Consulting lawyer › Criminal law
Send
- Listening concept
- Reasons for carrying out
- Exclusion of evidence
- Return of the case
- Suspension or termination
- Procedural order
- Final decisions
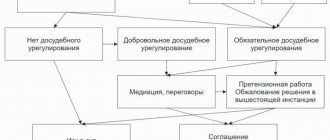
A special form of court hearing is a preliminary hearing in criminal proceedings. For it to begin, the legally established conditions must be present. It is these issues that are considered by the judge, as a result of which a final decision is made, stated in the protocol.
Listening concept
The main purpose of conducting a preliminary hearing is to get rid of possible obstacles in the case materials for further rapid consideration of it during the trial. In addition, at the stage of the criminal process, whenever possible, violations of regulations are identified and eliminated. The latter action leads to the fact that material evidence is completely excluded from the case and is recognized as inadmissible for proving a person’s guilt.
The temporary period for holding hearings is the appointment of a court hearing. Some scientists generally distinguish it as an independent stage, but this is not entirely correct. Basically, issues of correct conduct of the meeting itself with the presence of the parties are resolved here.
Since it is the parties to the process who initiate the hearing before the meeting, they are among the equal participants who are able to express their point of view. They indicate the need to restore their interests, which may have been violated during the investigation. At the same time, they must provide compelling arguments in their favor.
The essence of a preliminary hearing in a criminal case
Preparation for the trial is determined by the adoption of one of the decisions, in accordance with which the court holds a hearing. It can be issued by the court on its own initiative or upon a request for a preliminary hearing in a criminal case if there are a number of grounds. Among them:
- A party's request to exclude evidence.
- Grounds for termination/suspension of the case.
- A petition to conduct a trial in the absence of the accused who is located outside the Russian Federation or who is avoiding appearing at the hearing.
- Grounds for returning the case materials to the prosecutor.
A preliminary hearing in a criminal case is held in the absence of the accused who is not in Russia or who is avoiding appearing in court if the subject has committed a serious/especially serious act and:
- was not held accountable for his actions on the territory of a foreign state;
- there is a petition from the perpetrator to involve a jury in the trial;
- there is a sentence providing for a suspended sentence for a citizen that did not come into effect when a case was brought against him for a crime he had previously committed;
- there are grounds for separating the case into separate proceedings.
Reasons for carrying out
The procedure for conducting a preliminary hearing is enshrined in procedural rules. In addition to the petition of the parties, the court itself has the right to act as an initiator. True, here the grounds for holding a preliminary hearing established by Article 229 of the Code of Criminal Procedure of the Russian Federation must be observed, which include:
- A petition was received from the parties with the need to “throw out” certain evidence from the case materials. There are certain deadlines for this.
- Upon receipt of a request for a desire to hold the hearing itself in court without the defendant. The latter must commit at least a serious crime and hide from coming to court. An additional factor in relation to the defendant is his presence outside the country and the absence of his involvement in the territory of another state in the case brought to court.
- There are conditions to return the case to the prosecutor under the Code of Criminal Procedure of the Russian Federation or to make a decision to suspend or terminate the criminal case as a whole. Situations arise when it is necessary to separate the materials under consideration into separate production. The opposite situation is when the parties file a corresponding petition to combine several cases in one proceeding if they are being considered on different facts of one event or in relation to one person.
- The case must be tried with an additional jury.
- There is a court conviction on the conditional sentence of a person, for which the deadlines for entering into legal force have not passed. This person should be considered the same person against whom the case was brought for consideration in court.
If the above grounds are present, the judge draws up a resolution to schedule a preliminary hearing, based on the Code of Criminal Procedure of the Russian Federation, while simultaneously sending notices to all parties to the trial about the date.
Types of solutions
The preparatory consideration of the case ends when a decision is made:
- Transfer materials to another jurisdiction.
- Return the materials to the prosecutor.
- Suspend the judicial procedure.
- Stop the criminal process.
- Schedule a meeting.
- Postpone the hearing if a sentence was passed against the defendant for another act, providing for a suspended sentence and which has not entered into legal force.
- Separate the case into separate proceedings or if such is impossible, schedule a meeting.
- To combine cases into a single proceeding or if this is not possible, schedule a meeting.
As you can see, the outcome depends on the basis for holding a preliminary hearing in criminal proceedings.
A decision is drawn up in the form of a resolution, which reflects the results of all appeals.
When the case is terminated due to the imposition of a court fine on the accused, the decision shall indicate its size, duration, and procedure for execution. In case of exclusion of evidence, it is indicated which particular argument is excluded, which particular materials of the case are not examined, not disclosed and not used in the case. When the prosecutor changes the charge, this is reflected in the decision and, if necessary, the case is sent to the jurisdiction. If it turns out that the materials of the completed investigation were not presented to the accused within the prescribed period, and his period of detention has expired, the court makes a decision to change the measure of restraint and determines the period for familiarization with the documents.
The judge's ruling can be appealed.
Return of the case to the prosecutor
The case is returned to the prosecutor under the following circumstances:
- the indictment document was drawn up in violation of criminal procedural law;
- the accused was not given a copy of the indictment unless it was found lawful to do so;
- it is necessary to draw up a resolution on medical measures;
- possible connection of cases;
- the rights of the accused are not explained;
- the need to change the classification of the act to a more serious act. In this case, the judge indicates only the basis for qualifying the actions as a more serious offense without commenting on the articles of the Special Part of the Criminal Code of the Russian Federation;
- the presence of circumstances precluding the conduct of a criminal case in an abbreviated form;
- the presence of new dangerous consequences of the act, due to which there are grounds to bring charges of a more serious assault;
- the presence of a canceled court order, the basis of which was the circumstances that led to the accusation of a more serious act.
Thus, obstacles to further consideration of the case are removed. It is possible to take measures against the accused, including increasing the period of detention.
Grounds for suspension and termination of the case
The case is suspended if:
- The defendant is hiding, his whereabouts are unknown.
- The defendant is seriously ill, as confirmed by the medical report.
- An appeal has been sent to the Constitutional Court of the Russian Federation or a complaint has been received regarding compliance with constitutional legislation.
- It is impossible to ensure the participation of the accused in the court case, although his location is known.
- The accused, who is in custody, absconded from court.
The trial does not continue unless there is a reason for it.
The grounds for termination of the case or prosecution are specified in Part 1, Part 2 of Art. 239 Code of Criminal Procedure of the Russian Federation. These include the expiration of the statute of limitations for prosecution, the existence of an act of amnesty, repentance of the defendant, reconciliation of both parties, refusal of the prosecutor to charge, and more. The court decides to terminate the criminal case, sending a copy of the document to the prosecutor and the parties within a five-day period from the moment it was issued.
Exclusion of evidence
When the judge has a petition in his hands regarding the need to exclude some material evidence in a criminal case, the opinion of the other party on this matter is clarified, whether there are any objections. The request will be granted instantly if everyone agrees. This requirement is specified in the Code of Criminal Procedure of the Russian Federation. That is, a resolution is immediately drawn up to hold a hearing in court.
Additionally, the document states the exclusion of certain evidence, and indicates those materials of the case that were based on material evidence that do not make sense for consideration during the trial in court. The main thing is that there are grounds to recognize it as unacceptable and resulting from a violation of procedural law.
A preliminary hearing is conducted with the aim of removing from the case materials those material evidence that will not have legal force. Here the judge has the right to interrogate witnesses and consider possible documents that allow making a categorical conclusion regarding the subjects of the case. This is clarified before the court hearing.
The main difference of the preliminary hearing is that the judge conducts it without additional assistants together with the participants who appeared at the trial behind closed doors under the Code of Criminal Procedure of the Russian Federation. If a request is received from the accused about his unwillingness to attend the hearing, it will be held without him. There is no legislative provision for the procedure in the event that the accused does not show up at all and there is no acquittal document. Then the judge can consider all the issues without him or find ways for him to appear in the courtroom.
When both parties agree to exclude evidence, then no questions should arise. But if the accused points out the need to add additional material evidence to the case materials, then there is no way to do without it. After all, you will have to listen to his demands on the petition and listen to his opinion. But this happens extremely rarely.
If you have any questions, please take advantage of free legal advice by phone.
Motion to exclude evidence
The above procedure for conducting a preliminary hearing in criminal proceedings is specified depending on the circumstances. When a petition is received to exclude evidence, the court must decide the issue of eliminating certain information from the list that will be considered at the hearing. This statement from the party must be submitted in writing. In this case, the form established in Art. 235, part 2 of the Code of Criminal Procedure. The motion must specifically identify the evidence that the party believes should be excluded. In addition, the applicant must provide the reasons on which this decision was made and the circumstances confirming them. The judge, in turn, must review the petition. During the process, he has the right to interrogate witnesses, attach the document specified in the application to the case, and announce the contents of acts and other documents. If the petition was filed on the basis that the evidence was obtained in violation of the provisions of the Code of Criminal Procedure, the prosecutor will have to refute these arguments. In other cases, the defense is required to prove the validity of the grounds.
Return of the case
At the initiative of the court or the participants in the process, materials may be returned to the prosecutor. This is done to get rid of errors that will prevent a full consideration of the materials on their merits. The return judge finds the following in the case:
- Lack of information about delivery of a copy of the accusation to the direct participant. If the accused evades delivery of the document and the prosecutor indicates this, the judge leaves the case and prepares for consideration.
- There are conditions to connect the case with another, prescribed in Article 153 of the Code of Criminal Procedure of the Russian Federation. This includes not only the complicity of several persons in the commission of one act, but also the commission by one person of several illegal acts, which were simultaneously being investigated.
- The indictment was written based on violations of the law. All other papers in the case from the judge cannot be based on such a document. True, not all errors can serve as a condition for returning the case to the prosecutor.
- The accusation must be drawn up together with a decision on the use of medical measures against the perpetrator.
- There is no information about the accused being familiarized with his rights at the end of the investigation and his familiarization with the materials.
There may be a request from the party to return the case to the prosecutor to organize amendments. To do this, new reasons must arise in the case. That is, as a result of the bodily harm caused, on the basis of which the accusation against the person was based, more serious consequences occurred (for example, the death of a person or a significant deterioration in health). That is, the charge itself must include a different article of criminal law.
When sending the case to the prosecutor, the court must resolve the issue as it is suppressed. It remains the same (undertaking not to leave), is extended or changed to a more strict or lenient one. Everything will depend on the specific life circumstances and behavior of the accused.
Nuances
Issues relating to the selection or extension of a preventive measure are resolved at the request of the prosecutor or at the initiative of the court with the participation of the accused, a lawyer or his other representative, the prosecutor in a court hearing or at a preliminary hearing.
Participants are notified of the date, time, and place of the hearing no less than 3 days before its start.
Suspension or termination
There are grounds for terminating a criminal case or suspending it at the preparatory stage for the hearing. As for the suspension, the grounds completely coincide with the conditions during the investigation. The only exception is the requirement to send a request to the Constitutional Court. Additionally, a preventive measure may be chosen if the accused took measures to conceal it.
Termination also does not cause any particular difficulties, since they are fully consistent with the general provisions. In some cases, just to terminate a case or prosecution against a person, the judge must obtain consent from the convicted person.
Based on the results of the decision, an appropriate resolution is issued, a copy of which is additionally sent to the prosecutor and the accused and the victim. This is done within 5 days after the document is drawn up.
Preliminary hearing: what is it?
A preliminary hearing (PTH) is a procedure conducted by judges alone as part of the preparation of a case for the main proceedings.
It is assigned in individual cases on the basis of Art. 152 of the Code of Civil Procedure of the Russian Federation, if the judge still has questions without which it is impossible to objectively consider the dispute.
Reasons for appointment
The basis for assigning a PSZ may be:
- Consolidation of the administrative actions of the participants: modification or waiver of claims, conclusion of a settlement agreement, recognition of claims by the defendant.
- Reinstatement of a missed statute of limitations. The plaintiff provides evidence of the reason why he failed to file the claim in a timely manner. If the court finds the evidence admissible, the case is scheduled for trial.
- Identification of significant circumstances: requesting additional documents, interviewing the parties, obtaining additional information for objective decision-making.
- Determining the sufficiency of evidence: requesting additional evidence, filing petitions to call witnesses, order an examination.
Note! When considering disputes about children between parents within the framework of the legal settlement, the court has the right to determine their place of residence with one of the spouses, with mandatory consideration of the opinions of minors. The judge is guided solely by their interests. The participation of representatives of the guardianship authorities is mandatory.
When is it appointed?
To understand at what stage the PSZ is carried out, it is enough to familiarize yourself with the step-by-step algorithm:
- Receipt of an application to the court. Within 5 days, the judge makes a decision on accepting the documents for production, and the parties are notified.
- Preparation for the trial. After consideration of the application, a determination on preparation is made; it is a mandatory stage of legal proceedings. Appointed to clarify factual circumstances, determine legislative norms for proceedings, resolve the issue of the number and composition of participants, provide additional evidence, reconcile the plaintiff and the defendant. If necessary, a PSZ is prescribed.
- Trial. Based on the results of the preparation, the court determines a trial, unless a settlement agreement is concluded. During the hearing, the attendance of the participants is checked, the composition of the court is announced, and rights and obligations are explained. Witnesses are also questioned, experts are invited, explanations are accepted from participants, and judicial debates are held.
- Decision-making. At the end of the trial, the court retires to the deliberation room to make a decision.
Thus, the PZ is appointed by the judge only if procedural confirmation of the actions of the participants and the presentation of additional documents is required, if the evidence presented is insufficient to clarify the circumstances, and the case cannot be assigned for consideration in court proceedings.
Time frame for preparing for the trial
The Civil Procedure Code of the Russian Federation does not limit the preparation time - they are set by judges depending on the complexity of the process and other circumstances.
However, they are required to adhere to the general deadlines for the consideration of disputes:
- total period – 2 months;
- within 1 month, issues of collecting alimony, challenging dismissal with subsequent reinstatement, demolition of unauthorized buildings, challenging acts of municipal authorities on demolition, etc. are considered (Article 154 of the Code of Civil Procedure of the Russian Federation).
For certain processes, shortened trial periods are established:
| Subject of dispute | Term |
| Challenging inaction or illegal actions of government bodies and municipalities | 10 days |
| Protection of the right to participate in referendums during preparations for them and during election campaigns | 5 days |
| Violation of citizens' electoral rights based on applications received on or after voting days | Immediately |
| Resolving the issue of forced hospitalization of a mentally ill citizen | 5 days |
Important! The calculation of deadlines begins from the day the citizen submits an application to the court. If necessary, they can be extended for no more than 1 month. The periods for which proceedings are postponed for conciliation procedures are not included in the total period.
As for the PSZ, it is assigned within 5-10 days from the date of receipt of the statement of claim, depending on the situation. The issue is decided by the judge individually. In particularly complex cases, the court may assign a legal period beyond the general time limits for legal proceedings, taking into account the opinions of the parties.
Preliminary and main meeting: differences
The preliminary hearing is the second step used in preparing for the trial, while the main hearing is the third step, during which witnesses are heard, experts are invited, and debates are held. Essentially, these are different stages of legal proceedings.
According to the Code of Civil Procedure, a stage-by-stage review is required, so preparation is indispensable. At the same time, a court order is appointed only if there are grounds for a court ruling to accept the statement of claim for proceedings, prepare for proceedings, or schedule the main trial.
Procedural order
The preliminary hearing is conducted in compliance with the rules of procedural law. There is even an entire article 234 of the Criminal Procedure Code (procedure for conducting a preliminary hearing) dedicated to this. It states that issues are resolved by the judge together with the participants in the trial behind closed doors. Before the start of the hearing, all of them are notified by sending the appropriate notice no later than 3 days before the start.
The accused may be excluded from the list of participants if a petition of similar content is received from him. In addition, there may be appropriate conditions for considering the issue in the absence of one of the parties. If everyone is given notice of a hearing and someone fails to show up, the hearing cannot be delayed because of that. This does not create any obstacle.
The defense may make a motion to add other material evidence to the case materials, about which nothing was said during the investigation or was not given importance. Such a request is considered by the judge at a hearing. The main thing is that they have significance for correctly obtaining the outcome of the court hearing. In this case, additional witnesses included in the petition may be questioned. The exception here is if a person has witness immunity.
Throughout the preliminary hearings, a protocol is written, which at the end is presented to the participants in the courtroom. All information in it must find a valid display.
The procedure for conducting a preliminary hearing in criminal proceedings
Based on Art. 234 of the Code of Criminal Procedure of the Russian Federation, a preliminary hearing in a criminal case takes place in the following mode.
The parties call by notice, which must be sent in advance - at least three days before the date of the preliminary hearing. The accused may be absent if a corresponding petition is sent on his behalf or on behalf of one of the parties. If other participants notified on time do not appear at the hearing, it will not be postponed and will take place without them.
In case of an exclusive evidentiary request of the party, which is submitted within the framework of Art. 235 of the Code of Criminal Procedure of the Russian Federation, the judge determines whether there are any objections. If there are none, such a request is granted. Then a court hearing is scheduled.
A request for additional evidence or items submitted by the defense will be granted if these additions are valuable to the case.
Those who know anything about the investigative actions carried out, the seizure and inclusion of documents in the criminal record, can (at the request of the parties) be questioned as witnesses. Only holders of witness immunity are not interrogated in this regime (clause 40 of Article 5 of the Code).
Minutes are taken during the hearing.
Final decisions
From all that has been said, we can conclude exactly what decisions the judge makes based on the totality of the preliminary hearing:
- Refers the case to jurisdiction if such a need arises.
- Terminates or suspends production.
- A decision is made to schedule a meeting.
- The materials are returned to the prosecutor.
- Postponement of the case due to the presence of a court verdict that has not entered into force (in case of a suspended sentence).
- Separation of the case into separate proceedings or the absence of the possibility of such separation.
We remind you that you can always get legal advice over the phone for free.
Similar articles
The procedure for confiscation of property in criminal law
Punishment for theft of state property under article
Creating a financial pyramid is an article of the criminal code
Sample cassation appeal in a criminal case
DO YOU NEED FREE LAWYER CONSULTATION?
Results of satisfying the application
Recognition of a statement means that specific evidence loses its legal effect and cannot be taken into account when making a sentence or other decision. In addition, it cannot be used or examined during the trial. If a preliminary hearing in a criminal case involves a jury, the parties or other entities involved in the consideration of the materials do not have the right to inform the assessors about the existence of evidence excluded by the court from the list. Disclosure of the circumstances justifying this decision is also prohibited. The court order scheduling a hearing based on the results of the preliminary hearing must indicate both the excluded evidence and the materials in accordance with which it was excluded from the process. At the same time, it is allowed, during subsequent consideration, to file a petition to recognize them as admissible.
Difficulties in practice
When examining a motion to exclude any evidence, the court must find out whether the other party has any objections to it. In their absence, the applicant's request is granted.
The legislation regulates in some detail the procedure for considering applications to exclude evidence in court at a preliminary hearing in a criminal case. Meanwhile, as practice shows, judges most often refuse to satisfy such requests. At the same time, they refer to the possibility of the parties to declare it during the consideration of the case on the merits. However, during the trial, the judges also rejected the repeated petition, assuring that they would give a legal assessment of the relevant evidence when rendering a verdict in the deliberation room. In such cases, there is a violation of criminal procedural norms.
According to many lawyers, it is advisable to submit a petition to exclude evidence to the court along with a request for a hearing or indicate in it that the appointment of a hearing is directly related to the need to exclude certain materials from the case. Otherwise, the court will refuse to consider the application.