What are the Rules for?
This regulatory document establishes:
- procedure for hiring and dismissing employees,
- work and rest schedule at the enterprise,
- conditions for the provision of bonuses, benefits, financial assistance,
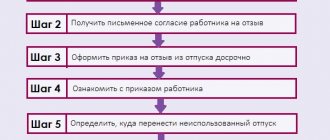
- procedure for sending employees on vacations, business trips,
- obligations and rights of the parties, etc.
The document is written based on the needs and capabilities of the organization, taking into account the regulatory legal framework based on articles of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation and state standards and can contain any number of points.
The main objective of the Rules: to promote the competent distribution and use of working time, strengthen labor discipline, increase the efficiency of the production process, etc.
It should be noted that not all enterprises in the commercial sector use the Rules in their personnel records, which today is not a violation of the law. There is only one important condition: the relationship between the employer and subordinates must fit within the framework of the current legislation. But state budgetary institutions are required to use these Rules in their work, and their drafting is regulated to the smallest detail.
The internal regulations apply to all personnel of the organization, regardless of the position of a particular employee, so everyone must be familiarized with them upon signature.
The drafting of the Rules must be treated with extreme care, since in some cases they can become evidence in court when resolving labor conflicts and disagreements, both on the part of the employer and the subordinate.
In order to put the Rules into effect, the enterprise must issue an order on behalf of the manager. Moreover, if the company has a trade union organization, its representatives must be familiar with the Rules even before their approval.
Procedure for applying the order
Internal regulations are a special regulatory act developed by a business entity, which establishes during what periods of time employees must perform their duties and during what periods they must rest.
In addition, this document can also consider any other work features that arise between employees and administration in the process of conducting business.
Employees from different professions may be invited to develop the document. At the same time, on the final version they will have to put down their personal data, as well as the “Agreed” stamp.
Once the document has been developed, it must be put into effect.
Usually a special order is issued for these purposes. Attention: if the company has an active trade union body, then the drawn up Rules must be sent there for approval.
Otherwise, you can skip this step. Internal regulations can function both as an independent document and as an annex to another internal regulatory act - for example, to a Collective Agreement. In such a situation, there is no need to draw up a separate order to start using it.
Most often, the responsibility for issuing an order falls on the personnel department or the office management department. They must draw up a draft order and submit it to the manager for signature.
It must be remembered that only persons authorized by this Charter have the right to put the Rules into effect. Usually, this is the director.
Attention: if the Rules are put into effect by order, then they must go to it as an appendix.
After approval, a special o is placed on the document and the details of the order by which this was done are indicated.
The order by which the rules were put into effect can be stored with them, or next to other orders for the main activity, and a copy of it is attached to the rules.
Direct order issuer
An order to approve the Rules can be written by any employee of the organization whose job responsibilities include this function or by an employee authorized to formulate orders by a separate order of the manager. It could be:
- legal adviser,
- head or HR specialist,
- secretary, etc.
After drawing up the form, it should be given to the director of the organization for approval - without his signature it will not be considered valid and it can be easily challenged through a court or labor inspectorate.
An order for approval of the Internal Labor Regulations must be drawn up both during the initial formation of the document and in cases where any changes have been made to the Rules or they have been completely “reformatted”.
Who makes up
The drawing up of rules can be done by any employee who is listed at the headquarters of the organization and whose responsibilities include the formation of orders. These workers may include:
- secretary;
- HR employee;
- legal adviser and others.
After the rules are formed, the document must be submitted to the director of the organization, who must confirm the validity of the order with his signature. If at an enterprise such a document does not have the certification of the director, then it is considered that there is no specific labor schedule in the company.
Submitting a document for signature must be done not only when drawing up an order, but also when making changes of any scale.
Rationale and basis for creating an order
Like any other administrative document, this order must have some basis, i.e. justification and basis.
The substantiating point in this case is the reason for creating the order, i.e. the need of the company that the document solves (for example, to organize the activities of the work team, prevent labor conflicts and disputes, etc.).
As a basis , you can refer to the clause of the law of the Russian Federation, which regulates the creation of internal labor regulations.
Are the Rules mandatory for all enterprises?
The Rules must be developed and adopted in accordance with Art. 189 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, however, this is not necessary for all enterprises.
According to Art. 309.2 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, employers, in accordance with Federal Law-209 of July 24, 2007.
small businesses classified as microenterprises may not accept them. At the same time, on the basis of Art.
4 of this law, these include fairly large enterprises with a staff of up to 100 people and an income of up to 2 billion rubles per year. In this case, all important aspects of labor organization must be reflected in the employment contract with the employee.
Why the internal labor regulations should be amended in 2021, the sample for an LLC has been clarified, we’ll look into it further.
The internal labor regulations, in accordance with the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, reflect the procedure for hiring, the procedure for dismissal, and the fundamental rights of the parties. That is, they also regulate office work, in which the legislator is now implementing the principle of eliminating paper documents.
In this regard, the internal labor regulations in 2020 (sample for LLC) need to be clarified.
Nuances of document preparation
The order does not have a single unified model approved at the legislative level. So enterprises and organizations can write it in free form or according to a template approved within the company. In this case, there is a number of information that must be indicated in the document:
- number, date,
- place of compilation,
- full company name,
- basis for formation.
The order also needs to give a specific instruction, usually drawn up in the form of separate paragraphs. In this part, you should definitely include the number and date of preparation of the approved Internal Labor Regulations, as well as the date of their entry into force. All other information is prescribed based on the needs of the enterprise.
It is necessary to note the employees responsible for its implementation (these issues are usually controlled by the personnel officer), and as an appendix, indicate the rules themselves and, if necessary, other attached documents.
How to correctly draw up an order approving internal labor regulations
Let's look at an example of drawing up an order to approve the rules.
The law does not define any special form for it. Therefore, organizations can draw it up in any form, including using a company letterhead.
Typically, the preparation of an order must begin with the full name of the business entity, location address, and registration codes.
Then the name of the document and its serial number are written down. Under these data, the document will need to be recorded in the order register for the enterprise.
The next step is to record the place where the order was drawn up and the date on which it was made.
Next, the name of the order is written on a new line. Then comes the text of the order. First, you need to justify the reason why you decided to draw up and start using the Rules.
For example, you can write the following line: “For the purpose of regulating issues of organizing working conditions, and maintaining discipline at work and in production.” Here it is advisable to provide links to articles from the Labor Code that regulate these actions of the administration.
Next, separately on a new line you need to put the word “I order”, after which you need to list the manager’s orders in the form of a list.
Here you can enter the following:
- Approve the developed rules and put them into effect from a certain date.
- When some rules are replaced by a new version, it is necessary to declare the old similar local act invalid in the order.
- Establish that this document should be used in everyday work, regulating the work schedule of employees.
- Establish a responsible person who will be entrusted with monitoring compliance with the rules and the procedure for familiarizing with this local act. It is important to remember that familiarization must be carried out against the signature of the manager.
- Separately, it is necessary to bring the norms of this act to the attention of incoming new employees. It is also recommended to identify a responsible employee here.
- Appoint a person responsible who will monitor the execution of this order of the manager.
In the approval order, you can set the period during which these internal rules will be in force in the company. However, if this is done, then after this period it will be necessary to develop and put into effect new rules.
Attention: if the Rules are put into effect by order, then they are an appendix to it. Therefore, in the text of the order itself, it is necessary to indicate that there is an appendix to it and record the number of sheets of the Rules.
The order must be certified by the manager, who affixes his visa, position, and personal information.
All persons who were designated in the order as responsible must also affix their signatures and decipher their full names, as well as indicate the date of familiarization with this document.
What to pay attention to when placing an order
There are no special requirements for the execution of the order, as well as for its content: it can be written by hand (with a ballpoint pen of any color, but not with a pencil) or printed on a computer. To create a document, both the organization’s letterhead and a simple blank sheet of paper are suitable.
Only one condition must be observed: the order must be signed by the head of the company or his representative and the employees responsible for its implementation.
Today, it is not necessary to certify a form using a seal or stamp, since the use of stamp products is no longer a norm prescribed by law, even for legal entities (the exception is those organizations in which the obligation to use seals and stamps is approved in internal regulations).
Why are house rules needed?
Their functions at the enterprise are to regulate the following points:
- algorithm for processing the reception of citizens;
- work and rest schedule for employees;
- calculation and conditions for calculating remunerations, bonuses, material support and other monetary payments;
- obligations and rights of the employer and employees to comply with labor discipline;
- accounting for standard working hours and overtime hours.
The document is drawn up based on the capabilities and requirements of the organization in compliance with the norms of the Labor Code and other legislative acts. Some of its clauses may duplicate corresponding provisions in contracts, where they relate to only one employee. A distinctive feature of the work regime prescribed in the local regulatory act is that it applies to all employees of the company, including management positions.
What changes need to be made
Making changes to the PVTR is associated not only with the electronic work book, but also with the cancellation of SNILS, if this has not already been done, since this document usually also appears in the Rules in the sections on the procedure for registering employment.
What changes and points need to be made in this regard:
- in paragraphs where labor is mentioned, it is advisable to add the following wording “... and information on labor activity established by law.” It is mentioned, as a rule, in such sections as “Hiring an employee”, “Termination of a contract”, “Transfer to another job”, “Rewarding employees and the procedure for imposing disciplinary sanctions”;
- where SNIL is mentioned, it is necessary to add the text “or PFR certificate”;
- if necessary, it is worth defining in the Rules the procedure for electronic interaction between the administration and workers.
Important "disciplinary" section
Compliance with labor discipline is one of the most important issues that requires scrupulous study. Without this, the VTR rules will be insufficient and incomplete. Special attention is paid to the disciplinary issue, and in certain industries they do not limit themselves to the section of the VTR rules, but develop separate provisions or disciplinary statutes.
The disciplinary section consists of 2 parts: penalties and rewards. The section on penalties is based on Art. 192 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, in which a disciplinary offense is defined as failure to perform or improper performance of labor duties by an employee, which may result in 3 types of penalties (reprimand, reprimand and dismissal). Labor legislation does not provide for any other penalties.
For more information about disciplinary sanctions provided for by the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, read the material “Types of disciplinary sanctions under the Labor Code of the Russian Federation.”
Additional penalties can only be discussed in cases where special disciplinary liability is imposed on the employee. They are indicated in federal legislation or disciplinary regulations for certain categories of workers (Part 2 of Article 192 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation). An example is the Law “On State Civil Service” dated July 27.
IMPORTANT! According to Art. 193 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, a disciplinary sanction will be legal if the employer follows a certain procedure (requests a written explanation from the employee, draws up a report, issues an order, etc.).
The VTR rules must also provide for all cases when a disciplinary sanction is lifted (Article 194 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
The VTR rules may not contain a section on incentives if this issue is already reflected in other local acts of the employer.
If this issue is not addressed anywhere, the VTR rules should reflect at least information about the types of incentives (gratitude, bonus, etc.) and the reasons for material or moral incentives (for work without marriage, etc.).
IMPORTANT! The section of the internal labor regulations dedicated to incentives allows you to fearlessly take into account bonuses and incentive allowances as part of salary expenses when calculating income tax (part 1 of article 255, paragraph 21 of article 270 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).