- 19773106
- 23 May 2021, 09:39
- maternity leavesocialmoneyBelaruschildren
Photo: onliner.by
Last Sunday, Minister of Labor and Social Protection Irina Kostevich said that maternity leave for three years is “a very expensive pleasure.” She gave the example of the amount of child benefit, which is more than the minimum wage. In fact, officials have long been hinting that parental leave in Belarus will still have to be reduced. Onliner.by tried to figure out whether this is realistic to do now and what the problems are.
Is it possible to go on maternity leave later (later than 30 weeks)?
The question is still theoretical, but very interesting to me. Is it possible not to go on maternity leave at all? That is, work until the birth, and then sit at home for a while and start going to work? Provided you feel well and have no problems with the child, of course.
If a woman is expecting the birth of 2 or more babies, then the duration of maternity leave is 194 days (84 days - leave before childbirth, 110 days - postpartum leave). Childbirth during which 2 or more children are born is always considered complicated.
This is taken into account when establishing long postpartum leave, and a separate sick leave for 16 days in this case is not issued. There are situations when, as a result of premature birth (less than 30 weeks), a woman simply does not have time to go on maternity leave.
In this case, upon the birth of a live child, she is fully granted the entire maternity leave (at least 156 days, since premature birth is always complicated). If the child was stillborn, then only the postnatal part of the leave is provided.
If premature birth occurs after 30 weeks (i.e.
“It’s very difficult to return to your field after 3-5 years of maternity leave”
Daria, who went on maternity leave twice, has a similar point of view:
“No matter what anyone proves, I believe that until the age of three, a child is not ready for kindergarten. It’s one thing to leave a child with his grandmother or nanny for a few hours, another thing is to take him to the garden full-time from morning to evening, when he doesn’t understand anything, his psyche is immature. Therefore, I believe that three years of maternity leave should remain.
Many children get a lot of stress when they are sent to kindergarten, and after that they begin to have other serious problems.
At the same time, Daria says that a long maternity leave does not always have a positive effect on the mother of a child.
— It’s very difficult to return to your field after 3-5 years of maternity leave. In fact, at work you will have to start from scratch, even if you had previous experience,” she explains. “Therefore, I think that a mother should work immediately after giving birth, only this should be limited in time - an hour or two a day.
— To do this, you need to use assistants in the form of grandmothers or nannies. We have a stereotype that a woman should look after her child and still manage to do everything: bear the entire household burden and not get discouraged while on maternity leave. It won't work that way.
To prevent mom from dropping out of social life (and this often happens), help is needed.
At first my grandmothers helped me and my husband, and then we hired a nanny, who came once or twice a week and really relieved me of my workload.
Is it possible not to go on prenatal leave?
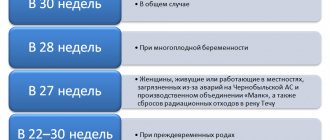
Therefore, calculating when to go on maternity leave is more important than it might seem at first glance. It is believed that work leave is granted at the thirtieth week of pregnancy.
If the doctor diagnoses that there will be two or more children, the release is granted as early as the twenty-eighth week. Why is it so important to know when to go on maternity leave? The date of maternity leave is important for calculating maternity benefits. In addition to the above-mentioned need to prepare a full-fledged replacement for the absent employee, it is important to know from what period she will be absent also for calculating benefits.
This is important to know: Additional leave to care for a disabled child in 2021
Employees who work under a formal employment contract concluded for an indefinite period can take full advantage of the right to this leave. This category of working women is the most protected from the point of view of the law. After completing maternity leave, they can freely go on parental leave until the child reaches 3 years of age. In the case when the expectant mother works temporarily, that is, under an employment contract drawn up for a specific period, the following situations are possible: Subscribe to our channel in Yandex.Zen! Subscribe to the channel
- If the contract expires after the end of maternity leave, then the employee can go on maternity leave on a general basis.
- If the term of the employment contract ends during pregnancy, the employer is obliged to extend it until the end of pregnancy.
Mothers on maternity leave: no nursery, nanny costs about $200 per week
The IPM Research Center, together with BEROC, conducted a survey in 2021, according to which 80% of respondents consider three years optimal for maternity leave. 72% of respondents spent all three years on maternity leave. But those who left earlier did so for financial reasons.
20.3% of survey participants who have children admitted that they would leave maternity leave earlier if relatives had the opportunity to look after the child, and 10% - if there was an opportunity to place him in a nursery or kindergarten.
Meanwhile, almost 11% of respondents are ready for two years of maternity leave with increased benefits, another 10% are hesitant, as they are not completely confident in this option. We asked two mothers who were on maternity leave how they assessed the possibility of reducing it?
Tatyana was on maternity leave three times. From the first I went to work when the child was one year old. The next two times I didn’t do this and took the opportunity to be with the children until they were 3 years old.
— I left my first maternity leave when the child was one year old. I was able to do this because my salary allowed me to hire a nanny and I still had money left for living.
I would be positive about the idea of shortening the maternity leave by a year, provided that the mother’s salary allows her to hire a nanny for the child.
And the nanny, by the way, charges $3.5 per hour (that comes out to almost $200 a week with an 8-hour working day. - Onliner note).
Tatyana, as a mother of three children, is skeptical about the idea that a child can be sent to kindergarten at the age of 2:
— I think that very young children are sent to kindergarten by those parents who find themselves in a hopeless situation.
Two year olds are too small for the garden. It’s rare that a teacher will calm a child who is crying because his mother has left. Even with three-year-olds, we don’t always know how to behave.
And here they offer to leave these little chickens in the garden at two years old... They say that abroad maternity leave lasts three months, but there the salary allows the mother to hire a nanny. Mom goes to work, a nanny sits with the baby.
Also, a mother with many children believes that benefits are important financial support for the family.
— When maternity leave ends, the payments end, and it becomes more difficult. Fortunately, my husband supports me. What to do if a mother is raising her children alone, her maternity leave is over, and the child is not ready to go to kindergarten? - says Tatyana and emphasizes that not every employer is happy to see a mother of two or three children.
Is it possible not to take maternity leave before giving birth?
However, they are entitled to maternity benefits if they paid social insurance contributions for themselves during the previous calendar year. How long is maternity leave under the Labor Code of the Russian Federation? In most cases, the expectant mother goes on maternity leave at 30 weeks of pregnancy.
If twins, triplets (or more babies) are expected, then in this case the maternity leave period begins earlier - at 28 weeks. The duration of maternity leave depends on the number of children born, as well as on the presence of complications during childbirth.
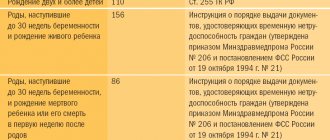
If 1 baby was born and the birth went without complications, then the maternity period will be 140 days (including 70 days of leave before childbirth and the same amount after). In the case of complicated childbirth, postpartum leave will be 86 days; in this case, the woman after childbirth is additionally issued a sick leave certificate for a period of 16 days.
- if the birth is classified as complicated, then a certificate of incapacity for work is issued for 16 days;
- If only during childbirth it turns out that the pregnancy is multiple, then the woman is entitled to additional sick leave for 54 days.
Is it possible to go on maternity leave early? Many expectant mothers who are not feeling well are interested in the question of whether early maternity leave is appropriate for health reasons. You should not be afraid of the boss’s promises to fire you under the article, since the dismissal of a pregnant employee for violating official discipline is unacceptable. If an employee knows that the employer has a negative view of her plans to go on maternity leave, then when submitting an application for leave, she needs to get a note from the personnel service about its acceptance. If, after filing an application, the manager still does not issue an order to grant leave and, accordingly, does not pay benefits, then you will have to defend your rights. First of all, you should file a complaint (you can make it in any form) to the labor inspection unit - this is the most expeditious way to protect your labor rights. If such an appeal does not produce a visible result, then the next possible step is filing a complaint with the prosecutor’s office. The legislation answers this question in the negative, since the only reason for going on maternity leave before 30 weeks is the presence of a multiple pregnancy. However, labor legislation allows a pregnant employee to be temporarily released from work even before going on maternity leave, and several options are possible:
- Even if a pregnant woman has worked in the organization for only a short time, she has the right to go on annual leave immediately before maternity leave. Such leave is paid in the amount of average earnings. A woman planning to go on vacation before maternity leave should ask her doctor about the exact start date of maternity leave at 22–24 weeks.
A woman who has adopted a newborn child can also go on maternity leave. Leave is granted from the moment of adoption, but its duration is calculated from the date of birth of the child (70 days, if 2 or more children are adopted at once - 110 days).
What documents are needed to apply for maternity leave Registration for maternity leave is a fairly simple procedure. When the pregnancy reaches 30 weeks, the antenatal clinic issues a certificate of incapacity for work, which reflects the start and end dates of temporary disability due to pregnancy and childbirth.
The gestational age is determined by the doctor based on ultrasound data and other examinations. After receiving the document from the antenatal clinic, the expectant mother must write an application for leave at her place of work, attaching the original sick leave certificate to it.
How long is maternity leave for our neighbors?
Russia
Leave is granted until the child reaches three years of age. The care allowance is paid until the child reaches the age of one and a half years; as a general rule, it is 40% of the average earnings of the person caring for the child. That is, a person with an average salary in Belarus would be paid approximately 550 Belarusian rubles.
Ukraine
Paid parental leave lasts three years. Further, it is possible to take out unpaid leave to care for a child under six years of age for medical reasons - in connection with the child’s frequent illnesses (the employer is obliged to reserve a place for his employee). The amount of maternity leave has not changed for several years, it is 41,280 hryvnia, which is about 3,800 Belarusian rubles. About 10,000 hryvnia - approximately 900 Belarusian rubles - are paid immediately, the rest is divided over three years.
Poland
Maternity leave depends on the number of children born, its minimum duration is 20 weeks, the benefit during this period will be 100% of the mother’s salary. Parental leave also depends on the number of children born at a time and is 32 weeks for the birth of one child and 34 for the birth of several. This leave can be divided into parts and used until the child reaches the age of six. During this period, the benefit will be 60% of the salary. In addition, there is so-called paternity leave, which is 14 weeks.
Lithuania
The maximum period of parental leave is three years, but after the third year the benefit is no longer paid. The amount of the benefit depends on the period of receipt and the salary of the person on leave. You can receive benefits for two years, and then in the first year they will pay 54.31% of your salary and 31.03% in the second year. If you receive benefits for one year, the monthly payment will be 77.58% of your salary.
Latvia
The so-called parental benefit can be received until the child reaches one year (it will be 60% of the salary) or one and a half years (43.75% of the salary). Further payment of the benefit in the amount of 70 euros continues until the child’s 18th birthday.
Is it possible not to go on maternity leave when a child is born?
Procedure for registration Officially, maternity leave is issued at the place of work, just like annual paid leave. The relevant documents are provided to the personnel department by the mother after she is issued a sick leave certificate (usually at the 30th week of pregnancy or later, in case of multiple pregnancy - from the 28th week), and by other family members after the birth of the baby. Within 10 days, the company management must calculate all benefits to be assigned, and also issue an order to grant leave. important: Registration of maternity leave for one child is usually accompanied by filing an application for child benefits. They can only be received by the relative of the child who is going on maternity leave. He also retains the right to work part-time or part-week at his place of employment. In this case, the right to receive benefits is not lost.
Is it possible not to go on maternity leave at all?
And this is the only case when dismissal is permitted by law. At the same time, the woman retains the same rights as other employees: she must be notified of dismissal 2 months in writing. But what about maternity benefits? Who will pay it, since the company no longer exists? In this situation, all payments are calculated by the local branch of the Social Insurance Fund.
- certificate of incapacity for work (sick leave) for pregnancy and childbirth;
- application for appropriate leave;
- certificates from the previous place of work (if available): about the average income for the previous two full calendar years, about exception periods not included in the calculation of benefits;
- copy of passport;
- Bank details where to transfer benefits.
The employer is required to prepare response orders within 10 days. He only calculates how much you should receive from the Social Insurance Fund of the Russian Federation 1.
Maternity leave
How to apply for maternity leave? The most important issue, especially for mothers with difficult financial situations, is money. The process of processing payments is not complicated, but it does take time. In the last month of pregnancy, the expectant mother is given a sick leave certificate, which she takes to work.
Algorithm for obtaining maternity leave. Collection of necessary documents:
- sick leave;
- certificate of registration for pregnancy (it is needed in order to be paid for the entire pregnancy);
- application for leave;
- photocopy of passport;
- certificate 2-NDFL for the last year;
- bank statement with current account number.
If a girl works, then she writes an application addressed to the head of the company for maternity leave. It is important to write that you are asking for maternity benefits.
When do they go on maternity leave?
But in fact, maternity leave begins even before childbirth. Maternity leave is not only free time from work exclusively after childbirth. This leave also applies to the short prenatal period.
If a woman works officially, then the employer, according to the law, does not have the right to force the woman to work longer than the period specified in official documents. The employee is required to provide a certificate of incapacity for work and an application for leave. Do you lead a healthy lifestyle? Do you like to run in the morning? Find out if pregnant women can continue running in the morning? And what kind of sport is best to do during pregnancy? Do you like to lie in the bathroom? Is it possible to take a bath during pregnancy? Find out here. When do you go on maternity leave? By law, expectant mothers are granted leave from the thirtieth week of pregnancy.
When is maternity leave granted, how to apply for it and receive payments
That is, in this case, the employee is guaranteed only the prenatal part of the leave.
- If the contract expires during pregnancy, and the expectant mother works in the position of a temporarily absent employee who intends to return to work, then she must be transferred to another job until the end of the pregnancy. If there is no other suitable job in the organization, the employer has the right to fire her.
- In addition to employees working under an employment contract, maternity leave is granted to state and municipal employees, as well as women serving in the military. Full-time students can take academic leave instead of maternity leave.
Women engaged in private business activities do not take maternity leave.
And then the maternity leave is renewed. Thus, the vacation turns out to be longer, and also paid. In fact, the duration of maternity leave can be adjusted depending on your wishes. Along with maternity leave, you can take regular leave and relax for your own pleasure for a longer period of time.
Duration of maternity leave In total, 3 durations of leave can be distinguished:
- 140 days (70 days before the expected date of birth and 70 days after) for normal pregnancy;
- 194 days (84 days before the birth of the child and 110 after), usually when two or more children are born.
- 156 days with complicated labor.
Is it possible not to go on maternity leave when a child is born?
Therefore, calculating when to go on maternity leave is more important than it might seem at first glance. It is believed that work leave is granted at the thirtieth week of pregnancy. If the doctor diagnoses that there will be two or more children, the release is granted as early as the twenty-eighth week. Why is it so important to know when to go on maternity leave? The date of maternity leave is important for calculating maternity benefits. In addition to the above-mentioned need to prepare a full-fledged replacement for the absent employee, it is important to know from what period she will be absent also for calculating benefits.
Is it possible not to go on maternity leave at all?
- 140 in general >
- 154 for multiple pregnancies>
- 156, if the birth was complicated>
- 180 if two or more children were born.
The doctor will tell you which month they go on maternity leave; the total duration of the vacation is divided in half. Additional days, if necessary, are given after childbirth - for example, childbirth with complications is not always predictable. But an employee may decide not to use all the days allotted to her, then she must independently calculate the maternity leave and notify the employer about this.
After all, benefits are paid for each day of vacation, so it is advisable to notify management in advance.
What if you don’t change anything?
— Of course, you can leave the maternity leave configuration unchanged, especially since everyone seems to be happy with everything. But we see that three years of parental leave is a luxury that does not have a positive effect on the birth rate, because it continues to decline,” says Natalya.
— We assume that the resources of the Federal Social Protection Fund are limited and tasks are being set to optimize them. Now we have a unique opportunity to change something almost painlessly for the birth rate (after all, it is already declining), and thanks to new solutions, as painlessly as possible for families. The variability of parental leave will give families the opportunity to adapt to new conditions as quickly as possible,” the expert concludes.
Maternity leave for the birth of a second child
But the benefit will be paid to only one person. During this time, he cannot be fired or removed from his position. According to the law, maternity payments are provided at the request of the child’s mother or a person replacing her, if the application for them follows no later than six months from the date of the end of the maternity leave. - before childbirth - at any time at the request of the employee after receiving maternity sick leave from the antenatal clinic, which is issued at the obstetric period of 30 weeks of pregnancy (28 - for multiple births); - after childbirth - at any time after the birth of a child if you have a sick leave certificate, but no later than six months after the end of the period for leaving maternity leave indicated in it. After submitting the application, the employer will make a decision within ten days to provide maternity leave and maternity benefits.
Maternity leave - what to do with a right that an employee does not want to use
An employee’s right to leave, including a woman’s right to maternity leave (hereinafter referred to as Maternity Leave) is supported by the employer’s responsibilities enshrined in legislation and has well-established procedures for the employee to influence an unscrupulous employer.
On the contrary, a situation where a company does not want to take on risks associated with the health of a female employee who is planning to give birth any day now - risks associated with disruption of production, technological and other processes of the enterprise’s economic activity are not regulated by law or practice .
What to do with the desire of a pregnant woman (or who has just given birth) to work, despite the right and initiative of the employer to send her on leave provided for by law? Or in a situation where she herself is an executive body (director, general director, president), a top manager and does not go on the required vacation? Is an organization punishable if it fails to send a pregnant woman on legal leave on time? The employer needs to resolve this issue in such a way as not to violate the rights of the employee and the interests of the company.
First of all, it is necessary to determine the right of signature of the absent employee - the executive body of the documents.
The legislation does not provide for the unconditional termination of the powers of the head of an organization in the event of an employee’s leave, including maternity leave, if the employee is the sole executive body of a legal entity.
In accordance with paragraph 1 of Art. 27 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, persons authorized to represent an organization on the basis of the law or its constituent documents are recognized as legal representatives of the taxpayer-organization.
The established arbitration court practice recognizes the right of a manager who is on vacation or sick leave to represent the interests of society. Such conclusions are contained in the Resolution of the Presidium of the Supreme Arbitration Court of the Russian Federation dated 02/09/1999 No. 6164/98, as well as in the judicial acts of the FAS of the Central District dated 11/17/2003 in case No. A54-2182/03-С3, FAS of the North Caucasus District dated 08/20/2007 case No. F08-4564/2007-1978A.
Thus, the general director, even while on fiscal leave, can sign tax returns of the taxpayer organization he heads, and contracts within the limits of the authority established by the company for his position. The legislation does not provide that the powers of an official are terminated (suspended) due to his leave or incapacity for work.
At the same time, the actual performance of a labor function by an employee on maternity leave is the basis for paying her wages. Since the meaning of the maternity benefit provided for by the Federal Law “On Compulsory Social Insurance in Case of Temporary Disability and in Connection with Maternity” dated December 29, 2006 No. 255-FZ is compensation to the employee (insured person) for lost earnings, then the grounds for There are no payments to the employee for employment and labor benefits for the period of work that coincided with the vacation period (see, for example, the resolution of the Federal Antimonopoly Service of the Far Eastern District dated February 27, 2010 No. F03-778/2010, the resolution of the Federal Antimonopoly Service of the Northwestern District dated March 12, 2009 No. A13-9831 /2008, resolution of the Federal Antimonopoly Service of the West Siberian District dated January 25, 2010 in case No. A45-9720/2009).
Moreover, in cases where the employee and the employer are the same person, the relationship between the company and the director as an employee is also regulated by labor law.
According to Art. 255 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, leave for labor and labor is provided by the employer at the request of the employee and in accordance with a medical report (that is, in the presence of a sick leave certificate). Thus, labor legislation does not provide for the possibility (and obligation) to provide maternity leave at the initiative of the employer without a corresponding application from the employee.
The absence of an obligation for an employee who has a certificate of incapacity for work, issued within the established period, to immediately go on leave under the Labor and Employment Regulations allows her to independently determine when she will go on leave.
Article 12 of Federal Law No. 255-FZ of December 29, 2006 “On compulsory social insurance in case of temporary disability and in connection with maternity” provides for the right of an employee to apply to the employer for temporary disability benefits no later than six months from the date of termination of maternity leave .
However, if a woman submits an application for leave under the BiR later than the date indicated on the sick leave certificate, regardless of the start time of using the leave, its end is determined based on the terms specified in the temporary disability certificate , i.e., if the woman began to use the leave on pregnancy and childbirth later, it is automatically reduced, as is the period (and therefore the total amount) of payment of maternity benefits.
Judicial practice confirms the absence of the possibility of postponing the end of vacation, which was reflected in the decision of the Supreme Court of the Russian Federation dated November 14, 2012 No. AKPI12-1204. If an employee decides to exercise her right to leave under the BiR later than the date from which she, according to the sick leave, is released from work, then the employer will be obliged to provide it from the day specified in her application until the day the sick leave ends.
Accordingly, for the time that has elapsed from the moment the sick leave is issued to the actual start of using the leave, the B&R benefit is not paid, but working days are paid in the general manner based on the terms of the employment contract. The employee must choose between maternity benefits and wages.
It seems that there is nothing terrible for the company, since this is the personal desire of the employee. And the duration of pregnancy can be hidden for a long time. However, if labor protection comes, it is the employer who will have to prove that it is not you who are not letting the employee go, but it is her desire and initiative - not to submit to the company an application for maternity leave, which, together with the issued sick leave, is the basis for the calculation manuals for B&R.
The doctor does not ask the expectant mother on what day she wants to go on maternity leave, but sends her on sick leave from the 30th week of pregnancy (if the pregnancy is multiple - from the 28th). It then depends on the employee whether to give sick leave to the company or to work.
However, the employer, while maintaining the right of the pregnant employee to work, must comply with the requirements provided for by the Labor Code of the Russian Federation to facilitate the work of this category of workers.
An employee who is expecting a baby cannot be involved in work (even with her consent!):
— at night (from 10 p.m. to 6 a.m.);
- overtime;
- on weekends;
- on holidays that are non-working days.
In addition, the law also prohibits sending a pregnant woman (regardless of her consent and desire) on business trips.
The Labor Code of the Russian Federation establishes that every pregnant woman has the right to go to work on a reduced schedule. The law does not stipulate the exact number of working hours to which the expectant mother’s time should be reduced, so the issue is resolved by agreement with the employer. It is important to know that with this mode of work, wages will be reduced accordingly.
And the current Sanitary Rules (SanPiN) provide for other restrictions on the working conditions of pregnant women. Thus, they cannot work: in basements, in drafts, in conditions of wet clothes and shoes, in conditions of exposure to harmful production factors, in other unfavorable conditions provided for by SanPiN, and also if the work involves constant lifting of heavy objects, then the mass of the moved cargo cannot be more than 1.25 kg, and when alternating lifting with other work - more than 2.5 kg.
A pregnant woman, on the basis of her application and medical report, should have production and service standards reduced (Part 1 of Article 254 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation). In accordance with the general provisions of the Hygienic Recommendations for the rational employment of pregnant women, approved by the State Committee for Sanitary and Epidemiological Supervision of Russia on December 21, 1993, and the Ministry of Health of Russia on December 23, 1993, pregnant workers are given a differentiated production rate with a reduction on average to 40 percent of the constant rate while maintaining the average earnings as before work. During the period of reduction in standards, the woman retains the average salary.
In accordance with Part 1 of Art. 254 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, a pregnant woman, on the basis of a medical report and at her request, is transferred to another job that excludes the impact of adverse production factors, while maintaining the average earnings for her previous job. For example, according to clause 13.2 of the Sanitary and Epidemiological Rules and Standards “Hygienic requirements for personal electronic computers and work organization. SanPiN 2.2.2/2.4.1340-03" (approved by the Chief State Sanitary Doctor of the Russian Federation on May 30, 2003) women from the time of pregnancy are transferred to work not related to the use of a PC, or the time they work with a PC is limited (no more than three hours per work shift) subject to compliance with the hygienic requirements provided for by sanitary rules.
There are also certain industry restrictions. Thus, in accordance with the Federal Aviation Rules “Medical examination of flight, dispatch personnel, flight attendants, cadets and candidates entering civil aviation educational institutions”, approved by Order of the Ministry of Transport of Russia dated April 22, 2002 No. 50, from the moment pregnancy is established, aviation personnel are recognized as unfit for flight, dispatch work, to work as a flight attendant.
And paragraph 2.2 of the Resolution of the Supreme Court of the RSFSR dated November 1, 1990 No. 298/3-1 established a ban on the use of labor by pregnant women in crop production and livestock production from the moment pregnancy is detected.
Thus, in cases where the work performed by a woman is contraindicated during pregnancy, she should be transferred to another job suitable for her.
A pregnant employee also has the right to take time off from doctor’s appointments as needed, and the employer is obliged to provide the pregnant employee with the opportunity to freely undergo medical examinations, laboratory and other diagnostic tests. And during such an examination, the employee also retains the average salary at her place of work. The basis for providing this guarantee is a certificate from a medical institution confirming the state of pregnancy (Part 3 of Article 254 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
Such rules are established by clause 3 of the Regulations approved by Order of the Ministry of Health and Social Development of Russia dated March 30, 2006 No. 224, clause 4 of the Procedure approved by Order of the Ministry of Health and Social Development of Russia dated October 2, 2009 No. 808n.
An employer does not have the right to prevent a pregnant employee from undergoing a medical examination and regard absence from work as a disciplinary offense. Such conclusions are confirmed by judicial practice, for example, the ruling of the Moscow City Court dated March 24, 2011 No. 33-8111.
As we can see, the employer is significantly limited in its actions by the requirements of labor legislation; the legality of the company’s actions related to the validity and procedure for calculating benefits under Labor and Labor, payment of wages to employees who have sick leave under Labor is controlled by the territorial bodies of the Social Insurance Fund and labor inspectorates.
It is not the employer’s fault that the employee, instead of going on vacation, continues to show up at the office every day. And the expectant mother can understand. However, in order to avoid even hypothetical claims from inspectors, you can ask the employee to write a free-form statement about her voluntary decision to work after the right to maternity leave arises. After all , the closer the date of birth, the greater the risk that the labor inspectorate will see pressure on the employee from the company behind such hard work.
If the employer is determined to persuade an employee to use her right to leave under the BiR, it is better to appeal to Part 2 of Art. 212 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, according to which the employer is obliged not to allow employees to perform their job duties without undergoing mandatory medical examinations, mandatory psychiatric examinations, as well as in the case of medical contraindications, and Art. 213 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation - the employer is obliged to organize preliminary (upon admission) and periodic medical examinations for certain categories of employees.
These requirements are ensured by the administrative responsibility of the employer provided for in paragraph 3 of Art. 5.27.1 of the Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation - admission of an employee to the performance of labor duties without undergoing training in the established order and testing knowledge of labor protection requirements, as well as mandatory preliminary (upon entry to work) and periodic (during employment) medical examinations, mandatory medical examinations at the beginning of a working day (shift), mandatory psychiatric examinations or in the presence of medical contraindications shall entail the imposition of an administrative fine on officials in the amount of fifteen thousand to twenty-five thousand rubles; for persons carrying out entrepreneurial activities without forming a legal entity - from fifteen thousand to twenty-five thousand rubles; for legal entities - from one hundred ten thousand to one hundred thirty thousand rubles.
Accordingly, when applying the specified norms of labor and administrative legislation, it is necessary to request from the employee a medical report or a certificate of the absence of medical contraindications for performing work according to the position held and make sure that there is no other work at the enterprise to which it is possible and permissible to transfer the employee due to medical and labor requirements.
If both parties to the employment contract are interested in performing the work, it is possible for the employer and employee to draw up a civil contract to perform certain work for a certain period of time. Not forgetting that regulatory authorities will painstakingly and carefully check compliance with all formalities under such agreements.
The contract for paid services regulates relations not according to the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, but according to the Civil Code of the Russian Federation. These relationships are not labor relations and are of a short-term nature. In accordance with the concluded agreement, the subject of the agreement will be the performance of services for which remuneration is provided, and not work for wages. In this case, there will be no deductions of insurance contributions to the Social Insurance Fund from paid remuneration.
Maternity leave
In all cases of complications of childbirth, several more days of leave are additionally provided. For example, if a girl needs a caesarean section. If you want to go on maternity leave earlier, then in this case, you need to consult your doctor. If the relationship is trusting, then any person will make a concession and set the deadline earlier.
How long does maternity leave last? When you are going on maternity leave, the most worrying question is how long this period will last. This is very important for planning your own time, as well as calculating working hours. Maternity leave lasts the same amount of time as the time before giving birth.
When do they go on maternity leave?
If there was a complicated birth, then the second part will be 86 days instead of 70. Additionally, parental leave can last up to 3 years, but this period is not strictly established. You can go to work earlier - at any time convenient for parents. If a mother wants to go to work earlier than expected, then she has every right to do so.
She only needs to write an application for early leave addressed to her boss, indicating the date of her expected return. At the same time, she can start working on a part-time basis or a reduced work week. There are also a number of possibilities to extend the holidays.
What options did the authorities offer for reducing maternity leave?
At the end of November, Alexander Lukashenko said that he “considers it important to also discuss the possibility of reducing parental leave, which in Belarus currently lasts until children reach three years of age and is one of the longest in the world.”
Three weeks later, Minister of Labor and Social Protection Irina Kostevich even proposed possible options: leave three years, of which only two are paid, or two years for everyone, three for large families.
A couple of weeks later, news appeared: maternity leave would not be reduced. Nevertheless, let us remind you: in 2015 they said that there would be no increase in the retirement age, but in 2017 a full-fledged pension reform began. But pensioners receive money in the same place as women on maternity leave - in the social security fund, which has been experiencing financial stress for several years and requires subsidies.
When is maternity leave granted, how to apply for it and receive payments
In fact, it is correct to consider the time of two leaves as maternity leave: for pregnancy and childbirth, and for caring for a child under 3 years of age. Moreover, each period lasts a different time and is also paid differently. “Maternity holidays” are considered to be the time that a girl will rest, that is, if she leaves maternity leave early, then the holidays will end, accordingly. Our article is devoted to answering the question of when maternity leave is given.
- 1 When do they go on maternity leave?
- 2 How long is maternity leave?
- 3 How to apply for maternity leave?
- 4 Is it possible to go on maternity leave earlier or later?
- 5 How do you pay for maternity leave?
- 6 How to go on maternity leave?
- 7 How to go to work?
When do they go on maternity leave? If the work is not official, then you can go on maternity leave at any time. Is it possible not to go on maternity leave? The expectant mother herself decides how many months to go on maternity leave. The following question may arise: is it possible not to go on vacation at all - only for the period of childbirth, and be at work the rest of the time? Of course, if your health allows it, you can. But it’s better to arrange the days of childbirth and postpartum recovery as maternity leave: firstly, for benefits, so as not to lose money, and secondly, for safety net. Moreover, as an employee - if something goes wrong, for example, the child is born weak and sickly, and she will need more time to care for him than she originally planned> secondly, for the employer - if everything is documented right away, as it should be , he will have a guarantee that the employee will not subsequently accuse him of not allowing her to go on maternity leave.
What was maternity leave like before?
Parental leave in Belarus was not always three years. For example, in the early 1980s, maternity leave lasted 6 months. Then it was increased to 1.5 years, thanks to which the country received a surge in the birth rate in 1982-1984. Later an unpaid period was added, another 1.5 years to the vacation.
The biggest effect was achieved by increasing vacation time from 6 months to 1.5 years. And after the entire period became paid in 1991, such efficiency no longer existed. Due to the collapse of the Union and economic problems, the birth rate fell, the consequences of Chernobyl slowed down the implementation of reproductive goals. It’s not that people didn’t want to give birth—they put it off until later.
Nowadays it is not always easy to get into kindergartens, but in the Soviet period Belarus had a fairly good preschool infrastructure, there was a system of departmental kindergartens and nurseries at factories and state enterprises.
There was a nursery with a long shift, until 10 pm. In the 1990s, when the birth rate dropped markedly, these institutions began to close due to lack of use.
Before 1991, there were 1.5 years of paid maternity leave and another 1.5 unpaid. Then, due to the consequences of the Chernobyl accident, it was decided that all three years should be paid - in the hope that this would help people and have a beneficial effect on their health.
And for 30 years now, Belarus has existed with three years of paid parental leave. There have been no major changes in this matter.