;
- Fines and penalties during certification.
How to prevent violations?
In order to prevent increased noise levels in the office, the employer should pay attention to two things:
- Equipment purchased for the office. In 2021, there are many different technologies available to reduce the noise generated by equipment. High-quality equipment will reduce the burden on workers and avoid liability for exceeding acceptable levels.
- Construction materials used for the premises. The employer should choose those materials that reduce external noise, and he should also pay attention to various types of sound insulation in order to create the most comfortable working conditions for his employees.
In addition, you can use personal noise protection equipment. For example, helmets, headphones or earbuds.
Federal Labor Safety Inspectorate
If an employee’s rights are violated and the workplace is equipped incorrectly and does not comply with SanPin standards, he has the right to contact the Federal Labor Inspectorate in accordance with Article 352 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation.
It is necessary to write an appeal, statement or complaint, attaching supporting documents, photos and video materials, if any. If a violation is confirmed, the department will draw up an order to eliminate the violations or send information to the executive authorities to take measures to eliminate them.
Local union
Almost every large organization has its own trade unions, to which an employee can file a complaint against the employer in case of violations. The only condition is membership in this organization.
The trade union must consider the complaint and respond within a week . If the violations recorded in the document have not been eliminated, the complaint is transferred to higher executive authorities for further proceedings.
Court
An extreme measure, which is recommended to be resorted to in case of serious violations and ignoring of your complaints by the employer.
Labor disputes can be considered by the court in accordance with Art. 391 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation at the request of one of the parties. This form involves not only a request to eliminate violations in the workplace, but also the recovery of moral or material damage, if any.
Rospotrebnadzor
If it is impossible to contact the above organizations, the employee has the right to contact Rospotrebnadzor with a request to conduct an inspection of the employer’s compliance with sanitary and epidemiological standards.
Another important requirement for office space is its fire safety. It is useful to know your rights and the procedure to follow if they are violated, but do not get excited: you can try to resolve the issue peacefully and not go into conflict. Talk to the management, perhaps the authorities will listen to your complaints and meet them halfway.
It is easier for a manager to eliminate a violation than to receive an administrative fine, remember this. Only if your requests are ignored and outright neglect, complain to higher authorities.
Sources
- https://101urist.com/nedvizhimost/nezhilaya/kommercheskaya/vidy/ofisy/trebovaniya/normy-metrazha-na-cheloveka.html
- https://clubtk.ru/trebovaniya-k-rabochemu-mestu-chem-nuzhno-rukovodstvovatsya
- https://myrealproperty.ru/nedvizhimost/commercial/raznovidnosti/ofisy/trebovaniya-k-pomeshheniyam/normy-metrazha-na-cheloveka.html
- https://drakkar11.com/sanpin-norma-ploschadi-na-odno-rabochee-mesto/
- https://officemaps.ru/raschet-metrazha-ofisa
- https://monolit-mebel.ru/normative-rabochego-mesta
- https://www.klerk.ru/buh/articles/482881/
- https://www.audit-it.ru/articles/personnel/a134855/979628.html
- https://shukhova14.ru/normy-rabochego-mesta-v-ofise/