Where is the Committee for the Protection of Children's Rights located?
Commissioner for the Rights of the Child under the President of the Russian Federation Tasks: ensuring the protection of the rights of the child and promoting the restoration of violated rights of the child; legal education in the field of protection of children's rights; requests and receipt in the prescribed manner of necessary information, documents and materials from federal government bodies, government bodies of constituent entities of the Russian Federation, local government bodies, organizations and officials; unhindered visits to federal government bodies, government bodies of constituent entities of the Russian Federation, local government bodies, organizations; conducting, independently or jointly with authorized state bodies and officials, inspections of the activities of federal executive authorities, state authorities of constituent entities of the Russian Federation, as well as officials, and receiving appropriate explanations from them; sending to the federal executive authorities, state authorities of the constituent entities of the Russian Federation, local government bodies and officials, in whose decisions or actions (inaction) he sees a violation of the rights and interests of the child, his conclusion containing recommendations regarding possible and necessary measures to restore these rights and interests; attracting, in accordance with the established procedure, scientific and other organizations, as well as scientists and specialists, for the implementation of expert and scientific-analytical work related to the protection of children’s rights, including on a contractual basis
The Commissioner for Children's Rights (OCPR) is an official who is primarily guided by the interests of children and, if necessary, takes measures to protect the rights of the child. This position exists in more than sixty countries around the world.
Who is the Commissioner for Human and Children's Rights, what responsibilities are assigned to him and how can ordinary citizens contact him? Where should citizens go if the rights of a minor have been violated, how to write an appeal and where to find the address of the committee?
What rights does every child have?
From birth, children become citizens of the Russian Federation and have certain rights. Due to their age, young citizens cannot protect and provide for themselves; responsibility lies with their parents and legal representatives. Legislative acts aimed at protecting minors: the Constitution of Russia, federal laws “On the protection of children from information harmful to their health and development”, “On guardianship and trusteeship”, “On education”, “On basic guarantees of the rights of the child in the Russian Federation” , articles of the Family Code, the international “Convention on the Rights of the Child” (we recommend reading:).
Children are considered to be persons who have not reached the age of majority. In addition to the basic rights of citizens of the Russian Federation, legislation provides for a number of special “children’s” rights. The rights that a child has from the moment of birth are presented in the table.
Who protects the rights of minors in the Russian Federation?
Protecting children's interests is primarily the responsibility of parents. If the baby does not have a mother and father or they do not fulfill their parental responsibilities, his interests are protected by:
In addition to the committee and other specified structures, a special role is assigned to the commissioner. At the same time, the UPPR is determined not only at the federal, but also at the regional level. The official is selected and appointed by the President. The first was Alexey Golovan, in 2009 Pavel Astakhov was appointed. In September 2021, Astakhov was replaced by Anna Kuznetsova.
The country's chief ombudsman
At the national level, the interests of the child are represented by the Commissioner under the President of Russia. UPPR is an independent official with great capabilities. For the first time, the institution of a defender was officially created in 1977 in Sweden, and in 1989, after the adoption of the UN Convention, ombudsmen for the protection of human and child rights appeared in most democratic countries (we recommend reading:).
In Russia, news about the position appeared relatively recently. For almost 7 years it was occupied by the famous lawyer Pavel Astakhov, who was relieved of his post after a conversation with V.V. Putin and submission of resignation. Now, instead of Astakhov, Anna Kuznetsova is engaged in human rights activities regarding minors at the state level.
The activities of the children's defender are ensured by the Public Chamber of the Russian Federation; he is not subordinate to the Cabinet of Ministers and other government agencies. You should contact him if the child’s rights have been violated, and the committee (commission) for minors’ affairs and other structures have shown negligence and failed to protect his interests.
Public and government organizations
If a child’s rights are violated or a threat to his health or life arises, both officials and ordinary citizens are obliged to notify the guardianship authority, which will take appropriate measures to protect the rights of the child. The activities of the guardianship and trusteeship body are as follows:
- providing guardianship to a child who needs it;
- checking the legality of property transactions affecting the interests of minors;
- selection and preparation of applicants wishing to adopt a child or become a guardian.
A girl or boy has the right to independently apply to the guardianship authority, and upon reaching the age of fourteen, to the court.
The protection of the rights of minors is not only carried out by the guardianship and trusteeship authority, it is the concern of society as a whole. The rights of the child are protected by the following organizations:
- the judiciary and the prosecutor's office, which protect young citizens in accordance with legal acts;
- commissions and inspections for juvenile affairs;
- centers for social rehabilitation of adolescents;
- public organizations.
How to contact the Committee with your problem
To implement the activities of the Committee on the Rights of Minors in Russia, the position of Commissioner for Children's Rights was introduced. This happened on September 1, 2009, when a children's ombudsman under the President of the Russian Federation was appointed for the first time.
Since the vast territory of the country does not allow multiple issues to be resolved from the center, children’s rights ombudsmen have also appeared in the constituent entities of the Federation. They are called regional children's ombudsmen and are called upon to oversee the observance of the interests of young citizens. The financing of their activities is entrusted to the regional authorities. At the same time, their service is led by the Federal Commissioner under the President.
All applications and complaints received on the official website of the federal ombudsman (from September 2021 this is Anna Yuryevna Kuznetsova) are redirected for consideration to a specific area, which is reported to the applicant in writing. Contacts for communication are also indicated.
The functions of the commissioners are determined by the activities of the Committee on the Rights of the Child. They must put into practice the ideas and recommendations of the international organization. The tasks of their work are as follows:
- Monitor compliance with Constitutional norms in relation to children.
- Develop recommendations for municipal authorities regarding the prevention and elimination of violations of the interests of minors.
- Monitor compliance with the rights of a special category of citizens: disabled children.
- Study and summarize existing practice on legal issues of compliance with children's rights.
- Inform teachers and parents about the rights of children, methods of their protection, changes in current legislation.
- Create projects to optimize work aimed at protecting children.
- Monitor how the rights and freedoms of minors are implemented in preschool and school institutions, as well as educational organizations for the vocational training of children.
In order for the ombudsman’s tasks to be accomplished, he is vested with certain official powers. He is allowed:
- visit any organization if necessary and monitor its activities;
- request the necessary information;
- demand clarification from officials both about work in general and about a specific case.
An important point in the activities of child protection ombudsmen is that regional ombudsmen have their own public reception areas. Any person, including a child, can come here to report a violation of the interests of minors. This is perhaps the only organization where a minor can act independently.
It is also important that you can contact a specific person directly, and not a law enforcement machine.
Features of the appointment of a commissioner for children's rights in Russia
The first ombudsman in Russia was appointed in 2009. Both the appointment and removal of a person from his position is carried out personally by the President (as P. Astakhov was appointed and dismissed).
Ombudsmen are also elected by local heads of regions. Moreover, each of the subjects of the federation has the right to adopt a law on the activities of a regional representative of children's interests. However, not every region has elected a children's rights activist. Officials in the regions do not depend on the Chief Ombudsman for Human and Children's Rights, but are actually his subordinates.
The procedure for electing and legal status of representatives at the regional level is different. Often this position is classified as an executive body. In areas where ombudsmen have recently appeared, the applicant for the position is approved after consultation with the legislative body. In this case, the defenders have parliamentary status. Thanks to this, officials have greater independence, which has a positive effect on the results of their activities.
Goals and objectives, rights and powers of a children's human rights defender
The priority task of the Ombudsman is to protect the rights and interests of minors in accordance with legislative norms, especially orphans and children who are left without parental care or who find themselves in difficult situations (more details in the article:). At the same time, the UPPR does not have the right to make a decision regarding the issue of the child’s residence. In accordance with the law, the main responsibilities and tasks are:
The Ombudsman has broad powers. They are listed in the Presidential Decree “On the Commissioner under the President of the Russian Federation for Children’s Rights.”
How to contact the Presidential Commissioner for Children's Rights?
The right of citizens to appeal to the UPPR is confirmed by Article 33 of the Russian Constitution. There are several ways to report a violation of rights against a minor to the Ombudsman.
The position of the Commissioner for Children's Rights under the President of Russia was established by the Decree of the Head of State of September 9, 2009 in order to ensure effective protection of the rights and interests of the child in the country.
According to the above-mentioned Decree of the President of Russia, the Commissioner for Children's Rights is appointed to the position and dismissed from it by the President of the Russian Federation. To carry out its human rights duties, the Ombudsman is vested with broad powers. In particular, he has the right:
· request and receive, in the prescribed manner, the necessary information, documents and materials from federal government bodies, government bodies of constituent entities of the Russian Federation, local government bodies, organizations and officials;
· freely visit federal government bodies, government bodies of constituent entities of the Russian Federation, local government bodies, organizations;
· carry out independently or jointly with authorized state bodies and officials an inspection of the activities of federal executive authorities, state authorities of constituent entities of the Russian Federation, as well as officials, and receive appropriate explanations from them;
· send to the federal executive authorities, state authorities of the constituent entities of the Russian Federation, local self-government bodies and officials, in whose decisions or actions (inaction) he sees a violation of the rights and interests of the child, his conclusion containing recommendations regarding possible and necessary measures to restore these rights and interests;
· to involve, in the prescribed manner, scientific and other organizations, as well as scientists and specialists, for the implementation of expert and scientific-analytical work related to the protection of children’s rights, including on a contractual basis. About the Commissioner under the President of the Russian Federation for Children’s Rights. Decree of the President of the Russian Federation of September 1, 2009 No. 986.
All these norms, in fact, are taken from the Federal Constitutional Law “On the Commissioner for Human Rights in the Russian Federation.” The Federal Commissioner for Human Rights is also endowed by law with the right to “entrust competent government institutions with conducting expert research and preparing opinions on issues to be clarified during the consideration of the complaint.” In addition, he is allowed to “get acquainted with criminal, civil cases and cases of administrative offenses, decisions (sentences) that have entered into legal force, as well as discontinued cases and materials for which the initiation of criminal cases has been refused.”
The Presidential Commissioner for Children's Rights does not have such rights. But, the Decree, which regulated the activities of the children's ombudsman, at the very end contained one more paragraph: “Recommend to the state authorities of the constituent entities of the Russian Federation to establish the position of ombudsman for children’s rights.”
The Commissioner informs government bodies and the public about his activities, the state of affairs in the field of observance of children's rights and freedoms in the country, interacts with federal and regional government bodies, with commissioners and commissions for children's rights in the constituent entities of the Russian Federation, non-governmental human rights organizations, and the media .
Preparation of annual reports on activities, as well as special reports, bringing them to the attention of officials and the general public allows the Commissioner to present his vision of the situation with ensuring the rights of the child both in the country as a whole and in certain areas of society, and is a powerful lever of influence on public opinion Osmanov T.S. Does the Commissioner for Human Rights have the right to appeal to the supervisory court // Lawyer. 2009. No. 6.- P. 21..
The bulk of cases related to the restoration of violated rights of a child are considered on the basis of written applications and complaints from citizens received by mail against decisions or actions (inaction) of state bodies, local governments, officials, and civil servants.
The Commissioner provides consulting assistance to citizens who wish to exercise their constitutional right to appeal to international human rights bodies (European Court, UN Human Rights Committee and others).
One of the main ways the Commissioner implements his control functions is the process of considering complaints from citizens of the Russian Federation, as well as appeals from foreign citizens and stateless persons.
A similar rule exists in New Zealand, Poland, Sweden and other countries.
The legislator establishes some exceptions from the scope of competence of the Commissioner, according to which the Commissioner does not consider complaints against decisions of the Federation Council and the State Duma of the Federal Assembly of the Russian Federation, as well as legislative (representative) bodies of the constituent entities of the Russian Federation.
A child can submit his complaint to both the authorized entity and the authorized representative at the federal level. If a child initially filed a complaint with the Commissioner for Children’s Rights in a constituent entity of the Russian Federation, this is not a reason for the Commissioner for Children’s Rights in the Russian Federation to refuse to accept a complaint on a similar problem.
The competence of the Commissioner extends to complaints from citizens in places of forced detention, for example, in prisons, pre-trial detention cells, colonies, etc. The administration of places of forced detention is obliged to send to the Commissioner appeals from persons detained in these places within a clearly defined period of time, which is equal to 24 hours from the moment the appeal is received by the administration. The administration does not have the right to open these letters or otherwise view them.
The Commissioner has free discretion when deciding whether to initiate proceedings on a complaint or not. Russian legislation provides the Commissioner with four options.
Firstly, he can accept the complaint for consideration if the applicant previously appealed against decisions or actions (inaction) of state bodies, local government bodies, officials, civil servants in a judicial or administrative manner, but was dissatisfied with the decision taken on his complaint. In addition, the Commissioner accepts a complaint if it is submitted to him no later than one year from the date of violation of the applicant’s rights and freedoms or from the day when the applicant became aware of their violation.
Secondly, the Commissioner has the right not to accept a complaint, citing Art. 16 of the Law, but to explain to the applicant where he should turn first to protect his rights and freedoms.
Thirdly, the Commissioner, if necessary, has the right to transfer the complaint himself to a state body, local government body or official whose competence includes resolving the complaint on the merits.
Fourthly, the Commissioner has the right to refuse to accept a complaint for consideration.
The Commissioner is obliged to notify the applicant of his decision within ten days. If the Commissioner accepts a complaint for his consideration, he is also obliged to inform about this the relevant state body, local government body or official whose decisions or actions (inaction) are being appealed.
The Commissioner is vested with broad powers when conducting inspection activities. In accordance with the Law, he has the right to visit any government bodies, local government bodies, enterprises, institutions, organizations, regardless of organizational and legal forms and forms of ownership, military units, public associations. No one should interfere with the Commissioner in the exercise of his rights Khamaneva N.Yu. Article-by-article commentary to the Federal Constitutional Law on the Commissioner for Human Rights in the Russian Federation. — System GARANT, 2009..
The authorized person can carry out verification actions both independently and jointly with competent government bodies, officials, and civil servants. He has the right to instruct competent government agencies, if necessary, to conduct an examination and, based on its results, prepare conclusions on those issues that need to be clarified in the course of working with the complaint.
Taking into account the broad competence of the Commissioner, his rights also include familiarization with criminal, civil cases, cases of administrative offenses, decisions (sentences) on which have entered into legal force. In addition, he can get acquainted with discontinued cases and materials on which the initiation of criminal cases was refused.
When exercising his powers, the Commissioner enjoys the right to promptly receive all managers and other officials of all structures located on the territory of the Russian Federation.
They protect various organizations, including committees vested with special powers. Such bodies perform a variety of functions aimed at organizing and maintaining activities to protect children's rights.
In Russia, such an institution exists; moreover, in each region there are special departments that work with the population. One of the main tasks of such an organization is to provide assistance to a child in need and to bring to justice people who have committed criminal acts against a minor.
In this article we will look in detail at the aspects of the work of such an organization and tell you where to turn if a problem situation arises.
This organization operates at the state level and is responsible for the implementation of all provisions previously adopted by the majority of states. The committee consists of independent experts who are responsible for the correct and timely performance of their duties. At least three times a year, special sessions are held in Geneva, which are necessary for the proper organization of the work of individual representative offices of the organization around the world.
Each state was initially given recommendations to develop and implement an independent mechanism aimed at protecting and promoting the rights of the child. Initially, the body was vested with the rights to consider incoming complaints about violations of the rights of minors.
On the territory of the Russian Federation, the mechanism was developed in 1998, initiated by the Ministry of Health and Social Development. The United Nations Children's Fund (UNICEF) also took part in the development. It was this organization that was called upon to coordinate the implementation of each program in the interests of children.
Can't find requested page.
The web-server couldn't locate the page you requested. To find the page you can use a search or site map.
- Within a week, the incidence of COVID-19 in the district decreased by a third
- Andrey Ivanov held a meeting with representatives of the Zvenigorod public
- The Dobrodel portal is collecting proposals for choosing forest parks for improvement
- From May 29, travel from Trekhgorka to the Northern Bypass of Odintsovo will become paid
- To eliminate emergency situations in the power supply, Odintsovo District created 9 emergency teams
- Questions received from residents by the Council of Deputies and the Public Chamber were discussed at a meeting in Zvenigorod
- Resolution of the Administration of the Odintsovo urban district of the Moscow region dated May 25, 2021 No. 1818
- Resolution of the Administration of the Odintsovo urban district of the Moscow region dated May 26, 2021 No. 1820
- Party supporters organized a trip to Naro-Fominsk for Odintsovo veterans
- The exhibition “Healers of Souls and Bodies” will open on May 29 at the Museum of the Orthodox Educational
- News Press archive
- Press center messages
- Story
- Municipal periodicals
- Investment project questionnaire
- Adverse weather conditions
- Information How to get there
- Museums
- Attention entrepreneurs
- Industry (brief information)
- Announcement
- Structure
- Annual address of the Chapter
- Housing and communal services Lighting News
- Public services
- Odintsovo urban district
- Financial and treasury department
- Budget execution report for 2013
- Reports on the results of control activities
- Anti-Terrorism Commission
- Anti-corruption expertise
Who is the Ombudsman for Children's Rights?
As part of the work of the committee, a special position was established -. Alas, the activities of the commissioner are not recorded at the federal level, and control on this issue rests solely with regional legislative acts. Moreover, in certain territories and regions of the country the responsible person works on a voluntary basis or as an employee of the executive body of government.
Such a structure acquires the greatest independence when it acts as a separate body called upon to assess from the outside the degree of state participation in the sphere of protecting the rights of minors. In some cases, there is a “absorption” of this structure by institutions such as the labor inspectorate or social security authorities. This option is unacceptable, since it does not allow the UPPR to fulfill its duties in full.
The child rights representative is tasked with the following tasks:
- ensuring the protection of the rights of children and assistance in their restoration;
- organizing events aimed at ensuring legal awareness of children and adults;
- sending requests to various organizations and enterprises;
- obtaining the necessary materials and information at any level;
- unhindered visits to any organizations and carrying out the necessary checks;
- attracting experts and sending statements to executive authorities on behalf of the child about violations of his rights.
Where to go for help?
In recent years, departments for the protection of children's rights have begun to appear in the regions. The main tasks of such organizations were to resolve the following issues:
- Consideration of received oral and written complaints.
- Legal education and provision of consulting services to the population.
- Conducting an expert assessment of issued acts.
- Making individual proposals to improve legislation within the framework of the functioning of the institution.
In addition to these departments, children can be helped by:
- Guardianship and trusteeship authorities are most often located in the regional administration or in the educational department.
- Prosecutor's office.
- Inspectorate for Juvenile Affairs.
- Commissions for the affairs of minors located in municipalities.
Each of these bodies is vested with certain powers to resolve issues related to violations of the rights of minors.
In what cases and how do you contact ombudsmen?
To resolve issues related to the infringement of children's rights, commissions for children's affairs are created under the administrations of municipalities.
At meetings of such a commission, heads of departments submit reports and resolve issues in the main areas of activity. Complaints received by the department for juvenile affairs and protection of their rights may also be considered. Sometimes such activities are not enough. To resolve an individual problem with the participation of the Ombudsman for Children, you can use several methods:
- find out the address of his public reception in a particular city, go there in person (the list of authorized representatives, unfortunately, is not presented on the official website);
- write a letter to the address of the regional or central ombudsman;
- leave a message on the official website of the Presidential Commissioner for Children's Rights or contact them by phone.
In any case, the case will be considered by officials in a particular city. If their work is unsatisfactory, it is possible to send your complaint higher. Ombudsmen are contacted in various situations:
- conflict between parents and school management over the quality of education provided to the child;
- legal advice on children's rights;
- proposals to make changes to improve the educational and educational process;
- obtaining information about hygiene and sanitary standards at school, as well as other cases.
However, legal experts always remind that it is better to solve the case on your own first, since in some cases this is quite possible and productive. It is necessary to complain to the commissioner when it is not possible to resolve the issue on the spot.
Child protection is a national interest for every state. The activities of the Committee on the Rights of the Child are aimed at improving the situation of minors in the world as a whole and in specific countries. To implement the tasks assigned to him, the position of Commissioner for Children's Rights has been created in Russia, to whom any citizen can directly contact on an issue related to the violation of the rights of minors.
Procedure for contacting an authorized organization
A child has the right to seek help from the guardianship authorities at his place of residence if he is 14 years old. He can also file an application with the court.
If we are talking about a child no older than the specified age, then officials or citizens who witnessed the event are required to report the offense against the child.
In addition to the message, they are obliged to take certain measures to eliminate the negative impact on the baby, taking into account the specific situation. Most often, all work in this direction is led by a child protection inspector. Additional assistance is provided by other organizations, for example, a social psychologist or teacher, social rehabilitation centers.
Application procedure
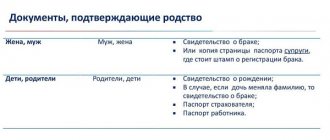
According to general rules, anyone interested has the right to write a complaint to the Committee for the Protection of the Rights of the Child. This is done through an authorized person. Pedagogical and medical workers, neighbors, family acquaintances, and officials have the right to initiate the procedure. First you need to fill out an application. It is drawn up in writing on a regular sheet of office paper.
The text should indicate the following:
- The name and address of the authority to which the initiator applies.
- Information about when and where the rights of the child were violated, and how this was expressed.
- List of attached documents.
- Date of application and signature of the applicant.
After this, you will need to collect papers that will confirm the validity of the application.
These include:
- Passport or other document on the basis of which the interested person acts.
- Characteristics of the parents from the place of residence, work or educational institution where the child is located.
- Certificates from police and medical authorities.
This list is not exhaustive. Other information may also be attached to the request. If the initiator does not have the necessary information, the authorized official body requests it itself. Next, the collected data must be transferred to its destination. There are several ways you can do this.
Most often people do this on their own. This option allows for filing an application on the spot, as well as the opportunity to receive clarification on issues of interest and make sure that the application has been accepted for consideration.
Postal forwarding involves filing a complaint independently and also excludes consultation. In this case, it would be correct to use special correspondence. The initiator will receive written notification of delivery of the letter to the addressee.
Internet forwarding is used extremely rarely. In this case, the initiator needs to have access to email and digitize all data. This method is used extremely rarely.
You can also transmit information during online communication with the authorized person on a special forum. In this case, the data is presented by the initiator in electronic form.